Motor areas of the frontal lobe by Jarrod Blinch
... supplementary somatosensory area, and the posterior parietal cortex and terminate mostly in the dorsal horn of the spinal grey matter. The termination in the dorsal horn makes it unlikely that these fibers directly influence motor behaviour. It has been suggested that corticospinal fibers that origi ...
... supplementary somatosensory area, and the posterior parietal cortex and terminate mostly in the dorsal horn of the spinal grey matter. The termination in the dorsal horn makes it unlikely that these fibers directly influence motor behaviour. It has been suggested that corticospinal fibers that origi ...
Anatomical organization of the central olfactory
... signal is one of the issues separating vertebrates and insects. In vertebrates, the chemosensory receptors belong to the G-protein-coupled family that generates action potentials via intracellular events (Buck & Axel, 1991). Insect odor receptors are however structurally, and genetically unrelated t ...
... signal is one of the issues separating vertebrates and insects. In vertebrates, the chemosensory receptors belong to the G-protein-coupled family that generates action potentials via intracellular events (Buck & Axel, 1991). Insect odor receptors are however structurally, and genetically unrelated t ...
Reward and Aversion
... (DA) was once considered almost synonymous with reward, but investigation of exactly which of the above components DA signals has just started. Furthermore, the field has begun to appreciate the huge degree of heterogeneity in the reward system in terms of functionality, cell composition, transmitte ...
... (DA) was once considered almost synonymous with reward, but investigation of exactly which of the above components DA signals has just started. Furthermore, the field has begun to appreciate the huge degree of heterogeneity in the reward system in terms of functionality, cell composition, transmitte ...
PARK9-Associated ATP13A2 Localizes to Intracellular
... ATP13A2 mutations in order to confirm dopaminergic neuronal loss. To directly explore the impact of ATP13A2 loss-of-function on the viability and integrity of dopaminergic neurons, we employed mir-30adapted short hairpin RNA (shRNA) constructs to silence the expression of endogenous ATP13A2. To vali ...
... ATP13A2 mutations in order to confirm dopaminergic neuronal loss. To directly explore the impact of ATP13A2 loss-of-function on the viability and integrity of dopaminergic neurons, we employed mir-30adapted short hairpin RNA (shRNA) constructs to silence the expression of endogenous ATP13A2. To vali ...
fulltext
... A major challenge in the field of neuroscience is to link behavior with specific neuronal circuitries and cellular events. One way of facing this challenge is to identify unique cellular markers and thus have the ability to, through various mouse genetics tools, mimic, manipulate and control various ...
... A major challenge in the field of neuroscience is to link behavior with specific neuronal circuitries and cellular events. One way of facing this challenge is to identify unique cellular markers and thus have the ability to, through various mouse genetics tools, mimic, manipulate and control various ...
MECHANISMS OF VERTEBRATE SYNAPTOGENESIS
... from the ventral horn of the spinal cord delay synapse formation until they innervate muscle fibers some distance away (Burden 2002, Sanes & Lichtman 2001). In these examples not only is synapse formation delayed until axons reach specific target regions, but even within these target regions there are ...
... from the ventral horn of the spinal cord delay synapse formation until they innervate muscle fibers some distance away (Burden 2002, Sanes & Lichtman 2001). In these examples not only is synapse formation delayed until axons reach specific target regions, but even within these target regions there are ...
Favorable Recording Criteria for Spike Sorting
... Spike sorting is the generic term used to describe the procedure for identifying spikes in multi-neuron recordings and categorizing them according to waveform and amplitude differences. Correctly relating each spike to a category and accurately estimating its time of occurrence is prerequisite to pr ...
... Spike sorting is the generic term used to describe the procedure for identifying spikes in multi-neuron recordings and categorizing them according to waveform and amplitude differences. Correctly relating each spike to a category and accurately estimating its time of occurrence is prerequisite to pr ...
the distribution of the cells of origin of callosal projections in cat
... Figures 2 and 3. In rostral coronal sections, the region of area 17 containing labeled neurons extended medially no further than the suprasplenial sulcus (Figs. 2, A to C, and 3, A to F ). At caudal anterior-posterior levels, the region of label did not extend more medially than the crown of the lat ...
... Figures 2 and 3. In rostral coronal sections, the region of area 17 containing labeled neurons extended medially no further than the suprasplenial sulcus (Figs. 2, A to C, and 3, A to F ). At caudal anterior-posterior levels, the region of label did not extend more medially than the crown of the lat ...
Article - Perelman School of Medicine at the University of
... are unable to assume proper laminar position, a critical and very early differentiation step of postmitotic neurons. We next examined how each of the three sequentially born subtypes of CFu neurons is specifically affected by loss of SOX5. Nissl staining shows absence of a morphological SP in Sox5!/ ...
... are unable to assume proper laminar position, a critical and very early differentiation step of postmitotic neurons. We next examined how each of the three sequentially born subtypes of CFu neurons is specifically affected by loss of SOX5. Nissl staining shows absence of a morphological SP in Sox5!/ ...
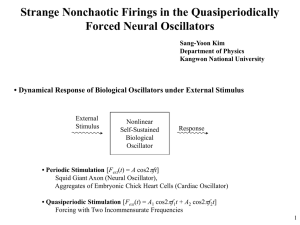
I dc
... Phase Sensitivity: Characterized by Differentiating V with respect to at a discrete time t=nP1 (P1=1/f1) |Sn|: bounded for all n Smooth Geometry |Sn|: unbounded (a dense set of singularities) ...
... Phase Sensitivity: Characterized by Differentiating V with respect to at a discrete time t=nP1 (P1=1/f1) |Sn|: bounded for all n Smooth Geometry |Sn|: unbounded (a dense set of singularities) ...
Event-Driven Simulation Scheme for Spiking Neural Networks Using
... cells is represented internally by two events. The first one (the firing event) is marked with the time instant when the source neuron fires the spike. The second one (the propagated event) is marked with the time instant when the spike reaches the target neuron. Most neurons have large synaptic div ...
... cells is represented internally by two events. The first one (the firing event) is marked with the time instant when the source neuron fires the spike. The second one (the propagated event) is marked with the time instant when the spike reaches the target neuron. Most neurons have large synaptic div ...
Loss of TDP-43 causes age-dependent progressive motor neuron
... of knockout of transactive response DNA-binding protein 43 in mouse postnatal motor neurons using Cre/loxp system. These mice developed progressive weight loss and motor impairment around the age of 60 weeks, and exhibited degeneration of large motor axon, grouped atrophy of the skeletal muscle, and ...
... of knockout of transactive response DNA-binding protein 43 in mouse postnatal motor neurons using Cre/loxp system. These mice developed progressive weight loss and motor impairment around the age of 60 weeks, and exhibited degeneration of large motor axon, grouped atrophy of the skeletal muscle, and ...
Hypothalamic regulation of sleep and circadian rhythms
... two groups of investigators again simultaneously found that a lack of orexins or their type 2 receptor can cause symptoms of narcolepsy in experimental animals46,47. The following year, it was reported that humans who have narcolepsy with cataplexy have few orexin neurons a ...
... two groups of investigators again simultaneously found that a lack of orexins or their type 2 receptor can cause symptoms of narcolepsy in experimental animals46,47. The following year, it was reported that humans who have narcolepsy with cataplexy have few orexin neurons a ...
MECHANISMS OF VERTEBRATE SYNAPTOGENESIS
... from the ventral horn of the spinal cord delay synapse formation until they innervate muscle fibers some distance away (Burden 2002, Sanes & Lichtman 2001). In these examples not only is synapse formation delayed until axons reach specific target regions, but even within these target regions there are ...
... from the ventral horn of the spinal cord delay synapse formation until they innervate muscle fibers some distance away (Burden 2002, Sanes & Lichtman 2001). In these examples not only is synapse formation delayed until axons reach specific target regions, but even within these target regions there are ...
Inhibitory Plasticity Balances Excitation and Inhibition in Sensory
... established and maintained during ongoing sensory experiences. Inspired by recent experimental results (7), we investigated the hypothesis that synaptic plasticity at inhibitory synapses plays a central role in balancing the excitatory and inhibitory inputs a cell receives. We simulated a single pos ...
... established and maintained during ongoing sensory experiences. Inspired by recent experimental results (7), we investigated the hypothesis that synaptic plasticity at inhibitory synapses plays a central role in balancing the excitatory and inhibitory inputs a cell receives. We simulated a single pos ...
Degeneration and Regeneration in Crustacean
... sensory fibers can be identified by recording from medial branches of the meropodite thick bundle that contain at most one or two motor axons whose large spikes are clearly separable from those of the smaller sensory axons in extracellular recordings. It is possible to elicit sensory action potentia ...
... sensory fibers can be identified by recording from medial branches of the meropodite thick bundle that contain at most one or two motor axons whose large spikes are clearly separable from those of the smaller sensory axons in extracellular recordings. It is possible to elicit sensory action potentia ...
Kalirin, a Multifunctional Rho Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor
... inserted into pCMS cut with EcoRI, blunted, and cut with NotI. This yields a His6-myc-Kal-GEF1 construct under the control of the CMV promoter (May et al., 2002). pCMS-GFP-Kal-antisense. PCR primers were designed to excise the fragment encoding E 738-LFHERK to KEYGE-F 1150 of Kalirin-7 with NotI–Spe ...
... inserted into pCMS cut with EcoRI, blunted, and cut with NotI. This yields a His6-myc-Kal-GEF1 construct under the control of the CMV promoter (May et al., 2002). pCMS-GFP-Kal-antisense. PCR primers were designed to excise the fragment encoding E 738-LFHERK to KEYGE-F 1150 of Kalirin-7 with NotI–Spe ...
(2007) The most superficial sublamina of rat superior colluculus
... entered the SGS1. The main body of our data presented here is based on recordings made from the neurons encountered within the SGS1 layer, the upper 100 m after SC surface penetration. The SGS1 was identified, in the presence of visual stimulation, by a very characteristic noise produced by “juxtaz ...
... entered the SGS1. The main body of our data presented here is based on recordings made from the neurons encountered within the SGS1 layer, the upper 100 m after SC surface penetration. The SGS1 was identified, in the presence of visual stimulation, by a very characteristic noise produced by “juxtaz ...
M1 Corticospinal Mirror Neurons and Their Role in
... Mirror neurons are particularly fascinating in that they are activated not only by one’s own actions but also by the actions of others. Mirror neurons in macaque area F5 were originally shown to respond during both the monkey’s own grasping action and during observation of grasp carried out by a hum ...
... Mirror neurons are particularly fascinating in that they are activated not only by one’s own actions but also by the actions of others. Mirror neurons in macaque area F5 were originally shown to respond during both the monkey’s own grasping action and during observation of grasp carried out by a hum ...
The neurophysiological correlates of motor tics following focal
... locked to the tics. Consistent with theoretical models of tic generation, transient inhibition of the basal ganglia output nucleus prior to and during tic expression was observed. The phasic reduction of basal ganglia output was correlated with a disinhibition of cortical activity, manifesting as sh ...
... locked to the tics. Consistent with theoretical models of tic generation, transient inhibition of the basal ganglia output nucleus prior to and during tic expression was observed. The phasic reduction of basal ganglia output was correlated with a disinhibition of cortical activity, manifesting as sh ...
Visual and Oculomotor Functions of Monkey Subthalamic Nucleus
... of this window wasmadelarger for more eccentrictargets.When (2 PA for 200 s) through the recording electrodes.The marks eyepositionwasmaintainedwithin the fixation window, a reward madefor eachpenetration usually wereplacedat similar depths, wasgiven 300 ms after the dimming; failure to maintain fix ...
... of this window wasmadelarger for more eccentrictargets.When (2 PA for 200 s) through the recording electrodes.The marks eyepositionwasmaintainedwithin the fixation window, a reward madefor eachpenetration usually wereplacedat similar depths, wasgiven 300 ms after the dimming; failure to maintain fix ...
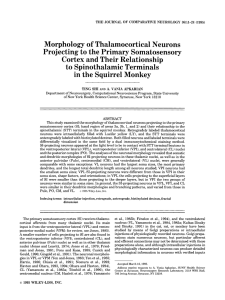
Morphology of Thalamocortical Neurons Projecting
... shown in Figure 2. Most SI-projecting neurons in VPI were medium-sized or small, and had four to eight primary dendrites (see Fig. 3). The labeled SI-projecting neurons in Pulo were medium-sized to large, multipolar, and usually had five to nine primary dendrites with many branches (see Fig. 4). lab ...
... shown in Figure 2. Most SI-projecting neurons in VPI were medium-sized or small, and had four to eight primary dendrites (see Fig. 3). The labeled SI-projecting neurons in Pulo were medium-sized to large, multipolar, and usually had five to nine primary dendrites with many branches (see Fig. 4). lab ...
Midbrain fMRI: Applications, Limitations and Challenges
... of one coherent dopaminergic cell complex (e.g. Beckstead et al. 1979; but also see McRitchie et al. (1996) for subtle differences in cell orientation, size and density between these cell groups). Further DA neurons are located in nearby regions such as the hypothalamus, periaqueductal grey, rostral ...
... of one coherent dopaminergic cell complex (e.g. Beckstead et al. 1979; but also see McRitchie et al. (1996) for subtle differences in cell orientation, size and density between these cell groups). Further DA neurons are located in nearby regions such as the hypothalamus, periaqueductal grey, rostral ...
Full text
... common localization of GnRH and NPY containg neurons especially in IN and ME was shown [2, 14]. This neuroanatomical colocalization implicates some physiological interactions which are associated with hormone release. Recently, Advis et al. [1] showed, using the push-pull technique, that NPY release ...
... common localization of GnRH and NPY containg neurons especially in IN and ME was shown [2, 14]. This neuroanatomical colocalization implicates some physiological interactions which are associated with hormone release. Recently, Advis et al. [1] showed, using the push-pull technique, that NPY release ...
Dynamics of Propofol-Induced Loss of Consciousness Across
... using the Chronux toolbox for MATLAB was ipsilateral to the recording hemisphere). The animal is required to keep its hand on the button until the end of the trial to be able used to generate spectra (Fig. 2C,D), spectro- to gain a liquid reward and then to release the button during the intertrial i ...
... using the Chronux toolbox for MATLAB was ipsilateral to the recording hemisphere). The animal is required to keep its hand on the button until the end of the trial to be able used to generate spectra (Fig. 2C,D), spectro- to gain a liquid reward and then to release the button during the intertrial i ...
Caridoid escape reaction

The caridoid escape reaction, also known as lobstering or tail-flipping, refers to an innate escape mechanism in marine and freshwater crustaceans such as lobsters, krill, shrimp and crayfish.The reaction, most extensively researched in crayfish, allows crustaceans to escape predators through rapid abdominal flexions that produce powerful swimming strokes — thrusting the crustacean backwards through the water and away from danger. The type of response depends on the part of the crustacean stimulated, but this behavior is complex and is regulated both spatially and temporally through the interactions of several neurons.