here
... or sensory receptors. They are connected to the cell body (the control centre). The impulse travels from the cell body along the axon, where is stops at the axon terminal. Myelin sheaths allow nerve impulses to transmit more quickly along the axon. Sensory neurons – carry nerve impulses (e.g. vision ...
... or sensory receptors. They are connected to the cell body (the control centre). The impulse travels from the cell body along the axon, where is stops at the axon terminal. Myelin sheaths allow nerve impulses to transmit more quickly along the axon. Sensory neurons – carry nerve impulses (e.g. vision ...
Nervous Systems
... Central nervous system (CNS) = brain + spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) = nerves throughout body Sensory receptors: collect info Sensory neurons: body CNS Motor neurons: CNS body (muscles, glands) Interneurons: connect sensory & motor neurons Nerves = bundles of neurons C ...
... Central nervous system (CNS) = brain + spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) = nerves throughout body Sensory receptors: collect info Sensory neurons: body CNS Motor neurons: CNS body (muscles, glands) Interneurons: connect sensory & motor neurons Nerves = bundles of neurons C ...
Crayfish Physiology
... Crayfish Physiology External Anatomy Carapace – Outer covering of the crayfish that provides support to the internal structure and also provides protection from predators. Rostrum – Part of the carapace. Antennae and Antennules – These sense organs allow the crayfish to sense touch and chemical diff ...
... Crayfish Physiology External Anatomy Carapace – Outer covering of the crayfish that provides support to the internal structure and also provides protection from predators. Rostrum – Part of the carapace. Antennae and Antennules – These sense organs allow the crayfish to sense touch and chemical diff ...
Nervous System
... The function of the nervous system is to allow the animal to quickly detect, communicate and coordinate information about its external and internal environment. The two major parts of our nervous system are the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS is made of ...
... The function of the nervous system is to allow the animal to quickly detect, communicate and coordinate information about its external and internal environment. The two major parts of our nervous system are the central nervous system (CNS) and peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS is made of ...
Nervous System - Cloudfront.net
... Neuron Structure Neurons are composed of dendrites that receive signals, a cell body with a nucleus, and an axon that conducts a nerve impulse away. Sensory neurons take information from sensory receptors to the CNS. Interneurons occur within the CNS and integrate input (nonmyelinated). Motor neuro ...
... Neuron Structure Neurons are composed of dendrites that receive signals, a cell body with a nucleus, and an axon that conducts a nerve impulse away. Sensory neurons take information from sensory receptors to the CNS. Interneurons occur within the CNS and integrate input (nonmyelinated). Motor neuro ...
Elicited Behavior Chapter 2 pp. 32-53 and the internet if you can`t
... 3. What do reflexes have to do with elicited behavior? 4. What three neurons are involved in a simple reflex? 5. How can other neurons be involved in the production of a reflex? 6. What are modal action patterns and why are they called modal action patterns? 7. What is a releasing stimulus? 8. How a ...
... 3. What do reflexes have to do with elicited behavior? 4. What three neurons are involved in a simple reflex? 5. How can other neurons be involved in the production of a reflex? 6. What are modal action patterns and why are they called modal action patterns? 7. What is a releasing stimulus? 8. How a ...
1. Intro to Nervous System WEB
... hillock & travel along the axon to the axon terminal • Arrival of action potential causes the release of neurotransmitters across a synapse to the dentrites of the next neuron • Neurotransmitters can excite or inhibit the next neuron ...
... hillock & travel along the axon to the axon terminal • Arrival of action potential causes the release of neurotransmitters across a synapse to the dentrites of the next neuron • Neurotransmitters can excite or inhibit the next neuron ...
Slide ()
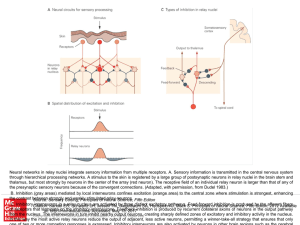
... through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the brain stem and thalamus, but most strongly by neurons in the center of the array (red neuron). The receptive field of an individual relay neuron is larger th ...
... through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the brain stem and thalamus, but most strongly by neurons in the center of the array (red neuron). The receptive field of an individual relay neuron is larger th ...
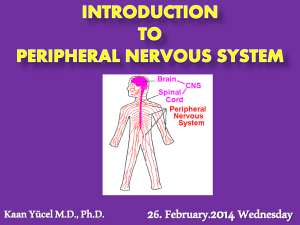
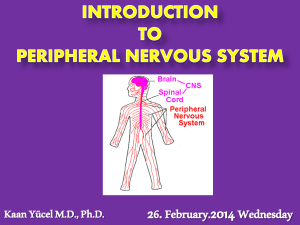
Peripheral Nervous System
... C) Mixed: Sensory & motor functions are unrelated (i.e. sense taste but control facial expression) ...
... C) Mixed: Sensory & motor functions are unrelated (i.e. sense taste but control facial expression) ...
nervous system 2 notes - Hicksville Public Schools
... Sensory Neuron: receives stimulus from the environment and carry them to the brainFound and spinal cord. in Receptors!! Ex. ...
... Sensory Neuron: receives stimulus from the environment and carry them to the brainFound and spinal cord. in Receptors!! Ex. ...
Tail Region of the Primary Somatosensory Cortex and Its Relation to
... area of the SI. Therefore, there are about 94 000 neurons in the estimated 0.8 mm2 of the SI that are involved in processing sensory signals from the tail. Anteroposteriorly oriented, evenly spaced 16-channel microwires were chronically implanted in the frontoparietooccipital cortex that was centere ...
... area of the SI. Therefore, there are about 94 000 neurons in the estimated 0.8 mm2 of the SI that are involved in processing sensory signals from the tail. Anteroposteriorly oriented, evenly spaced 16-channel microwires were chronically implanted in the frontoparietooccipital cortex that was centere ...
The Nervous Systeminofnotes
... • 4. The motor neuron sends the message to the muscles to carry out your response. ...
... • 4. The motor neuron sends the message to the muscles to carry out your response. ...
Slide ()
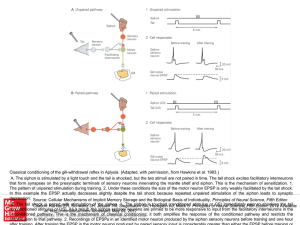
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
... Classical conditioning of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. (Adapted, with permission, from Hawkins et al. 1983.) A. The siphon is stimulated by a light touch and the tail is shocked, but the two stimuli are not paired in time. The tail shock excites facilitatory interneurons that form synapses ...
Slide ()
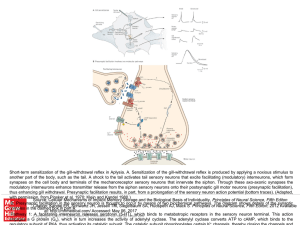
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
... Short-term sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex in Aplysia. A. Sensitization of the gill-withdrawal reflex is produced by applying a noxious stimulus to another part of the body, such as the tail. A shock to the tail activates tail sensory neurons that excite facilitating (modulatory) interne ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.