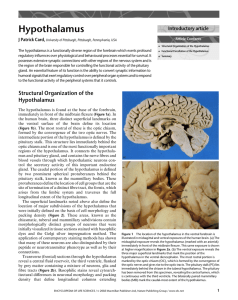
Hypothalamus
... physiological and behavioural processes. This is accomplished by compact cell groups in the rostral hypothalamus, known as the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN). SCN neurons exhibit a genetically derived circadian rhythm of neuronal activity in which neuronal activity is high for 12 h of the light dark c ...
... physiological and behavioural processes. This is accomplished by compact cell groups in the rostral hypothalamus, known as the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN). SCN neurons exhibit a genetically derived circadian rhythm of neuronal activity in which neuronal activity is high for 12 h of the light dark c ...
The mirror mechanism: recent findings and perspectives
... between the executed and the observed motor act [2– 5]. Some mirror neurons show a strict correspondence between the effective observed and executed motor act; others show a correspondence in the goal of the observed and executed motor act, but not in the precise movements necessary to achieve the g ...
... between the executed and the observed motor act [2– 5]. Some mirror neurons show a strict correspondence between the effective observed and executed motor act; others show a correspondence in the goal of the observed and executed motor act, but not in the precise movements necessary to achieve the g ...
Linköping University Post Print the developmental age of the cells
... It has been reported that peripheral nerves from younger rats are more vulnerable to prolonged severe hypoglycemia than those from older animals (Yasaki and Dyck 1990). In the brain, Kim and colleagues (2005) observed more cell injury in hypoglycemic mice at postnatal day 7 (P7) than at P21. In addi ...
... It has been reported that peripheral nerves from younger rats are more vulnerable to prolonged severe hypoglycemia than those from older animals (Yasaki and Dyck 1990). In the brain, Kim and colleagues (2005) observed more cell injury in hypoglycemic mice at postnatal day 7 (P7) than at P21. In addi ...
Chapter 9b final
... If wakefulness is prolonged, more adenosine accumulates, inhibits neural activity Produces cognitive and emotional effects of sleep ...
... If wakefulness is prolonged, more adenosine accumulates, inhibits neural activity Produces cognitive and emotional effects of sleep ...
Encoding of Movement Fragments in the Motor Cortex
... Example of a single successful behavioral trial in the RTP task starting with the blue target, proceeding through the green targets, and ending at the red target. A sample trajectory (400 ms long) is also shown (blue and red lines), which was used to compute the preferred direction shifts as a funct ...
... Example of a single successful behavioral trial in the RTP task starting with the blue target, proceeding through the green targets, and ending at the red target. A sample trajectory (400 ms long) is also shown (blue and red lines), which was used to compute the preferred direction shifts as a funct ...
Basics of electromagnetic field mapping
... The physics that relate the activity of a given dipole source in the brain to a measurable electric and/or magnetic field on the scalp is well known. It is defined by the geometry and, in the case of EEG, the volume conduction properties of the tissues of the head (brain, liquor, skull, scalp, hair, ...
... The physics that relate the activity of a given dipole source in the brain to a measurable electric and/or magnetic field on the scalp is well known. It is defined by the geometry and, in the case of EEG, the volume conduction properties of the tissues of the head (brain, liquor, skull, scalp, hair, ...
PDF
... Units recorded from optic fibre terminals in the superficial neuropil of the optic tectum were classified according to their responses to moving black stimuli, to spots of light and to changes in background illumination. 96 % of units were easily classifiable into one of three categories (Keating & ...
... Units recorded from optic fibre terminals in the superficial neuropil of the optic tectum were classified according to their responses to moving black stimuli, to spots of light and to changes in background illumination. 96 % of units were easily classifiable into one of three categories (Keating & ...
Sleep and Biological Rhythms
... experience some dreaming during sleep We may recall very little of the mental activity that occurred during sleep ...
... experience some dreaming during sleep We may recall very little of the mental activity that occurred during sleep ...
The hippocampo-cortical loop: Spatio
... between states which are coded on one neuron (‘‘Transition cell’’, see below). In all our models, neurons are modeled as analog units. However this single neuron activity is representative of what is assumed to be a population code in-vivo (see Section 5 for a discussion). According to Gaussier, Rev ...
... between states which are coded on one neuron (‘‘Transition cell’’, see below). In all our models, neurons are modeled as analog units. However this single neuron activity is representative of what is assumed to be a population code in-vivo (see Section 5 for a discussion). According to Gaussier, Rev ...
Lineage origins of GABAergic versus glutamatergic neurons in the
... most layer VI projection neurons project to the thalamus, while layer V neurons connect to basal ganglia, midbrain, hindbrain and spinal cord. By contrast, layer IV spiny stellate neurons receive most of the inputs from the thalamus and project locally within the neocortex, while layer II and III pr ...
... most layer VI projection neurons project to the thalamus, while layer V neurons connect to basal ganglia, midbrain, hindbrain and spinal cord. By contrast, layer IV spiny stellate neurons receive most of the inputs from the thalamus and project locally within the neocortex, while layer II and III pr ...
PDF
... P2X2 expression, or with laser illumination alone (not shown), induced only minimal changes in preference (Figure 5A, columns f–h). These changes are in all likelihood due to a small intrinsically aversive effect of intense ultraviolet irradiation. Sources of Dopaminergic Reinforcement Signals The d ...
... P2X2 expression, or with laser illumination alone (not shown), induced only minimal changes in preference (Figure 5A, columns f–h). These changes are in all likelihood due to a small intrinsically aversive effect of intense ultraviolet irradiation. Sources of Dopaminergic Reinforcement Signals The d ...
Spike-timing dependent plasticity and the cognitive map
... Mathematically, with s = tpost − tpre being the time difference between pre- and post-synaptic spiking, the change in the weight of a synapse (∆w) according to a standard implementation of additive STDP can be calculated using Eq. 2. The parameters A+ and A− correspond to the maximum possible ch ...
... Mathematically, with s = tpost − tpre being the time difference between pre- and post-synaptic spiking, the change in the weight of a synapse (∆w) according to a standard implementation of additive STDP can be calculated using Eq. 2. The parameters A+ and A− correspond to the maximum possible ch ...
General anaesthesia: from molecular targets to neuronal
... a century, loss of the righting reflex (LORR) in animals has been used effectively as a surrogate measure. The data in FIG. 1 show that there is an excellent correlation between LOC in humans and LORR in animals over a range of potency exceeding five orders of magnitude. Similarly, there is an equal ...
... a century, loss of the righting reflex (LORR) in animals has been used effectively as a surrogate measure. The data in FIG. 1 show that there is an excellent correlation between LOC in humans and LORR in animals over a range of potency exceeding five orders of magnitude. Similarly, there is an equal ...
The elephant brain in numbers
... series of 16 sections (Kruskal-Wallis test, p = 0.0019; Figure 3B). These findings are consistent with a larger average size of neurons (including soma, axons and dendrites) in the anterior-most portion of the elephant cerebral cortex (Jacobs et al., 2011), as has been seen in primates (Elston et al ...
... series of 16 sections (Kruskal-Wallis test, p = 0.0019; Figure 3B). These findings are consistent with a larger average size of neurons (including soma, axons and dendrites) in the anterior-most portion of the elephant cerebral cortex (Jacobs et al., 2011), as has been seen in primates (Elston et al ...
Watching synapses during sensory information
... brain slice preparations, several working models of how dendrites organize feature-specific synaptic inputs have been proposed: (1) All inputs to a neuron are specific for a single ...
... brain slice preparations, several working models of how dendrites organize feature-specific synaptic inputs have been proposed: (1) All inputs to a neuron are specific for a single ...
Response characteristics of neurons in the pulvinar of awake cats to
... ing saccades but not to visual stimulation (n=27, 16% of characterized neurons; S neurons), second, neurons that responded to visual stimuli but not during saccades (n=86, 51% of characterized neurons; V neurons), and third, neurons that responded during saccades and to visual stimuli (n=53, 31% of ...
... ing saccades but not to visual stimulation (n=27, 16% of characterized neurons; S neurons), second, neurons that responded to visual stimuli but not during saccades (n=86, 51% of characterized neurons; V neurons), and third, neurons that responded during saccades and to visual stimuli (n=53, 31% of ...
Proceedings of 2013 BMI the Second International Conference on
... There is a growing body of research about the outcomes of using virtual avatars (and other mediated self-representations). For example, the Proteus Effect suggests that people behave in ways that conform to their avatars' characteristics, even after avatar use, e.g., using taller avatars leads to mo ...
... There is a growing body of research about the outcomes of using virtual avatars (and other mediated self-representations). For example, the Proteus Effect suggests that people behave in ways that conform to their avatars' characteristics, even after avatar use, e.g., using taller avatars leads to mo ...
Arbib, 2008 - Semantic Scholar
... In putting parity at stage center in this account, we adhere to the view that the primary function of language is communication. Others have espoused the alternative view that language evolution could have obeyed an adaptive pressure for developing higher cognitive abilities and that verbal communic ...
... In putting parity at stage center in this account, we adhere to the view that the primary function of language is communication. Others have espoused the alternative view that language evolution could have obeyed an adaptive pressure for developing higher cognitive abilities and that verbal communic ...
moth`s nervous system - Wageningen UR E
... moth Manduca sexta. Wehave investigated this model olfactory system extensively by meansof anatomical, ...
... moth Manduca sexta. Wehave investigated this model olfactory system extensively by meansof anatomical, ...
An Intrinsic Oscillation in Interneurons of the Rat Lateral Geniculate
... an axon to cortex. Local interneurons, which reside among the thalamocortical cells in the principal relay nuclei, and cells in the adjacent thalamic reticular nucleus (TRN) are GABAergic, and their axons are restricted to the thalamus. Thalamocortical and TRN cells are implicated heavily in oscilla ...
... an axon to cortex. Local interneurons, which reside among the thalamocortical cells in the principal relay nuclei, and cells in the adjacent thalamic reticular nucleus (TRN) are GABAergic, and their axons are restricted to the thalamus. Thalamocortical and TRN cells are implicated heavily in oscilla ...
Spiking Neurons - Computing Science and Mathematics
... These classical results show that the experimenter as an external observer can evaluate and classify neuronal firing by a spike count measure - but is this really the code used by neurons in the brain ? In other words , is a neuron which receives signals from a sensory neuron only looking at and rea ...
... These classical results show that the experimenter as an external observer can evaluate and classify neuronal firing by a spike count measure - but is this really the code used by neurons in the brain ? In other words , is a neuron which receives signals from a sensory neuron only looking at and rea ...
The Rat Ventromedial Thalamic Nucleus and Motor Control: Role of
... substantia nigra. In addition, the superior colliculus, the mesencephalic reticular formation, and the reticular thalamic nucleus contribute to the afferent input to the VM (Beckstead et al., 1979; Carter and Fibiger, 1978; Haroian et al., 198 1; Herkenham, 1979; Jones, 1975). In contrast to the pri ...
... substantia nigra. In addition, the superior colliculus, the mesencephalic reticular formation, and the reticular thalamic nucleus contribute to the afferent input to the VM (Beckstead et al., 1979; Carter and Fibiger, 1978; Haroian et al., 198 1; Herkenham, 1979; Jones, 1975). In contrast to the pri ...
Visual Categorization and the Primate Prefrontal Cortex
... “camera” instantly and effortlessly provides a great deal of information about its relevant parts and functions and spares us from having to learn anew each time we encounter a new individual. The ability to categorize stimuli is a cornerstone of complex behavior. Categories are evident in all senso ...
... “camera” instantly and effortlessly provides a great deal of information about its relevant parts and functions and spares us from having to learn anew each time we encounter a new individual. The ability to categorize stimuli is a cornerstone of complex behavior. Categories are evident in all senso ...
Neural oscillation

Neural oscillation is rhythmic or repetitive neural activity in the central nervous system. Neural tissue can generate oscillatory activity in many ways, driven either by mechanisms within individual neurons or by interactions between neurons. In individual neurons, oscillations can appear either as oscillations in membrane potential or as rhythmic patterns of action potentials, which then produce oscillatory activation of post-synaptic neurons. At the level of neural ensembles, synchronized activity of large numbers of neurons can give rise to macroscopic oscillations, which can be observed in the electroencephalogram (EEG). Oscillatory activity in groups of neurons generally arises from feedback connections between the neurons that result in the synchronization of their firing patterns. The interaction between neurons can give rise to oscillations at a different frequency than the firing frequency of individual neurons. A well-known example of macroscopic neural oscillations is alpha activity.Neural oscillations were observed by researchers as early as 1924 (by Hans Berger). More than 50 years later, intrinsic oscillatory behavior was encountered in vertebrate neurons, but its functional role is still not fully understood. The possible roles of neural oscillations include feature binding, information transfer mechanisms and the generation of rhythmic motor output. Over the last decades more insight has been gained, especially with advances in brain imaging. A major area of research in neuroscience involves determining how oscillations are generated and what their roles are. Oscillatory activity in the brain is widely observed at different levels of observation and is thought to play a key role in processing neural information. Numerous experimental studies support a functional role of neural oscillations; a unified interpretation, however, is still lacking.























