Mirror Neurons and Mirror Systems in Monkeys and Humans
... of goal. Motor act defines a series of movements performed to reach a goal (e.g., grasping an object). Finally, motor action is a series of motor acts (e.g., reaching, grasping, bringing to the mouth) that allows individuals to fulfill their intention (e.g., eating). The most widely accepted hypothe ...
... of goal. Motor act defines a series of movements performed to reach a goal (e.g., grasping an object). Finally, motor action is a series of motor acts (e.g., reaching, grasping, bringing to the mouth) that allows individuals to fulfill their intention (e.g., eating). The most widely accepted hypothe ...
Communication as an emergent metaphor for neuronal operation
... Biological evidence. Recent advances in neuroscience provide us with evidence that neurons are much more complex than previously thought [19]. In particular it has been hypothesised that neurons can select input depending on its spatial location on dendritic tree or temporal structure [19,20,21]. So ...
... Biological evidence. Recent advances in neuroscience provide us with evidence that neurons are much more complex than previously thought [19]. In particular it has been hypothesised that neurons can select input depending on its spatial location on dendritic tree or temporal structure [19,20,21]. So ...
Extra-Classical Tuning Predicts Stimulus
... the offset term and spike history filter differ only minimally between song and noise GLMs and contribute marginally and insignificantly to differences in predictive power. Before analyzing STRFs, we performed a 3⫻ up-sampling in each dimension using a cubic spline. To validate each GLM STRF as a mo ...
... the offset term and spike history filter differ only minimally between song and noise GLMs and contribute marginally and insignificantly to differences in predictive power. Before analyzing STRFs, we performed a 3⫻ up-sampling in each dimension using a cubic spline. To validate each GLM STRF as a mo ...
String Art: Axon Tracts in the Spinal Cord Spinal reflex arcs
... Sensory axons* originate in proprioceptive organs such as muscle spindle or golgi tendon organ Cell bodies of 1o sensory neurons Axons ascend in cuneate fasciculus Axons ascend in cuneate fasciculus Axons synapse with 2o neurons in accessory cuneate nucleus. Axons from these 2o neurons pass through ...
... Sensory axons* originate in proprioceptive organs such as muscle spindle or golgi tendon organ Cell bodies of 1o sensory neurons Axons ascend in cuneate fasciculus Axons ascend in cuneate fasciculus Axons synapse with 2o neurons in accessory cuneate nucleus. Axons from these 2o neurons pass through ...
Realizing Biological Spiking Network Models in a Configurable
... the major bottleneck limiting the gain in simulation speed achievable by parallelization [1]. In an accompanying paper [2], a parallel VLSI hardware architecture for the simulation of large-scale pulsed neural networks is presented, being developed within the European Union research project FACETS [ ...
... the major bottleneck limiting the gain in simulation speed achievable by parallelization [1]. In an accompanying paper [2], a parallel VLSI hardware architecture for the simulation of large-scale pulsed neural networks is presented, being developed within the European Union research project FACETS [ ...
Fig. 2 - eNeuro
... Similar taps were also applied to the tadpole head skin in immobilized tadpoles while whole-cell recordings were made. Electrical skin stimulation was delivered by a DS3 stimulator (Digitimer) to induce the KO response. During head-on clashes with Petri dish walls, the tadpole head touches the wall ...
... Similar taps were also applied to the tadpole head skin in immobilized tadpoles while whole-cell recordings were made. Electrical skin stimulation was delivered by a DS3 stimulator (Digitimer) to induce the KO response. During head-on clashes with Petri dish walls, the tadpole head touches the wall ...
Linking Neural Activity to Visual Perception: Separating Sensory and
... where the subject performs a slightly different task: motion detection. In such a task, the subject reports a change in the coherence of dot motion. The sensitivity of an MT neuron is judged by how different its firing rate is before and after the motion stimulus changes. Figure 3A shows an example ...
... where the subject performs a slightly different task: motion detection. In such a task, the subject reports a change in the coherence of dot motion. The sensitivity of an MT neuron is judged by how different its firing rate is before and after the motion stimulus changes. Figure 3A shows an example ...
PDF - Center for Theoretical Neuroscience
... sub? for so many different neuromodulatory for to determine, it is interesting stances, the modeach, the mechanism underlying of burst amplitude ulation and frequency and Flamm, (Harris-Warrick 1987). There are at least two different classes of general mechanisms by which such a large number of neur ...
... sub? for so many different neuromodulatory for to determine, it is interesting stances, the modeach, the mechanism underlying of burst amplitude ulation and frequency and Flamm, (Harris-Warrick 1987). There are at least two different classes of general mechanisms by which such a large number of neur ...
Genetic Analysis of the Drosophila Ellipsoid Body
... Staining was not exclusive to the eb nor to the nervous system. Non-cc staining aspects are described below. Chromosomal locations were obtained for most lines (Table 1) and reveal that, apart from just three pairs, all insertion sites were different. For each insertion pair, P{GAL4}-directed lacZ e ...
... Staining was not exclusive to the eb nor to the nervous system. Non-cc staining aspects are described below. Chromosomal locations were obtained for most lines (Table 1) and reveal that, apart from just three pairs, all insertion sites were different. For each insertion pair, P{GAL4}-directed lacZ e ...
Ultrastructural Characterization of Gerbil Olivocochlear Neurons
... also agree with the ones described in the gerbil LSO for LOC neurons labeled by retrograde transport of tritiated D-ASP from the cochlea (Ryan et al., 1987). It is still unresolved whether the small neurons compose the entire population of “intraLSO” OC neurons, as suggested by Ryan et al. (1987) or ...
... also agree with the ones described in the gerbil LSO for LOC neurons labeled by retrograde transport of tritiated D-ASP from the cochlea (Ryan et al., 1987). It is still unresolved whether the small neurons compose the entire population of “intraLSO” OC neurons, as suggested by Ryan et al. (1987) or ...
Processing of complex stimuli and natural scenes in the visual cortex
... when presented in isolation. However, they had a divisive effect on the response induced by concurrently presented optimal features. This demonstrates nicely how parts of a stimulus, which have no visible effect by themselves, exert an important influence on the overall response properties of these ...
... when presented in isolation. However, they had a divisive effect on the response induced by concurrently presented optimal features. This demonstrates nicely how parts of a stimulus, which have no visible effect by themselves, exert an important influence on the overall response properties of these ...
Fine-scale specificity of cortical networks depends on inhibitory cell
... (a) Reciprocally connected pair. (b) Pair with a one-way inhibitory connection. Plots at left of each panel show for each cell (FS or pyramidal) reconstructions of the locations of photostimulation sites (colored squares) relative to the locations of laminar borders and cell bodies of recorded neuro ...
... (a) Reciprocally connected pair. (b) Pair with a one-way inhibitory connection. Plots at left of each panel show for each cell (FS or pyramidal) reconstructions of the locations of photostimulation sites (colored squares) relative to the locations of laminar borders and cell bodies of recorded neuro ...
PINP: A New Method of Tagging Neuronal Populations
... Neural circuits are exquisitely organized, consisting of many different neuronal subpopulations. However, it is difficult to assess the functional roles of these subpopulations using conventional extracellular recording techniques because these techniques do not easily distinguish spikes from differ ...
... Neural circuits are exquisitely organized, consisting of many different neuronal subpopulations. However, it is difficult to assess the functional roles of these subpopulations using conventional extracellular recording techniques because these techniques do not easily distinguish spikes from differ ...
Neural Conduction - U
... • when the threshold of excitation (about 65mV) is reached, voltage-gated Na+ channels open momentarily, and Na+ ions rush into the neuron under tremendous pressure from both their concentration gradient and the electrostatic gradient; this drives the membrane potential to about ...
... • when the threshold of excitation (about 65mV) is reached, voltage-gated Na+ channels open momentarily, and Na+ ions rush into the neuron under tremendous pressure from both their concentration gradient and the electrostatic gradient; this drives the membrane potential to about ...
Historical analysis of the neural control of movement from the
... afferent fibers were shown to be the fast Ia afferents from the primary endings of muscle spindles, which are exquisitely sensitive to dynamic stretching. Much later the slower group II afferents from the spindle secondary endings were also found to contact the MNs monosynaptically, but on a much sm ...
... afferent fibers were shown to be the fast Ia afferents from the primary endings of muscle spindles, which are exquisitely sensitive to dynamic stretching. Much later the slower group II afferents from the spindle secondary endings were also found to contact the MNs monosynaptically, but on a much sm ...
Sparse Coding in the Neocortex
... Some motor neurons in layer 6 of rabbit motor cortex will produce just one spike during some movements (Beloozerova, Sirota and Swadlow, 2003). And stimulation of a single neuron in the rat is sufficient to deflect a whisker (Brecht et al., 2004). With respect to sparse coding, the most widely studi ...
... Some motor neurons in layer 6 of rabbit motor cortex will produce just one spike during some movements (Beloozerova, Sirota and Swadlow, 2003). And stimulation of a single neuron in the rat is sufficient to deflect a whisker (Brecht et al., 2004). With respect to sparse coding, the most widely studi ...
Activity of Defined Mushroom Body Output Neurons
... neurons induces avoidance behavior. We therefore propose that drive to the M4/6 neurons reflects odor-directed behavioral choice. ...
... neurons induces avoidance behavior. We therefore propose that drive to the M4/6 neurons reflects odor-directed behavioral choice. ...
A Self-Organizing Neural Network for Contour Integration through Synchronized Firing
... Whether contour integration occurs or not in the model depends on whether the cortical areas are connected with excitatory lateral connections or not. The model therefore suggests an explanation for the different contour integration capability of the different visual areas: integration is possible o ...
... Whether contour integration occurs or not in the model depends on whether the cortical areas are connected with excitatory lateral connections or not. The model therefore suggests an explanation for the different contour integration capability of the different visual areas: integration is possible o ...
as a PDF
... preganglionic neurons with axons exiting in VII and IX cranial nerves. Other brainstem parasympathetic preganglionic neurons (with axons exiting in III and X) do not appear to contain markers for NOS (Kowall and Mueller, 1988; W. P. Gai and W. W. Blessing, unpublished observations). The rostrally lo ...
... preganglionic neurons with axons exiting in VII and IX cranial nerves. Other brainstem parasympathetic preganglionic neurons (with axons exiting in III and X) do not appear to contain markers for NOS (Kowall and Mueller, 1988; W. P. Gai and W. W. Blessing, unpublished observations). The rostrally lo ...
INTERNEURONS OF THE NEOCORTICAL INHIBITORY SYSTEM
... with a depolarizing step current pulse69–72. The classification of these responses has been refined over the past decade. Originally, all inhibitory interneurons were described as fast spiking (FS)69,71, but subsequent recordings revealed other discharge patterns11,73, such as those of low-threshold ...
... with a depolarizing step current pulse69–72. The classification of these responses has been refined over the past decade. Originally, all inhibitory interneurons were described as fast spiking (FS)69,71, but subsequent recordings revealed other discharge patterns11,73, such as those of low-threshold ...
Neurons of human nucleus accumbens
... nucleus accumbens 12, 13. Our finding of type IV, multipolar neuron (Figures 11 and 12), corresponds to medium spiny neurons described by other authors. Medium spiny neurons consist of 2–6 primary dendrites, different thickness, with dense spines on secondary and third dendrite branches 14–17. We co ...
... nucleus accumbens 12, 13. Our finding of type IV, multipolar neuron (Figures 11 and 12), corresponds to medium spiny neurons described by other authors. Medium spiny neurons consist of 2–6 primary dendrites, different thickness, with dense spines on secondary and third dendrite branches 14–17. We co ...
Morphological and Functional Types of Neurons
... recordings began, a bilateral pneumothorax was performed in order to minimize movements associated with respiration. Before an animal was placed into the stereotaxic frame, silastic cuffs containing bipolar silver wire electrodes were placed bilaterally on the intact median and sciatic nerves. The n ...
... recordings began, a bilateral pneumothorax was performed in order to minimize movements associated with respiration. Before an animal was placed into the stereotaxic frame, silastic cuffs containing bipolar silver wire electrodes were placed bilaterally on the intact median and sciatic nerves. The n ...
Core Lab #1 - Reflex Responses
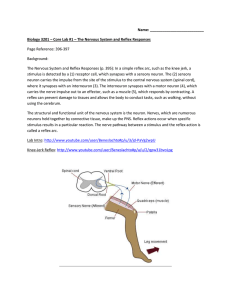
... where it synapses with an interneuron (3). The interneuron synapses with a motor neuron (4), which carries the nerve impulse out to an effector, such as a muscle (5), which responds by contracting. A reflex can prevent damage to tissues and allows the body to conduct tasks, such as walking, without ...
... where it synapses with an interneuron (3). The interneuron synapses with a motor neuron (4), which carries the nerve impulse out to an effector, such as a muscle (5), which responds by contracting. A reflex can prevent damage to tissues and allows the body to conduct tasks, such as walking, without ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.