Study Questions - Nervous System
... 8. Motor neurons can be very long cells because the cell body is always located ___________________ and the axon is located ____________________. (Fig 11.2) 9. About 80% of the cells in the nervous system are _________________ cells that (circle one) do/do not transmit impulses. One example of this ...
... 8. Motor neurons can be very long cells because the cell body is always located ___________________ and the axon is located ____________________. (Fig 11.2) 9. About 80% of the cells in the nervous system are _________________ cells that (circle one) do/do not transmit impulses. One example of this ...
BIOLOGY & BEHAVIOR
... because it is the basis of all behavior The NEURON is the fundamental unit of the nervous system ...
... because it is the basis of all behavior The NEURON is the fundamental unit of the nervous system ...
9.3 Synaptic Transmission
... Excitatory neurotransmitters cause an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron to continue the transmission of the nerve impulse. ...
... Excitatory neurotransmitters cause an action potential in the postsynaptic neuron to continue the transmission of the nerve impulse. ...
107B exam 1 test yourself
... EEG records coherence of firing patterns. (we’ll discuss later) Many data representations that we’ve been looking at (e.g. response fields) show response of ______________ cells (based on voltage recordings). Response fields carry information whose combined activity can be summed up by neurons downs ...
... EEG records coherence of firing patterns. (we’ll discuss later) Many data representations that we’ve been looking at (e.g. response fields) show response of ______________ cells (based on voltage recordings). Response fields carry information whose combined activity can be summed up by neurons downs ...
Signal Crayfish - GB non-native species secretariat
... • Burrows in banks of water body • Parts of dead animals including claws and body shell either on shoreline or stream edge, in bird or rodent nests, or discarded by predators ...
... • Burrows in banks of water body • Parts of dead animals including claws and body shell either on shoreline or stream edge, in bird or rodent nests, or discarded by predators ...
Neurotest 3a Answers MC E 2) A 3) E 4) A 5) B Defs Habituation
... 2) Broca’s is left frontotemporal region and patients can understand speech but not produce it intelligibly; Wernicke’s is left temporal-parietal region and patients cannot understand speech but can produce irrelevant grammatically correct utterances. 3) Increases processes (dendrites, basically) an ...
... 2) Broca’s is left frontotemporal region and patients can understand speech but not produce it intelligibly; Wernicke’s is left temporal-parietal region and patients cannot understand speech but can produce irrelevant grammatically correct utterances. 3) Increases processes (dendrites, basically) an ...
Human Body Systems
... Activity 2.2.1: The Neuron (30–35 Minutes) Your homework was to complete the diagrams of the neurons – those will be collected on Thursday! Part II: Relaying the Message (Partners) You will create a flow map of how the nervous system and body interact from the time of seeing a cockroach to yo ...
... Activity 2.2.1: The Neuron (30–35 Minutes) Your homework was to complete the diagrams of the neurons – those will be collected on Thursday! Part II: Relaying the Message (Partners) You will create a flow map of how the nervous system and body interact from the time of seeing a cockroach to yo ...
Neurons - Transcript - the Cassiopeia Project
... units of brain structure - the neurons. The human brain contains more than a hundred billion neurons. Just like a single ant could never build an anthill, a single neuron can't think or feel or remember. A neuron's power is a result of its connections to other neurons. Each neuron is connected to as ...
... units of brain structure - the neurons. The human brain contains more than a hundred billion neurons. Just like a single ant could never build an anthill, a single neuron can't think or feel or remember. A neuron's power is a result of its connections to other neurons. Each neuron is connected to as ...
Aim: How does the nervous system function? Do Now
... Axon – carry impulses away from the cell body Axon Terminals – the end of the axons, sends impulse to other neurons ...
... Axon – carry impulses away from the cell body Axon Terminals – the end of the axons, sends impulse to other neurons ...
Neurons - Cloudfront.net
... •brain •spinal cord •peripheral nerves •neurons Functions: •Body’s response to internal/external stimuli •Control body functions •Communication ...
... •brain •spinal cord •peripheral nerves •neurons Functions: •Body’s response to internal/external stimuli •Control body functions •Communication ...
Neurons - Seung Lab
... Dendrites and axons are types of neurites • They can be distinguished in some types of neurons. • Dendrites receive synaptic inputs. • Axons make synapses on other ...
... Dendrites and axons are types of neurites • They can be distinguished in some types of neurons. • Dendrites receive synaptic inputs. • Axons make synapses on other ...
Chapter 12 - FacultyWeb
... Both require a rapid succession of stimuli at a single synapse. Both are methods by which individual EPSPs combine to result in an action potential. Both occur when simultaneous stimuli are applied at different locations, causing a cumulative effect on ...
... Both require a rapid succession of stimuli at a single synapse. Both are methods by which individual EPSPs combine to result in an action potential. Both occur when simultaneous stimuli are applied at different locations, causing a cumulative effect on ...
301 Definitions – Revised Shannon Benson
... generate a “bigger” response; the neuron simply fires as opposed to not firing. If the stimulus does not exceed this potential, the neuron will not fire at all (Redman, 1990). Comparison and Contrast: Most neurons fall under one of three types: sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Senso ...
... generate a “bigger” response; the neuron simply fires as opposed to not firing. If the stimulus does not exceed this potential, the neuron will not fire at all (Redman, 1990). Comparison and Contrast: Most neurons fall under one of three types: sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Senso ...
Technical Definitions
... generate a “bigger” response; the neuron simply fires as opposed to not firing. If the stimulus does not exceed this potential, the neuron will not fire at all (Redman, 1990). Comparison and Contrast: Most neurons fall under one of three types: sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Senso ...
... generate a “bigger” response; the neuron simply fires as opposed to not firing. If the stimulus does not exceed this potential, the neuron will not fire at all (Redman, 1990). Comparison and Contrast: Most neurons fall under one of three types: sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. Senso ...
Neuron Unit 3A
... neuron across the synapse. • Reached its threshold- then fires based on the all-or-none response. • Process continues down axon to the axon terminal. • Terminal buttons turns electrical charge into chemical (neurotransmitter) and shoots message to next neuron across the synapse. ...
... neuron across the synapse. • Reached its threshold- then fires based on the all-or-none response. • Process continues down axon to the axon terminal. • Terminal buttons turns electrical charge into chemical (neurotransmitter) and shoots message to next neuron across the synapse. ...
Nerve cord
... Allows animals to detect and process signals to react to them Stimulus: a signal that causes an animal to react Example: touch, sound, smells, tastes Response: an animal’s reaction to a stimulus ...
... Allows animals to detect and process signals to react to them Stimulus: a signal that causes an animal to react Example: touch, sound, smells, tastes Response: an animal’s reaction to a stimulus ...
Nervous System Notes
... neurotransmitters(chemicals) to be released at the terminal, to stimulate the next neuron in the chain. ...
... neurotransmitters(chemicals) to be released at the terminal, to stimulate the next neuron in the chain. ...
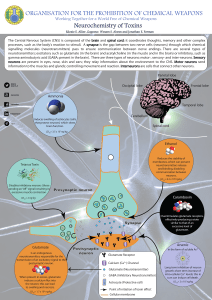
Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
... The Central Nervous System (CNS) is composed of the brain and spinal cord; it coordinates thoughts, memory and other complex processes, such as the body’s reaction to stimuli. A synapse is the gap between two nerve cells (neurons) through which chemical signalling molecules (neurotransmitters) pass ...
04 CRAYFISH 2008
... Ganglion for each segment Cerebral ganglion Fusion of many ganglion Nerve chord separates to go Around either side of esophagus Much local control Brainless crayfish -can eat -can’t see -can’t roll over ...
... Ganglion for each segment Cerebral ganglion Fusion of many ganglion Nerve chord separates to go Around either side of esophagus Much local control Brainless crayfish -can eat -can’t see -can’t roll over ...
Endocrine and nervous system
... 2. Dendrites: receives impulses to cell body (fingers) 3. Axon: carries impulses away from cell body (arm) 4. Axon Terminal: where impulses leave the neuron, contains chemical-filled vesicles (neurotransmitters) ...
... 2. Dendrites: receives impulses to cell body (fingers) 3. Axon: carries impulses away from cell body (arm) 4. Axon Terminal: where impulses leave the neuron, contains chemical-filled vesicles (neurotransmitters) ...
The Nervous System - OCPS TeacherPress
... synapse between sensory/motor neurons Motor neurons: Effector organ – muscle/gland that responds (the reflex) ...
... synapse between sensory/motor neurons Motor neurons: Effector organ – muscle/gland that responds (the reflex) ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.