Nervous System
... contains the general interpretive and speech centers and is responsible for language-based skills. The right hemisphere, or representational hemisphere, is concerned with spatial relationships and analyses. The diencephalon provides the switching and relay centers needed to integrate the conscious a ...
... contains the general interpretive and speech centers and is responsible for language-based skills. The right hemisphere, or representational hemisphere, is concerned with spatial relationships and analyses. The diencephalon provides the switching and relay centers needed to integrate the conscious a ...
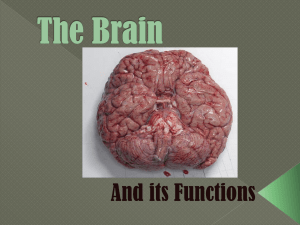
The Brain
... Axon - the elongated fiber that extends from the cell body to the terminal endings and transmits the neural signal. The larger the axon, the faster it transmits information Myelin Sheath - fatty substance called myelin that acts as an insulator. These myelinated axons transmit information much faste ...
... Axon - the elongated fiber that extends from the cell body to the terminal endings and transmits the neural signal. The larger the axon, the faster it transmits information Myelin Sheath - fatty substance called myelin that acts as an insulator. These myelinated axons transmit information much faste ...
Ch. 35.2
... Neurons may have many dendrites by only one axon Form NERVES when axons and dendrites are clustered together ...
... Neurons may have many dendrites by only one axon Form NERVES when axons and dendrites are clustered together ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior: The Neuron
... Acetylcholine: (Ach) Acetylcholine is particularly important in the stimulation of muscle tissue. Contributes the regulation of attention, arousal and memory. The poison curare blocks transmission of acetylcholine. Some nerve gases inhibit the breakdown of acetylcholine, producing a continuous stimu ...
... Acetylcholine: (Ach) Acetylcholine is particularly important in the stimulation of muscle tissue. Contributes the regulation of attention, arousal and memory. The poison curare blocks transmission of acetylcholine. Some nerve gases inhibit the breakdown of acetylcholine, producing a continuous stimu ...
PowerPoint
... • The Axon Terminals at a Synapse contain tiny vesicles, or sacs. These are known as NEUROTRANSMITTERS. ...
... • The Axon Terminals at a Synapse contain tiny vesicles, or sacs. These are known as NEUROTRANSMITTERS. ...
The Nervous System
... 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
... 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
hwk-4-pg-521 - WordPress.com
... Schwann cells, which produce the myelin sheath, and the glial cells, which provide nutritional and structural support for neurons. They facilitate the transmission of nerve impulses via neurons but do not provide nerve transmission themselves. 4. Reflexes have evolved to occur without the need for t ...
... Schwann cells, which produce the myelin sheath, and the glial cells, which provide nutritional and structural support for neurons. They facilitate the transmission of nerve impulses via neurons but do not provide nerve transmission themselves. 4. Reflexes have evolved to occur without the need for t ...
The Reflex Arc
... A. Stimulus – any change in the environment that causes a response (reaction). Ex: light, temperature, pressure. B. Response – the action or movement resulting from a stimulus. ...
... A. Stimulus – any change in the environment that causes a response (reaction). Ex: light, temperature, pressure. B. Response – the action or movement resulting from a stimulus. ...
The nervous system
... the cells to one another, to centers throughout the body or to other neurons. These neurons operate on excitation or inhibition and although nerve cells can vary in size and location their communication with one another determines their function. These nerves conduct impulses from sensory receptors ...
... the cells to one another, to centers throughout the body or to other neurons. These neurons operate on excitation or inhibition and although nerve cells can vary in size and location their communication with one another determines their function. These nerves conduct impulses from sensory receptors ...
nervous system
... together in the PNS= ganglia Satellite cells- surround neuron cell bodies, regulate environment Schwann cells- form a sheath around every axon, can myelinate axons ...
... together in the PNS= ganglia Satellite cells- surround neuron cell bodies, regulate environment Schwann cells- form a sheath around every axon, can myelinate axons ...
Sending Signals Notes
... • DEPOLARIZED = Inside the membrane becomes more positive than outside. • This causes a THRESHOLD to be REACHED and an impulse (ACTION POTENTIAL) begins in the second cell. • After the neurotransmitter relays it message it is rapidly REMOVED or DESTROYED, thus halting its effect. • The molecules of ...
... • DEPOLARIZED = Inside the membrane becomes more positive than outside. • This causes a THRESHOLD to be REACHED and an impulse (ACTION POTENTIAL) begins in the second cell. • After the neurotransmitter relays it message it is rapidly REMOVED or DESTROYED, thus halting its effect. • The molecules of ...
PPT - Wolfweb Websites
... Critical electrical signal is the Action Potential – Firecracker analogy – Driven by ions passing through ion channels – Electrical signal driven along very long axons to target cells – Guest lecturer: Dr Jim Kenyon, UNSOM – Axon computer lab ...
... Critical electrical signal is the Action Potential – Firecracker analogy – Driven by ions passing through ion channels – Electrical signal driven along very long axons to target cells – Guest lecturer: Dr Jim Kenyon, UNSOM – Axon computer lab ...
Neuron Powerpoint
... • A brief electrical charge that travels down an axon • Sent from neurons when stimulated by signals from our senses or when triggered by chemical signals from neighboring neurons. ...
... • A brief electrical charge that travels down an axon • Sent from neurons when stimulated by signals from our senses or when triggered by chemical signals from neighboring neurons. ...
2.2 Electrical Communication Study Guide by Hisrich
... 2.2 Electrical Communication Study Guide by Hisrich 2.2.a How does communication happen within the body? Electrical Signals Nervous System ...
... 2.2 Electrical Communication Study Guide by Hisrich 2.2.a How does communication happen within the body? Electrical Signals Nervous System ...
note taking guide
... Portion of PNS that functions ________________________ without a conscious effort ...
... Portion of PNS that functions ________________________ without a conscious effort ...
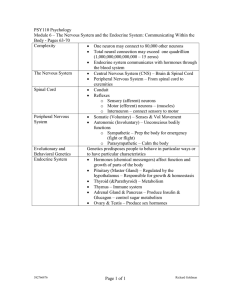
PSY110 Psychology
... One neuron may connect to 80,000 other neurons Total neural connection may exceed one quadrillion (1,000,000,000,000,000 – 15 zeros) Endocrine system communicates with hormones through the blood system The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) – Brain & Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous ...
... One neuron may connect to 80,000 other neurons Total neural connection may exceed one quadrillion (1,000,000,000,000,000 – 15 zeros) Endocrine system communicates with hormones through the blood system The Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) – Brain & Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous ...
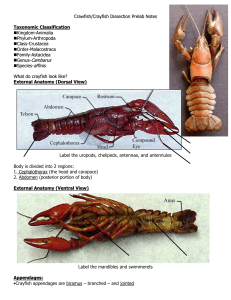
Crawfish/Crayfish Dissection Prelab Notes
... Label the uropods, chelipeds, antennae, and antennules Body is divided into 2 regions: 1. Cephalothorax (the head and carapace) 2. Abdomen (posterior portion of body) External Anatomy (Ventral View) ...
... Label the uropods, chelipeds, antennae, and antennules Body is divided into 2 regions: 1. Cephalothorax (the head and carapace) 2. Abdomen (posterior portion of body) External Anatomy (Ventral View) ...
Nervous System
... • This initiates an impulse in a sensory neuron • Impulse travels to the spinal cord • Impulse passes(by means of a synapse) to a connecting neuron called the relay neuron • Relay makes a synapse with one or more motor neurons that transmit the impulse to the muscles. • Causes muscles to contract an ...
... • This initiates an impulse in a sensory neuron • Impulse travels to the spinal cord • Impulse passes(by means of a synapse) to a connecting neuron called the relay neuron • Relay makes a synapse with one or more motor neurons that transmit the impulse to the muscles. • Causes muscles to contract an ...
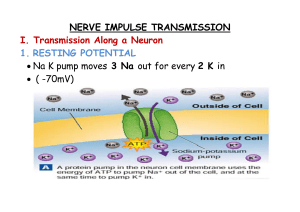
Organization of the Nervous System
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
... A neuron is at rest when it is not sending a signal and is in a negatively charged state. Even at rest, the neuron allows K to pass. Neuron pumps 3 Na ions out for every 2 K ions it pumps in. At rest, there are more Na ions outside and more K ions inside Resting & Action Potential ...
steps in nerve impulse transmission
... 1. Neurotransmitters (NT) are chemicals released from one neuron at the presynaptic nerve terminal. 2. NT then cross the synapse where they may be accepted by the next neuron at a specialized site called a receptor 3. The action that follows activation of a receptor site may be either depolarizati ...
... 1. Neurotransmitters (NT) are chemicals released from one neuron at the presynaptic nerve terminal. 2. NT then cross the synapse where they may be accepted by the next neuron at a specialized site called a receptor 3. The action that follows activation of a receptor site may be either depolarizati ...
Physiology 1B
... Interneurons- CNS neurons that internally communicate and intervene between the sensory inputs and the motor outputs Motor Neurons- Carry outgoing information from the CNS to muscle glands. ...
... Interneurons- CNS neurons that internally communicate and intervene between the sensory inputs and the motor outputs Motor Neurons- Carry outgoing information from the CNS to muscle glands. ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.