I) Mark right or false beside each sentence and correct the wrong
... to produce action potential. ( ) 4- The action potential in neurons moves unidirectional from axon terminals to axon to cell body to dendrite. ( اﻋﻛ)س 5- The signals are chemically transmitted from dendrite to cell body to axon while they are electrically transmitted from axon terminals to dendrit ...
... to produce action potential. ( ) 4- The action potential in neurons moves unidirectional from axon terminals to axon to cell body to dendrite. ( اﻋﻛ)س 5- The signals are chemically transmitted from dendrite to cell body to axon while they are electrically transmitted from axon terminals to dendrit ...
Neuroscience and Behavior - Bremerton School District
... A functional MRI scan shows the auditory cortex is active in patients who hallucinate. ...
... A functional MRI scan shows the auditory cortex is active in patients who hallucinate. ...
PowerPoint Chapter 29
... B. Homeostasis depends on ability of different systems in body to communicate with one another 1. Messages must be generated, delivered, interpreted, and acted upon by your body ...
... B. Homeostasis depends on ability of different systems in body to communicate with one another 1. Messages must be generated, delivered, interpreted, and acted upon by your body ...
How Does Caffeine Affect the Central Nervous System? (CNS)
... Research Reviews. U.S. National Library of Medicine, n.d. Web. 10 Apr. 2017. ...
... Research Reviews. U.S. National Library of Medicine, n.d. Web. 10 Apr. 2017. ...
Stephen Hawking
... muscles throughout the body. • Stephen Hawking is unable to move or speak* because of a disease called Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis ...
... muscles throughout the body. • Stephen Hawking is unable to move or speak* because of a disease called Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis ...
October 29
... Decussation – crossing of a bundle of fibers (axons) from one side of the brain to the other. Tract – a bundle of fibers going the same way ...
... Decussation – crossing of a bundle of fibers (axons) from one side of the brain to the other. Tract – a bundle of fibers going the same way ...
File
... Activity 34.2 The Human Cerebrum 1. What part of the brain controls muscle activity and maintaining balance. 2. What is the job of the frontal lobe? 3. What is the job of the parietal lobe? Activity 34.3 Structures of the Human Brain Practice the structures of the human brain. Interactive Tutorial 3 ...
... Activity 34.2 The Human Cerebrum 1. What part of the brain controls muscle activity and maintaining balance. 2. What is the job of the frontal lobe? 3. What is the job of the parietal lobe? Activity 34.3 Structures of the Human Brain Practice the structures of the human brain. Interactive Tutorial 3 ...
nervous systems
... Neurons are specialized cells of the nervous system that receive, encode, and transmit information. Neurons with their support cells (glial cells) make up nervous systems. Modified neurons called sensory cells receive information and convert or transduce it into electrical signals that are transmitt ...
... Neurons are specialized cells of the nervous system that receive, encode, and transmit information. Neurons with their support cells (glial cells) make up nervous systems. Modified neurons called sensory cells receive information and convert or transduce it into electrical signals that are transmitt ...
Nervous System Review Power Point
... But… if neurons never touch, how does the action potential (or nerve impulse) get between the small space between the end of one nerve cell and the beginning of the next nerve ...
... But… if neurons never touch, how does the action potential (or nerve impulse) get between the small space between the end of one nerve cell and the beginning of the next nerve ...
Technological integration and hyper-connectivity
... selection (1). Here, an attempt will be made to study the common evolutionary mechanisms found in some self-organisingcomplex adaptive systems (CAS), namely artificial networks, the human brain, and the Global Brain. The Global Brain (GB) is the worldwide network formed by the combined distributed i ...
... selection (1). Here, an attempt will be made to study the common evolutionary mechanisms found in some self-organisingcomplex adaptive systems (CAS), namely artificial networks, the human brain, and the Global Brain. The Global Brain (GB) is the worldwide network formed by the combined distributed i ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... The brain appears to survey the overall pattern of incoming sensory impulses and to take a “weighted average” of their taste messages as the perceived taste. Sense of Smell Approximately 80-90% of what we perceive as “taste” is actually due to the sense of smell, which is dependent on olfactory cell ...
... The brain appears to survey the overall pattern of incoming sensory impulses and to take a “weighted average” of their taste messages as the perceived taste. Sense of Smell Approximately 80-90% of what we perceive as “taste” is actually due to the sense of smell, which is dependent on olfactory cell ...
Nervous System
... Nerve impulses in auditory nerves travel to brain stem. In auditory areas of cerebral cortex, this is interpreted as sound. Spiral organ is narrow at its base and widens at tip; each part is sensitive to different pitches. Nerve fibers from each region (high pitch @ base or low pitch @ tip) lead to ...
... Nerve impulses in auditory nerves travel to brain stem. In auditory areas of cerebral cortex, this is interpreted as sound. Spiral organ is narrow at its base and widens at tip; each part is sensitive to different pitches. Nerve fibers from each region (high pitch @ base or low pitch @ tip) lead to ...
HW CH 5 PSY 2513 Submit your answers on canvas
... is less sensitive to environmental influences than other parts of the brain. d. fully develops during the third trimester of pregnancy. ...
... is less sensitive to environmental influences than other parts of the brain. d. fully develops during the third trimester of pregnancy. ...
Vladimirov et al., Nature Methods, 2014
... presence of the light sheets (Fig. 1c). We defined an optomotor index as the difference in swimming strength during and before stimulus presentation. This index was significantly positive in all fish tested, with or without the laser (P = 0.031 with laser and P = 0.031 without it; two-sided sign tes ...
... presence of the light sheets (Fig. 1c). We defined an optomotor index as the difference in swimming strength during and before stimulus presentation. This index was significantly positive in all fish tested, with or without the laser (P = 0.031 with laser and P = 0.031 without it; two-sided sign tes ...
The hidden side of the UPR signalling pathway - Reflexions
... Protein Response (UPR) has kept an unexpected activity well hidden up until now. It would also seem that it plays an important physiological role in the development of the nervous system. That's what Laurent Nguyen and his team reveal in an article published in Trends in Neurosciences. Pregnanc ...
... Protein Response (UPR) has kept an unexpected activity well hidden up until now. It would also seem that it plays an important physiological role in the development of the nervous system. That's what Laurent Nguyen and his team reveal in an article published in Trends in Neurosciences. Pregnanc ...
Chapters 1,2,3 - UCSD Cognitive Science
... Information is gathered from the environment by ______ ______. Movements are carried about by muscle contractions which are controlled by ______ ______. There are also interneurons that communicate between the ______ ______and ______ ______, located entirely within the ______ ______ ______. There ar ...
... Information is gathered from the environment by ______ ______. Movements are carried about by muscle contractions which are controlled by ______ ______. There are also interneurons that communicate between the ______ ______and ______ ______, located entirely within the ______ ______ ______. There ar ...
Nervous System
... which has changed a variable from its set point • from eyes, skin, blood vessels, ears, digestive tract, joints, muscles, lungs… • Integration – interpretation of sensory information by the CNS • type, location and magnitude of stimulus • Transmit motor information – propagate APs from the CNS to va ...
... which has changed a variable from its set point • from eyes, skin, blood vessels, ears, digestive tract, joints, muscles, lungs… • Integration – interpretation of sensory information by the CNS • type, location and magnitude of stimulus • Transmit motor information – propagate APs from the CNS to va ...
Nervous System
... which has changed a variable from its set point • from eyes, skin, blood vessels, ears, digestive tract, joints, muscles, lungs… • Integration – interpretation of sensory information by the CNS • type, location and magnitude of stimulus • Transmit motor information – propagate APs from the CNS to va ...
... which has changed a variable from its set point • from eyes, skin, blood vessels, ears, digestive tract, joints, muscles, lungs… • Integration – interpretation of sensory information by the CNS • type, location and magnitude of stimulus • Transmit motor information – propagate APs from the CNS to va ...
Receptive Fields
... Receptive Fields Introduction: Given the enormity of the sensory space through which our nervous system must guide us, it comes as intuitive that our sensory systems should parcel out sensitivity to specific sensory regions over large populations of neurons. Within these large populations, there are ...
... Receptive Fields Introduction: Given the enormity of the sensory space through which our nervous system must guide us, it comes as intuitive that our sensory systems should parcel out sensitivity to specific sensory regions over large populations of neurons. Within these large populations, there are ...
Robin Balbernie
... Jack P. Shonkoff and Deborah A. Phillips, eds. Washington D. C. :National Academy Press. ...
... Jack P. Shonkoff and Deborah A. Phillips, eds. Washington D. C. :National Academy Press. ...
Autonomic Nervous System ANS - Anderson School District One
... • α1 & β1 produce excitation when activated • α2 & β2 receptors cause inhibition of effector tissues • β3 found only on cells of brown adipose where activation causes thermogenesis (heat production) ...
... • α1 & β1 produce excitation when activated • α2 & β2 receptors cause inhibition of effector tissues • β3 found only on cells of brown adipose where activation causes thermogenesis (heat production) ...
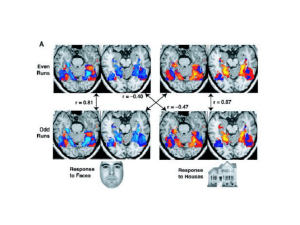
ppt - BIAC – Duke
... In this period of intense research in the neurosciences, nothing is more promising than functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) methods, which localize brain activities. These functional imaging methodologies map neurophysiological responses to cognitive, ...
... In this period of intense research in the neurosciences, nothing is more promising than functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) methods, which localize brain activities. These functional imaging methodologies map neurophysiological responses to cognitive, ...
HUMAN PHYSIOLOGY
... I. There are two different subtypes of ACh receptors: nicotinic and muscarinic. A. Nicotinic receptors enclose membrane channels and open when ACh bonds to the receptor. This causes a depolarization called an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) in skeletal muscle cells. B. The binding of ACh to ...
... I. There are two different subtypes of ACh receptors: nicotinic and muscarinic. A. Nicotinic receptors enclose membrane channels and open when ACh bonds to the receptor. This causes a depolarization called an excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) in skeletal muscle cells. B. The binding of ACh to ...
The Molecular Logic of Smell
... epithelium. A scanni ng electro n micrograph of the area reveals two interest ing types of cells. In this region, millions of neuron s, the signaling cells of se nso ry sys tems, provide a direct physical connec tion between the exte rnal world and the brain. From o ne end of each neuron , hairlike ...
... epithelium. A scanni ng electro n micrograph of the area reveals two interest ing types of cells. In this region, millions of neuron s, the signaling cells of se nso ry sys tems, provide a direct physical connec tion between the exte rnal world and the brain. From o ne end of each neuron , hairlike ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.