Chapter 15
... 2. Axons of olfactory neurons pass through holes of the ___________________ to the ____________________ 3. The olfactory tracts ________________________________________ 4. What is an olfactory vesicle? ______________________________________ 5. Where are olfactory hairs found? _______________________ ...
... 2. Axons of olfactory neurons pass through holes of the ___________________ to the ____________________ 3. The olfactory tracts ________________________________________ 4. What is an olfactory vesicle? ______________________________________ 5. Where are olfactory hairs found? _______________________ ...
Key Elements of Sensation
... specialized receptor cells for olfaction are hair cells, or _________. Researchers have been _______________ to identify specific basic smells, as they have for taste. It appears there are at least ________ different types of olfactory receptor cells that allow for the detections of over 10,000 diff ...
... specialized receptor cells for olfaction are hair cells, or _________. Researchers have been _______________ to identify specific basic smells, as they have for taste. It appears there are at least ________ different types of olfactory receptor cells that allow for the detections of over 10,000 diff ...
The Nervous System
... 1. Interneuron – Found in the CNS only. – They associate or “connect” sensory neurons and motor neurons. ...
... 1. Interneuron – Found in the CNS only. – They associate or “connect” sensory neurons and motor neurons. ...
Biology
... Dendrite or cell body picks up message If message is strong enough, neuron fires and impulse starts down the axon Out the end of the axon terminal to the ...
... Dendrite or cell body picks up message If message is strong enough, neuron fires and impulse starts down the axon Out the end of the axon terminal to the ...
Biology The Nervous System
... Dendrite or cell body picks up message If message is strong enough, neuron fires and impulse starts down the axon Out the end of the axon terminal to the synaptic ...
... Dendrite or cell body picks up message If message is strong enough, neuron fires and impulse starts down the axon Out the end of the axon terminal to the synaptic ...
Spinal Cord - Northside Middle School
... and developing well into our 80’s (current research states 80’s but it could be longer). Just because your biological hand may have dealt you a certain brain style doesn’t mean you can’t change, build, and reconstruct your brain. If you communicate indirectly you can practice communicating directly ...
... and developing well into our 80’s (current research states 80’s but it could be longer). Just because your biological hand may have dealt you a certain brain style doesn’t mean you can’t change, build, and reconstruct your brain. If you communicate indirectly you can practice communicating directly ...
The Nervous System
... - divided into 2 sections called ______________________, controlling the opposite side of the body - the _________ hemisphere may control creativity and artistic ability - the left hemisphere may control analytical and mathematical ability - site of learning, judgment, and _____________________ - th ...
... - divided into 2 sections called ______________________, controlling the opposite side of the body - the _________ hemisphere may control creativity and artistic ability - the left hemisphere may control analytical and mathematical ability - site of learning, judgment, and _____________________ - th ...
My Big List Thing
... o Pericranium: another name for periosteum around the skull Phosphatase: enzyme which removes phosphate group from substrate Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF): numerous growth factors, or proteins that regulate cell growth and division; significant in angiogenesis Schwann cell: mylenating glial ...
... o Pericranium: another name for periosteum around the skull Phosphatase: enzyme which removes phosphate group from substrate Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF): numerous growth factors, or proteins that regulate cell growth and division; significant in angiogenesis Schwann cell: mylenating glial ...
Redalyc.Normal neuronal migration
... and primary vesicles. Of the latter, the most rostral, the prosencephalon, two vesicles are bilaterally generated, the telencephalon and in the middle, the unpaired diencephalons. The telencepahlic vesicles generate the cerebral hemispheres and the lateral ventricles; the latter constitutes the main ...
... and primary vesicles. Of the latter, the most rostral, the prosencephalon, two vesicles are bilaterally generated, the telencephalon and in the middle, the unpaired diencephalons. The telencepahlic vesicles generate the cerebral hemispheres and the lateral ventricles; the latter constitutes the main ...
The Cerebral Cortex
... – Inside its field, a place cell may have a maximum rate of 20Hz or more, whereas outside its field, a place cell may fire less than 1 spike every 10 seconds (.1Hz). – Given a sufficient number, place cells and their fields are able to cover or "map" any given environment. – evidence from place cell ...
... – Inside its field, a place cell may have a maximum rate of 20Hz or more, whereas outside its field, a place cell may fire less than 1 spike every 10 seconds (.1Hz). – Given a sufficient number, place cells and their fields are able to cover or "map" any given environment. – evidence from place cell ...
ANPS 019 Black 11-30
... Why are the cerebral peduncles so much larger than the pyramids? Any cranial nerve that going to innervate head and neck must get information from the cortex What other tracts are in the cerebral peduncles? Corticobulbar Tract Function: -innervates cranial nerve nuclei in brainstem Descending Pathwa ...
... Why are the cerebral peduncles so much larger than the pyramids? Any cranial nerve that going to innervate head and neck must get information from the cortex What other tracts are in the cerebral peduncles? Corticobulbar Tract Function: -innervates cranial nerve nuclei in brainstem Descending Pathwa ...
Development from Neural Crest Cells
... • Integrin expression in NCCs upon migration (e.g. integrin α4β1) • When these integrin proteins are lacking, NCCs released from the neural tube become disoriented and often time undergo apoptosis. • Thrombospondin, expressed only in the anterior portion of the sclerotome, promotes NCC adhesion and ...
... • Integrin expression in NCCs upon migration (e.g. integrin α4β1) • When these integrin proteins are lacking, NCCs released from the neural tube become disoriented and often time undergo apoptosis. • Thrombospondin, expressed only in the anterior portion of the sclerotome, promotes NCC adhesion and ...
Posttraumatic stress disorder
... damage to their prefrontal cortex before age seven, developed abnormal social behavior, characterized by an inability to control their frustration, anger and aggression. • A brain imaging study of murderers found evidence that, on average, the prefrontal cortex as well as some deeper brain areas, in ...
... damage to their prefrontal cortex before age seven, developed abnormal social behavior, characterized by an inability to control their frustration, anger and aggression. • A brain imaging study of murderers found evidence that, on average, the prefrontal cortex as well as some deeper brain areas, in ...
File - Shifa Students Corner
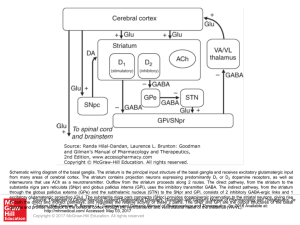
... The major output of the striatum is to the pallidum, and it is inhibitory. Excitatory input to the pallidum comes from the subthalamic nucleus The output of the pallidum, which is also inhibitory, is to various thalamic nuclei. The thalamic nuclei project to and excite the premotor and supplemen ...
... The major output of the striatum is to the pallidum, and it is inhibitory. Excitatory input to the pallidum comes from the subthalamic nucleus The output of the pallidum, which is also inhibitory, is to various thalamic nuclei. The thalamic nuclei project to and excite the premotor and supplemen ...
Slide ()
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Slide ()
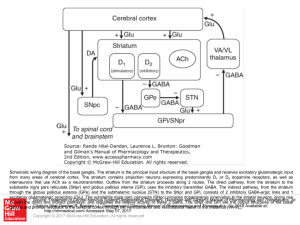
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
ATP-Sensitive Potassium Channels in Dopaminergic Neurons
... adapting electrical activity and in turn neuronal ATP consumption to the delicate metabolic state of neurons. KATP channel-mediated membrane hyperpolarization will reduce neuronal activity and neurotransmitter release and thus could counteract calcium overload and excitotoxicity. This mechanism coul ...
... adapting electrical activity and in turn neuronal ATP consumption to the delicate metabolic state of neurons. KATP channel-mediated membrane hyperpolarization will reduce neuronal activity and neurotransmitter release and thus could counteract calcium overload and excitotoxicity. This mechanism coul ...
BIOL 241 Autonomic Nervous System 1 I. Visceral Reflexes A. All
... f. all sympathetic postgangs arise from ganglia 4. Adrenal glands a. cortex -steroids b. medulla - derived from neural crest modified symp. ganglion epinephrine and norepinephrine some dopamine B. Parasympathetic division 1. vegetative activities 2. reduces heart rate and respiration 3. some cell bo ...
... f. all sympathetic postgangs arise from ganglia 4. Adrenal glands a. cortex -steroids b. medulla - derived from neural crest modified symp. ganglion epinephrine and norepinephrine some dopamine B. Parasympathetic division 1. vegetative activities 2. reduces heart rate and respiration 3. some cell bo ...
2_Vision
... How does the Visual System Create Color? • Color does not exist in the world, only in the mind---WHOA! – color is a sensation created when light waves are transduced (I have no idea if this is the correct past tense of transduction) and then processed in our visual cortex ...
... How does the Visual System Create Color? • Color does not exist in the world, only in the mind---WHOA! – color is a sensation created when light waves are transduced (I have no idea if this is the correct past tense of transduction) and then processed in our visual cortex ...
Reactivation of Latent Herpes Simplex Virus from Dissociated
... root ganglia of latently infected mice. The neurons in culture were identified morphologically and by using the specific anti-neuronal monoclonal antibody A2B5. HSV antigen expression during reactivation was first seen in neurons on day 3 after dissociation, and infectious virus was released subsequ ...
... root ganglia of latently infected mice. The neurons in culture were identified morphologically and by using the specific anti-neuronal monoclonal antibody A2B5. HSV antigen expression during reactivation was first seen in neurons on day 3 after dissociation, and infectious virus was released subsequ ...
Slide 1
... From signal perception (by a GPCR) to response (28/11 -13) Starting point: GPCR & a/b/g complex ...
... From signal perception (by a GPCR) to response (28/11 -13) Starting point: GPCR & a/b/g complex ...
Reactivation of Latent Herpes Simplex Virus from Dissociated
... root ganglia of latently infected mice. The neurons in culture were identified morphologically and by using the specific anti-neuronal monoclonal antibody A2B5. HSV antigen expression during reactivation was first seen in neurons on day 3 after dissociation, and infectious virus was released subsequ ...
... root ganglia of latently infected mice. The neurons in culture were identified morphologically and by using the specific anti-neuronal monoclonal antibody A2B5. HSV antigen expression during reactivation was first seen in neurons on day 3 after dissociation, and infectious virus was released subsequ ...
Notes
... Bipolar cells are retinal interneurons that receive synaptic input from rods and cones. The ON cells depolarize when glutamate secretion from photoreceptors is decreased (respond to a light stimulus) and OFF cells hyperpolarize in the same situation. OFF have kainic acid Glut receptors, and ON have ...
... Bipolar cells are retinal interneurons that receive synaptic input from rods and cones. The ON cells depolarize when glutamate secretion from photoreceptors is decreased (respond to a light stimulus) and OFF cells hyperpolarize in the same situation. OFF have kainic acid Glut receptors, and ON have ...
Final review quiz
... Can population firing rate vectors change over time? If so, how? In motor cortex, population firing rate vector refers to motor cortex neuron activations that result in pattern of muscle activations or ________________________ How do population firing rate vectors relate to the so-called “grandmothe ...
... Can population firing rate vectors change over time? If so, how? In motor cortex, population firing rate vector refers to motor cortex neuron activations that result in pattern of muscle activations or ________________________ How do population firing rate vectors relate to the so-called “grandmothe ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.