Structure of a Neuron
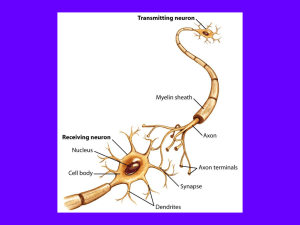
... 3. Dendrite: receives impulses from other neurons and carries them toward the cell body ...
... 3. Dendrite: receives impulses from other neurons and carries them toward the cell body ...
Slide ()
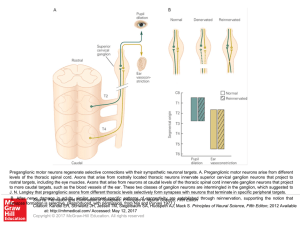
... rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons that project to more caudal targets, such as the blood vessels of the ear. These two classes of ganglion neurons are intermingled in the ganglion, which s ...
... rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons that project to more caudal targets, such as the blood vessels of the ear. These two classes of ganglion neurons are intermingled in the ganglion, which s ...
Brumberg - QC Queens College
... interconnections between the different elements. The focus of the Brumberg’s lab research is to characterize development and the neurons of the rodent barrel cortex with a dual emphasis on the interactions between the sensory and motor systems that govern the animals whisking behavior and the role t ...
... interconnections between the different elements. The focus of the Brumberg’s lab research is to characterize development and the neurons of the rodent barrel cortex with a dual emphasis on the interactions between the sensory and motor systems that govern the animals whisking behavior and the role t ...
A natural example of different circuit architectures for analogous
... membrane and synaptic parameters might produce relatively similar network outputs. However, there is still a general assumption that similar behaviors in related animal species originate from a common neural architecture. In this study, we show that two species produce similar behaviors using hom ...
... membrane and synaptic parameters might produce relatively similar network outputs. However, there is still a general assumption that similar behaviors in related animal species originate from a common neural architecture. In this study, we show that two species produce similar behaviors using hom ...
the nervous system
... sense organs to the spinal cord and brain Motor neurons – carry messages from the brain to muscles and glands Interneurons – connect sensory and motor neurons ...
... sense organs to the spinal cord and brain Motor neurons – carry messages from the brain to muscles and glands Interneurons – connect sensory and motor neurons ...
Ch. 48-49 Nervous System 9e S13
... • Central nervous system (CNS) = brain + spinal cord • Peripheral nervous system (PNS) = nerves throughout body – Sensory receptors: collect info – Sensory neurons: body CNS – Motor neurons: CNS body (muscles, glands) – Interneurons: connect sensory & motor neurons • Nerves = bundles of neurons ...
... • Central nervous system (CNS) = brain + spinal cord • Peripheral nervous system (PNS) = nerves throughout body – Sensory receptors: collect info – Sensory neurons: body CNS – Motor neurons: CNS body (muscles, glands) – Interneurons: connect sensory & motor neurons • Nerves = bundles of neurons ...
E1 – Stimulus and response - IBDPBiology-Dnl
... receptors, sensory neurons, relay neurons, motor neurons, synapses and effectors in the response of animals to stimuli. E.1.3 Draw and label a diagram of a reflex arc for a pain withdrawal reflex, including the spinal cord and its spinal nerves, the receptor cell, sensory neuron, relay neuron, mot ...
... receptors, sensory neurons, relay neurons, motor neurons, synapses and effectors in the response of animals to stimuli. E.1.3 Draw and label a diagram of a reflex arc for a pain withdrawal reflex, including the spinal cord and its spinal nerves, the receptor cell, sensory neuron, relay neuron, mot ...
Unit 3 Essential Vocabulary File - District 196 e
... You will also need to know (but are not required to complete flashcards for): the structure of the NERVOUS SYSTEM (peripheral and central). the parts and function of the NEURON. techniques for STUDYING THE BRAIN (MRI, fMRI, PET, EEG) Difference between identical and fraternal twins Genes, ...
... You will also need to know (but are not required to complete flashcards for): the structure of the NERVOUS SYSTEM (peripheral and central). the parts and function of the NEURON. techniques for STUDYING THE BRAIN (MRI, fMRI, PET, EEG) Difference between identical and fraternal twins Genes, ...
Arthropods Again: The Crustacean
... Thoracic Appendages Thoracic Segments 6-8: give off maxillipeds which are also used to manipulate food. Thoracic Segment 9: chelipeds (pinchers!!) are used for self-defense, getting, and manipulating food. Thoracic Segments 10-13: walking legs, which are used for locomotion. ...
... Thoracic Appendages Thoracic Segments 6-8: give off maxillipeds which are also used to manipulate food. Thoracic Segment 9: chelipeds (pinchers!!) are used for self-defense, getting, and manipulating food. Thoracic Segments 10-13: walking legs, which are used for locomotion. ...
The Nervous System
... electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause a brief electrical charge; if strong enough, the nerve fires **ALL OR NOTHING Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse; excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must equal a minimum intensi ...
... electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause a brief electrical charge; if strong enough, the nerve fires **ALL OR NOTHING Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse; excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must equal a minimum intensi ...
neuron and nervous system
... electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause a brief electrical charge; if strong enough, the nerve fires **ALL OR NOTHING Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse; excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must equal a minimum intensi ...
... electrical charge that travels down an axon **Neurons that are stimulated cause a brief electrical charge; if strong enough, the nerve fires **ALL OR NOTHING Threshold: level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse; excitatory signals minus inhibitory signals must equal a minimum intensi ...
Activity of Spiking Neurons Stimulated by External Signals of
... with each other. On average, each neuron is connected to other neurons through about 10 000 synapses. The brain network of neurons forms a massively parallel information processing system. This contrasts with conventional computers, in which a single processor executes a sequential series of instruc ...
... with each other. On average, each neuron is connected to other neurons through about 10 000 synapses. The brain network of neurons forms a massively parallel information processing system. This contrasts with conventional computers, in which a single processor executes a sequential series of instruc ...
ch. 48 Nervous System notes
... environments to CNS Interneurons: integrate sensory input and motor output (carry stimuli in the brain and spinal cord) Motor Neurons: convey impulses from CNS to effector cells in muscles or glands Glial cells: support, protect, and nourish neurons ...
... environments to CNS Interneurons: integrate sensory input and motor output (carry stimuli in the brain and spinal cord) Motor Neurons: convey impulses from CNS to effector cells in muscles or glands Glial cells: support, protect, and nourish neurons ...
Trainer 2 File
... All mammalian tissue is fairly uniform with tissue transitions that are fairly defined / complete so the cyst looks pretty aberrant (unusual) Embryo inside ...
... All mammalian tissue is fairly uniform with tissue transitions that are fairly defined / complete so the cyst looks pretty aberrant (unusual) Embryo inside ...
Chapter 8: Sensation and Perception
... Fluid interior of axon: negatively charged ions Fluid exterior of axon membrane: positively charged ions Level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse (action potential) Excitatory signals (accelerator) minus inhibitory signals (brakes) must reach minimum intensity ...
... Fluid interior of axon: negatively charged ions Fluid exterior of axon membrane: positively charged ions Level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse (action potential) Excitatory signals (accelerator) minus inhibitory signals (brakes) must reach minimum intensity ...
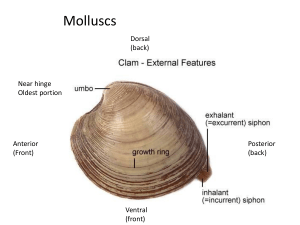
Introduction To Physiology ~ LECTURE NOTES
... The body is said to be in homeostasis when its cellular needs are adequately met and functional activities are occurring smoothly. Every organ system plays a role in maintaining the internal environment ...
... The body is said to be in homeostasis when its cellular needs are adequately met and functional activities are occurring smoothly. Every organ system plays a role in maintaining the internal environment ...
(A): The Neuron
... Fluid interior of axon: negatively charged ions Fluid exterior of axon membrane: positively charged ions Level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse (action potential) Excitatory signals (accelerator) minus inhibitory signals (brakes) must reach minimum intensity ...
... Fluid interior of axon: negatively charged ions Fluid exterior of axon membrane: positively charged ions Level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse (action potential) Excitatory signals (accelerator) minus inhibitory signals (brakes) must reach minimum intensity ...
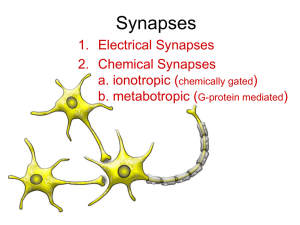
Synapses - Franklin College
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
Crayfish Dissection Lab
... Purpose: The purpose of this lab activity is to help you learn the anatomy of a crayfish and give you a better understanding of the anatomy of invertebrate animals in general. ...
... Purpose: The purpose of this lab activity is to help you learn the anatomy of a crayfish and give you a better understanding of the anatomy of invertebrate animals in general. ...
Chapter 3 – The nerve cell Study Guide Describe an integrate
... Fundamentals of Cognitive Neuroscience: A Beginner’s Guide Bernard J. Baars and Nicole M. Gage 2012 Academic Press ...
... Fundamentals of Cognitive Neuroscience: A Beginner’s Guide Bernard J. Baars and Nicole M. Gage 2012 Academic Press ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.