pptx
... • Subset of Artificial Neural Networks • Uses structure of neurons, along with training algorithm and an objective functional • Reduces problem to extremization of functional/function • Implement FLOOD Open Source Neural Networking library ...
... • Subset of Artificial Neural Networks • Uses structure of neurons, along with training algorithm and an objective functional • Reduces problem to extremization of functional/function • Implement FLOOD Open Source Neural Networking library ...
Exam - McLoon Lab
... A. Planning and initiation of goal-directed behavior is one of its functions. B. It is located in both frontal and temporal lobes. C. It has robust connections with occipital, parietal and temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex but not with the thalamus or the caudate nucleus. D. Sharing of emotions ...
... A. Planning and initiation of goal-directed behavior is one of its functions. B. It is located in both frontal and temporal lobes. C. It has robust connections with occipital, parietal and temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex but not with the thalamus or the caudate nucleus. D. Sharing of emotions ...
How Ca2+ triggers neurotransmitter release
... completed with the postsynaptic response. However, synaptic transmission is more than just the transfer of information between neurons – synaptic transmission also processes the transferred information, rendering each synapse a microcomputer that remembers previous events and that constitutes the mi ...
... completed with the postsynaptic response. However, synaptic transmission is more than just the transfer of information between neurons – synaptic transmission also processes the transferred information, rendering each synapse a microcomputer that remembers previous events and that constitutes the mi ...
242 BLADDER AFFERENT NEURONS SELECTIVELY INTERACT
... Hypothesis / aims of study The urothelium is capable of releasing a multitude of signalling factors including ATP, nitric oxide or prostaglandins to modulate the activity of sensory nerves innervating the suburothelium. In turn, sensory nerves innervating the urinary bladder are thought release neur ...
... Hypothesis / aims of study The urothelium is capable of releasing a multitude of signalling factors including ATP, nitric oxide or prostaglandins to modulate the activity of sensory nerves innervating the suburothelium. In turn, sensory nerves innervating the urinary bladder are thought release neur ...
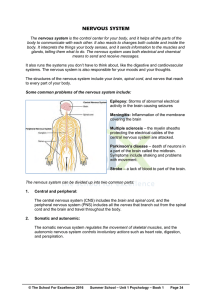
The Nervous System
... The nervous system directs the function of all the human body systems (Figure 8-1). The nervous system is divided into two subsystems: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). A nerve cell or neuron is the basic element of the nervous system. All neurons have three p ...
... The nervous system directs the function of all the human body systems (Figure 8-1). The nervous system is divided into two subsystems: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). A nerve cell or neuron is the basic element of the nervous system. All neurons have three p ...
Part 1: Multiple choice
... C. The fastest, strongest muscle fibers can produce the most sustained force output <––– D. Successive stimulation of muscles can produce force levels that build up over time E. Individual muscles can be used in a variety of different locomotor patterns or gaits 4. The patellar tendon (knee-jerk) re ...
... C. The fastest, strongest muscle fibers can produce the most sustained force output <––– D. Successive stimulation of muscles can produce force levels that build up over time E. Individual muscles can be used in a variety of different locomotor patterns or gaits 4. The patellar tendon (knee-jerk) re ...
Neural Development
... • Growth cone has receptor called CAM specific receptor • CAM and CAM receptor recognize each other to produce a chemical signal in neuron activation that causes elongation of neuron. ...
... • Growth cone has receptor called CAM specific receptor • CAM and CAM receptor recognize each other to produce a chemical signal in neuron activation that causes elongation of neuron. ...
Nervous Tissue
... • Neurons are electrically excitable due to the voltage difference across their membrane • Communicate with 2 types of electric signals – action potentials that can travel long distances – graded potentials that are local membrane changes only ...
... • Neurons are electrically excitable due to the voltage difference across their membrane • Communicate with 2 types of electric signals – action potentials that can travel long distances – graded potentials that are local membrane changes only ...
Bi150 (2005)
... decoction of lime-blossom which my aunt used to give me (although I did not yet know and must long postpone the discovery of why this memory made me so happy) immediately the old grey house upon the street, where her room was, rose up like a stage set to attach itself to the little pavilion opening ...
... decoction of lime-blossom which my aunt used to give me (although I did not yet know and must long postpone the discovery of why this memory made me so happy) immediately the old grey house upon the street, where her room was, rose up like a stage set to attach itself to the little pavilion opening ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... When a neuron is stimulated it generates an action potential. Action potentials are considered to be “all or nothing” responses; meaning an action potential is either generated or not once generated an action potential travels along the axon until it reaches the axon terminal, where it causes the re ...
... When a neuron is stimulated it generates an action potential. Action potentials are considered to be “all or nothing” responses; meaning an action potential is either generated or not once generated an action potential travels along the axon until it reaches the axon terminal, where it causes the re ...
Unit 3A Nervous System - Teacher Version
... spatial junctions between neurons. 3. coordinate the activation of the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems. 4. control pain through the release of opiate-like chemicals into the brain. 5. transmit signals to other neurons. ...
... spatial junctions between neurons. 3. coordinate the activation of the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems. 4. control pain through the release of opiate-like chemicals into the brain. 5. transmit signals to other neurons. ...
Prémio Artigo Destaque SPN_2011 Cellular and Molecular
... Neurons are capable of integrating information spatially and temporally. They can process electrical signals at specific locations called synapses, which can be excitatory or inhibitory. The information can then be built or not into an output signal, the action potential, carried by the axon. The dy ...
... Neurons are capable of integrating information spatially and temporally. They can process electrical signals at specific locations called synapses, which can be excitatory or inhibitory. The information can then be built or not into an output signal, the action potential, carried by the axon. The dy ...
special senses - Doctor Jade Main
... SENSES • systems that translate outside information into activity in nervous system • gather information by detecting energies • environment contains many different forms of energies ...
... SENSES • systems that translate outside information into activity in nervous system • gather information by detecting energies • environment contains many different forms of energies ...
abstract
... Reactive astrocytes and activated microglia are tightly associated with amyloid-β plaques in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Both cell types are likely to be involved in an inflammatory response that coincides with increased AD severity. The role of these activated glial cells is a topic of great scientif ...
... Reactive astrocytes and activated microglia are tightly associated with amyloid-β plaques in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Both cell types are likely to be involved in an inflammatory response that coincides with increased AD severity. The role of these activated glial cells is a topic of great scientif ...
Nervous system and senses
... and decision making. Near the back of the head, beneath the cerebrum, is the cerebellum. The cerebellum coordinates and balances the actions of the voluntary muscles. It makes your muscles move smooth and helps you keep your balance. Bundles of nerves from the cerebrum and cerebellum come together a ...
... and decision making. Near the back of the head, beneath the cerebrum, is the cerebellum. The cerebellum coordinates and balances the actions of the voluntary muscles. It makes your muscles move smooth and helps you keep your balance. Bundles of nerves from the cerebrum and cerebellum come together a ...
Workshop program booklet
... its limited amount of neural resources. Such a principled framework seems particularly important for understanding complex systems, where pure descriptive models often cannot provide satisfying answers. Normative models have had great success in explaining a wide range of aspects of neural processin ...
... its limited amount of neural resources. Such a principled framework seems particularly important for understanding complex systems, where pure descriptive models often cannot provide satisfying answers. Normative models have had great success in explaining a wide range of aspects of neural processin ...
Dopamine control of pyramidal neuron activity in the primary motor
... unbiased stereological quantification of dopamine transporter-immunostained fibers. We demonstrated for the first time in mice that DA innervates the deep layers of M1 targeting preferentially the forelimb representation area of M1. To address the functional role of the DA innervation on M1 neuronal ...
... unbiased stereological quantification of dopamine transporter-immunostained fibers. We demonstrated for the first time in mice that DA innervates the deep layers of M1 targeting preferentially the forelimb representation area of M1. To address the functional role of the DA innervation on M1 neuronal ...
Spiking Neurons with Boltzmann-like Properties to
... with the spike timed dependent plasticity having solid biological support [14]. It is possible to separate independent and principal components with Hebbian rules [15]. Anti-Hebbian rules force co-firing neurons apart to decorelate their behaviour. This is still a local rule. Another issue is topolo ...
... with the spike timed dependent plasticity having solid biological support [14]. It is possible to separate independent and principal components with Hebbian rules [15]. Anti-Hebbian rules force co-firing neurons apart to decorelate their behaviour. This is still a local rule. Another issue is topolo ...
Peripheral Nervous System - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... on the scalp, measure the electrical activity of a large number of nerve cells. Changes in EEG signals that are elicited by the presentation of sensory stimuli are referred to as sensory evoked potentials. Provides a measure of brain activity. ...
... on the scalp, measure the electrical activity of a large number of nerve cells. Changes in EEG signals that are elicited by the presentation of sensory stimuli are referred to as sensory evoked potentials. Provides a measure of brain activity. ...
L11Nervous tissue strusture 11
... Nervous systemmvary widely in their size and shape. However, all neurons have some features in common. A neuron consists of: 1. a cell body, called the soma, (Perikaryon) 2. with arms that reach out to connect to the network of other neurons in the brain. One arm, the dendrite, receives signals, 3. ...
... Nervous systemmvary widely in their size and shape. However, all neurons have some features in common. A neuron consists of: 1. a cell body, called the soma, (Perikaryon) 2. with arms that reach out to connect to the network of other neurons in the brain. One arm, the dendrite, receives signals, 3. ...
Motor
... neurons innervating axial musculature are located medially, whereas those innervating the distal musculature are located more laterally. ...
... neurons innervating axial musculature are located medially, whereas those innervating the distal musculature are located more laterally. ...
The Nervous System
... 2. Sensory neurons transmit the touch message. 3. Information is sorted and interpreted in the brain. A response in determined by interneurons. 4. Motor neurons transmit a response message to the shoulder muscles. 5. The shoulder muscles are activated, causing the head to turn. ...
... 2. Sensory neurons transmit the touch message. 3. Information is sorted and interpreted in the brain. A response in determined by interneurons. 4. Motor neurons transmit a response message to the shoulder muscles. 5. The shoulder muscles are activated, causing the head to turn. ...
03/14 PPT
... Glomerular structure is a general feature of olfactory systems • Fruit flies have 60 different receptors • Neurons with the same receptor project to one glomerulus ...
... Glomerular structure is a general feature of olfactory systems • Fruit flies have 60 different receptors • Neurons with the same receptor project to one glomerulus ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.