Local network regulation of orexin neurons in the lateral hypothalamus
... terminals to attenuate glutamate release (67, 135), while N/OFQ inhibits both excitatory and inhibitory transmission (135). Furthermore, synaptically released glutamate negatively regulates the presynaptic release of glutamate and GABA through group III metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) (2) ...
... terminals to attenuate glutamate release (67, 135), while N/OFQ inhibits both excitatory and inhibitory transmission (135). Furthermore, synaptically released glutamate negatively regulates the presynaptic release of glutamate and GABA through group III metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) (2) ...
Sustained conditioned responses in prelimbic prefrontal neurons are
... (for review, see Quirk et al., 2006; Quirk and Mueller, 2008). Multichannel unit recordings and unit analyses. Extracellular waveFailure to recall extinction results from deficient IL activity forms exceeding a voltage threshold were digitized at 40 kHz and stored (Herry and Garcia, 2002; Milad and ...
... (for review, see Quirk et al., 2006; Quirk and Mueller, 2008). Multichannel unit recordings and unit analyses. Extracellular waveFailure to recall extinction results from deficient IL activity forms exceeding a voltage threshold were digitized at 40 kHz and stored (Herry and Garcia, 2002; Milad and ...
Brain stem excitatory and inhibitory signaling pathways regulating
... which can be modulated by alterations in activity of neutral endopeptidases (156). In addition, endogenous substance P facilitates synaptic transmission in airway parasympathetic ganglia (34, 154), similar to the effect observed with cyclooxygenase activation and the release of prostaglandins in ant ...
... which can be modulated by alterations in activity of neutral endopeptidases (156). In addition, endogenous substance P facilitates synaptic transmission in airway parasympathetic ganglia (34, 154), similar to the effect observed with cyclooxygenase activation and the release of prostaglandins in ant ...
Physiological Plasticity of Single Neurons in Auditory Cortex of the
... associative effects on AI whereas the latter might be involved in learning-induced cortical discharge plasticity (Weinberger, in press). Additional analysis of this and many related issues requires investigation of the effects of learning on the discharge properties of single neurons in auditory cor ...
... associative effects on AI whereas the latter might be involved in learning-induced cortical discharge plasticity (Weinberger, in press). Additional analysis of this and many related issues requires investigation of the effects of learning on the discharge properties of single neurons in auditory cor ...
Preferential Termination of Corticorubral Axons on Spine
... Shatz, 1993; Goodman, 1996), but relatively little is known about what interactions occur within the final target. It is presumed that a cascade of complex events must take place at the target, because not only the presynaptic axons but also the postsynaptic cells must be continuously growing and re ...
... Shatz, 1993; Goodman, 1996), but relatively little is known about what interactions occur within the final target. It is presumed that a cascade of complex events must take place at the target, because not only the presynaptic axons but also the postsynaptic cells must be continuously growing and re ...
Central circuitries for body temperature regulation and fever
... Changes in environmental temperature have direct and more rapid effects on skin temperature than on temperatures within the body core. When environmental temperature is lowered, skin temperature rapidly falls, whereas brain and rectal temperatures are not affected or slightly increased in rats (17, ...
... Changes in environmental temperature have direct and more rapid effects on skin temperature than on temperatures within the body core. When environmental temperature is lowered, skin temperature rapidly falls, whereas brain and rectal temperatures are not affected or slightly increased in rats (17, ...
Auditory Neurons in the Dorsal Cortex of the Inferior Colliculus
... the auditory nerve. The cochlear nucleus is subdivided into ventral and dorsal divisions (VCN and DCN, respectively). The ventral division can be further subdivided into the anterior ventral cochlear nucleus (AVCN), and the posterior ventral cochlear nucleus (PVCN). Each division of the CN receives ...
... the auditory nerve. The cochlear nucleus is subdivided into ventral and dorsal divisions (VCN and DCN, respectively). The ventral division can be further subdivided into the anterior ventral cochlear nucleus (AVCN), and the posterior ventral cochlear nucleus (PVCN). Each division of the CN receives ...
Central circuitries for body temperature regulation and fever
... Changes in environmental temperature have direct and more rapid effects on skin temperature than on temperatures within the body core. When environmental temperature is lowered, skin temperature rapidly falls, whereas brain and rectal temperatures are not affected or slightly increased in rats (17, ...
... Changes in environmental temperature have direct and more rapid effects on skin temperature than on temperatures within the body core. When environmental temperature is lowered, skin temperature rapidly falls, whereas brain and rectal temperatures are not affected or slightly increased in rats (17, ...
Impact of prefrontal cortex in nicotine
... spectively. It has been reported that VTA DA neurons receive glutamatergic inputs directly or indirectly from the PFC (Kalivas, 1993; Charara et al., 1996; Carr and Sesack, 2000; Omelchenko and Sesack, 2007) and other brain regions (Geisler and Wise, 2008). In addition, the VTA receives cholinergic ...
... spectively. It has been reported that VTA DA neurons receive glutamatergic inputs directly or indirectly from the PFC (Kalivas, 1993; Charara et al., 1996; Carr and Sesack, 2000; Omelchenko and Sesack, 2007) and other brain regions (Geisler and Wise, 2008). In addition, the VTA receives cholinergic ...
Synaptic Regulation of Action Potential Timing in
... the giant cells, and summation of only two or three such potentials is sufficient to trigger an action potential (Wilson, 1993). Hence, these depolarizing potentials appear to be instrumental not only in the generation of the tonic irregular firing pattern observed in giant cells in vivo (Wilson et ...
... the giant cells, and summation of only two or three such potentials is sufficient to trigger an action potential (Wilson, 1993). Hence, these depolarizing potentials appear to be instrumental not only in the generation of the tonic irregular firing pattern observed in giant cells in vivo (Wilson et ...
Developmental Support - Mother Baby University
... germinal matrix to their eventual location within the CNS where they differentiate & take on their unique functions • Neurons formed early in life lie deeper in cortex & neurons formed later lie in more superficial layers • Cortex generally has complete component of neurons by 33 weeks gestation ...
... germinal matrix to their eventual location within the CNS where they differentiate & take on their unique functions • Neurons formed early in life lie deeper in cortex & neurons formed later lie in more superficial layers • Cortex generally has complete component of neurons by 33 weeks gestation ...
SOM
... • Neural networks for unsupervised learning attempt to discover special patterns from available data without using external help (i.e. RISK FUNCTION). – There is no information about the desired class (or output ) d of an example x. So only x is given. – Self Organising Maps (SOM) are neural network ...
... • Neural networks for unsupervised learning attempt to discover special patterns from available data without using external help (i.e. RISK FUNCTION). – There is no information about the desired class (or output ) d of an example x. So only x is given. – Self Organising Maps (SOM) are neural network ...
Molecules and mechanisms of dendrite development in Drosophila
... it is possible that this activity depends on signaling through endocytosed receptors (Satoh et al., 2008). Mutations in shrub, which encodes a homolog of yeast Snf7 involved in trafficking from endosomes to lysosomes, also lead to hyperbranching, potentially owing to the defective modulation of rece ...
... it is possible that this activity depends on signaling through endocytosed receptors (Satoh et al., 2008). Mutations in shrub, which encodes a homolog of yeast Snf7 involved in trafficking from endosomes to lysosomes, also lead to hyperbranching, potentially owing to the defective modulation of rece ...
Antennal Mechanosensory Neurons Mediate Wing Motor Reflexes
... Presentations of visual stimuli. We used a previously described light emitting diode (LED) display to present visual stimuli to the flies (Reiser and Dickinson, 2008). To separate the wavelength of the light emitted by the LED from the GCaMP3 fluorescence, we used blue LEDs (470 nm peak wavelength; ...
... Presentations of visual stimuli. We used a previously described light emitting diode (LED) display to present visual stimuli to the flies (Reiser and Dickinson, 2008). To separate the wavelength of the light emitted by the LED from the GCaMP3 fluorescence, we used blue LEDs (470 nm peak wavelength; ...
Central mechanisms regulating coordinated cardiovascular and
... external environment (i.e., psychological stressors) trigger highly coordinated defensive behavioral responses that are accompanied by appropriate autonomic and respiratory changes. As discussed in this review, several brain regions and pathways have major roles in subserving the cardiovascular and ...
... external environment (i.e., psychological stressors) trigger highly coordinated defensive behavioral responses that are accompanied by appropriate autonomic and respiratory changes. As discussed in this review, several brain regions and pathways have major roles in subserving the cardiovascular and ...
ANALYSIS OF THE ACTIVITY OF THE CHAINS
... of the different axons. The number and complexity of central pathways ar‘e best described by saying that, with but few exceptions, at least one pathway can be found connecting any two central neurons in a .manner so that an impulse may be conducted from one to the other neuron in the direction of ax ...
... of the different axons. The number and complexity of central pathways ar‘e best described by saying that, with but few exceptions, at least one pathway can be found connecting any two central neurons in a .manner so that an impulse may be conducted from one to the other neuron in the direction of ax ...
Neural Correlates of Object-Associated Choice Behavior
... provided the accuracy of the choice, and the rat moved its snout into the food tray (Fig. 1A). Raster plots. A raster plot was built by aligning spike timestamps with reference to the timestamp for the choice event (bin size ⫽ 50 ms, time window ⫽ 4 s before and after choice). Among the cells with m ...
... provided the accuracy of the choice, and the rat moved its snout into the food tray (Fig. 1A). Raster plots. A raster plot was built by aligning spike timestamps with reference to the timestamp for the choice event (bin size ⫽ 50 ms, time window ⫽ 4 s before and after choice). Among the cells with m ...
The Control of Rate and Timing of Spikes in the Deep Cerebellar
... Gex ⫹ Ein * Gin) / (Gex ⫹ Gin). The membrane potential trajectory (Fig. 1 B, black trace) followed fluctuations in Vsyn quite well. These fluctuations reflect the changing amplitude of the inhibitory conductance. During depolarizing membrane potential fluctuations, action potentials could be generat ...
... Gex ⫹ Ein * Gin) / (Gex ⫹ Gin). The membrane potential trajectory (Fig. 1 B, black trace) followed fluctuations in Vsyn quite well. These fluctuations reflect the changing amplitude of the inhibitory conductance. During depolarizing membrane potential fluctuations, action potentials could be generat ...
Computing with Spiking Neuron Networks
... the neuron more or less likely to fire for some duration of time. The transient impact a spike has on the neuron’s membrane potential is generally referred to as the postsynaptic potential, or PSP, and the PSP can either inhibit the future firing – inhibitory postsynaptic potential, IPSP – or excite ...
... the neuron more or less likely to fire for some duration of time. The transient impact a spike has on the neuron’s membrane potential is generally referred to as the postsynaptic potential, or PSP, and the PSP can either inhibit the future firing – inhibitory postsynaptic potential, IPSP – or excite ...
ARTICULOS PUBLICADOS EN REVISTAS ELECTRÓNICAS: TRABAJO 1:
... inhibitory and excitatory responses elicited by endogenous 5-HT in vivo. Nearly 60 % of the neurons in the PFC of the rat and mouse express the mRNAs of 5-HT1A and/or 5-HT2A receptors, with a high degree of co-expression (nearly 80% in most PFC areas; Amargós-Bosch et al., 2004). The vast majority o ...
... inhibitory and excitatory responses elicited by endogenous 5-HT in vivo. Nearly 60 % of the neurons in the PFC of the rat and mouse express the mRNAs of 5-HT1A and/or 5-HT2A receptors, with a high degree of co-expression (nearly 80% in most PFC areas; Amargós-Bosch et al., 2004). The vast majority o ...
Structural and functional architecture of respiratory networks in the
... architecture of brainstem respiratory circuits. Innate rhythmic movements such as breathing are thought to be produced by central pattern generator (CPG) networks. These are specialized neuronal circuits in the central nervous system that are intrinsically capable of generating rhythmic activity and ...
... architecture of brainstem respiratory circuits. Innate rhythmic movements such as breathing are thought to be produced by central pattern generator (CPG) networks. These are specialized neuronal circuits in the central nervous system that are intrinsically capable of generating rhythmic activity and ...
uncorrected proof - Illinois State University Websites
... The magnetic field of the earth provides many organisms with sufficient information to successfully navigate through their environments. While evidence suggests the widespread use of this sensory modality across many taxa, it remains an understudied sensory modality. We have recently showed that the ...
... The magnetic field of the earth provides many organisms with sufficient information to successfully navigate through their environments. While evidence suggests the widespread use of this sensory modality across many taxa, it remains an understudied sensory modality. We have recently showed that the ...
Outputs of Radula Mechanoafferent Neurons in Aplysia are
... the modulation produced by B4/5, whereas excitatory and/or electrical synapses were involved in the other instances. The data indicate that modulation is due to block of action potential invasion into synaptic release regions or to alterations of transmitter release as a function of the presynaptic ...
... the modulation produced by B4/5, whereas excitatory and/or electrical synapses were involved in the other instances. The data indicate that modulation is due to block of action potential invasion into synaptic release regions or to alterations of transmitter release as a function of the presynaptic ...
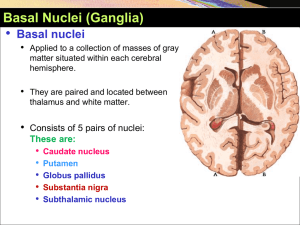
Basal Ganglia YAYDAR 2012-2013
... extent the movement will be fast, and how long it will last. Storage of motor programs of familiar motor actions: e.g. signature. ...
... extent the movement will be fast, and how long it will last. Storage of motor programs of familiar motor actions: e.g. signature. ...
Drives and emotions: the hypothalamus and limbic system
... visceral structures through its control over the pituitary gland (see Fig. 23-10). It can also stimulate somatic responses through connections with limbic structures that interconnect the hypothalamus and neocortex. The latter are two-way connections, providing us with a degree of voluntary control ...
... visceral structures through its control over the pituitary gland (see Fig. 23-10). It can also stimulate somatic responses through connections with limbic structures that interconnect the hypothalamus and neocortex. The latter are two-way connections, providing us with a degree of voluntary control ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.