Biological Bases of Behavior - Mrs. Short`s AP Psychology Class
... – the neural message being delivered in a synaptic transmission is carried across the synaptic gap by ...
... – the neural message being delivered in a synaptic transmission is carried across the synaptic gap by ...
Animal Systems: REGULATION
... Diseases and Disorders of the Nervous System 1. ___________________- a virus that attacks the spinal cord; eventually causes paralysis 2. _________________________________ (MS)- affects neurons; slows nerve impulses, causing muscle ...
... Diseases and Disorders of the Nervous System 1. ___________________- a virus that attacks the spinal cord; eventually causes paralysis 2. _________________________________ (MS)- affects neurons; slows nerve impulses, causing muscle ...
File
... These two systems do not just work in cooperation during stressful situations like a car accident, but also in happier situations, such as when you earn an unexpected “A,” or “fall in love.” ...
... These two systems do not just work in cooperation during stressful situations like a car accident, but also in happier situations, such as when you earn an unexpected “A,” or “fall in love.” ...
NervousSystem3
... pale with this stain, providing contrast. The large grey area dorsally is made up of a felt-work of fibers and neuron cell bodies, the reticular formation. From Gray’s Anatomy, 18th US edition; 1920. The figure was taken from Wikipedia. ...
... pale with this stain, providing contrast. The large grey area dorsally is made up of a felt-work of fibers and neuron cell bodies, the reticular formation. From Gray’s Anatomy, 18th US edition; 1920. The figure was taken from Wikipedia. ...
Chapter 2
... the cortex. The medulla secretes hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) during stressful and emotional situations, while the adrenal cortex regulates salt and carbohydrate metabolism. ...
... the cortex. The medulla secretes hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) during stressful and emotional situations, while the adrenal cortex regulates salt and carbohydrate metabolism. ...
Exam 3 2008 - student.ahc.umn.edu
... do so in writing on the sheet provided (the last page of these questions (page 6)). We will take into account such qualifications prior to establishing the final version of the "Key". In order for your written qualifications to be considered, they must be turned in with your answer sheet, and you mu ...
... do so in writing on the sheet provided (the last page of these questions (page 6)). We will take into account such qualifications prior to establishing the final version of the "Key". In order for your written qualifications to be considered, they must be turned in with your answer sheet, and you mu ...
BHG025.CHP:Corel VENTURA
... surfaces loose their ventricular attachments after terminal division and translocate their somata through pial-directed processes. However, as hypothesized by Morest (Morest, 1970), perikaryal translocation does not provide a plausible mechanism for the migration of later born cortical neurons, part ...
... surfaces loose their ventricular attachments after terminal division and translocate their somata through pial-directed processes. However, as hypothesized by Morest (Morest, 1970), perikaryal translocation does not provide a plausible mechanism for the migration of later born cortical neurons, part ...
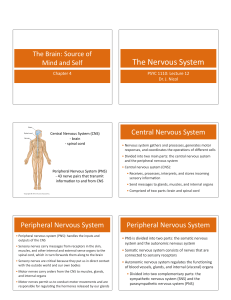
Central nervous system
... • More synapses a neuron has the greater its information-processing capability – cells in cerebral cortex with 40,000 synapses – cerebral cortex estimated to contain 100 trillion synapses ...
... • More synapses a neuron has the greater its information-processing capability – cells in cerebral cortex with 40,000 synapses – cerebral cortex estimated to contain 100 trillion synapses ...
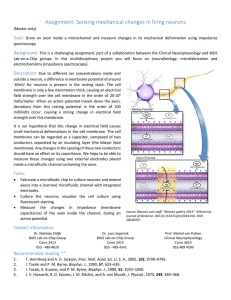
Assignment: Sensing mechanical changes in firing neurons
... field strength over the cell membrane in the order of 20∙106 Volts/meter. When an action potential travels down the axon, deviations from this resting potential in the order of 100 milliVolts occur, causing a strong change in electrical field strength over this membrane. It is our hypothesis that th ...
... field strength over the cell membrane in the order of 20∙106 Volts/meter. When an action potential travels down the axon, deviations from this resting potential in the order of 100 milliVolts occur, causing a strong change in electrical field strength over this membrane. It is our hypothesis that th ...
PPT - 서울대 Biointelligence lab
... One of the ways that faces might be represented in a distributed code across neurons and even brain regions is through the synchronized activity of relevant neurons. Hebb postulated that the neural representation of an event could be formed by cell assemblies. The brain regions responding to actual ...
... One of the ways that faces might be represented in a distributed code across neurons and even brain regions is through the synchronized activity of relevant neurons. Hebb postulated that the neural representation of an event could be formed by cell assemblies. The brain regions responding to actual ...
levin kuhlmann - Department of Cognitive and Neural Systems
... Studied single neuron modeling of Cochlear Nucleus neurons which play a role in the temporal processing of auditory signals. The model provided an analytical and numerical solution of how the temporal processing efficacy of these neurons was affected by the phase of incoming Auditory Nerve fiber Act ...
... Studied single neuron modeling of Cochlear Nucleus neurons which play a role in the temporal processing of auditory signals. The model provided an analytical and numerical solution of how the temporal processing efficacy of these neurons was affected by the phase of incoming Auditory Nerve fiber Act ...
Nervous System PPT - New Paltz Central School District
... Diencephalon: Midbrain - Thalamus, Epithalamus and Hypothalamus All sensory input goes through Thalamus before going to Cerebral Cortex. Hypothalamus does many functions for the autonomic nervous system ( Body Temp., Thirst, Appetite, Emotions, Mating, Sleep, Memory, Hormones ) ...
... Diencephalon: Midbrain - Thalamus, Epithalamus and Hypothalamus All sensory input goes through Thalamus before going to Cerebral Cortex. Hypothalamus does many functions for the autonomic nervous system ( Body Temp., Thirst, Appetite, Emotions, Mating, Sleep, Memory, Hormones ) ...
Ch. 3 S. 1
... Consists of the neurons of the spinal cord and the brain. The _____________________ extends from the brain down the back. It is a column of nerves about as thick as a ______________, and it is protected by the bones of the spine. It transmits messages between the brain and the muscles and the ______ ...
... Consists of the neurons of the spinal cord and the brain. The _____________________ extends from the brain down the back. It is a column of nerves about as thick as a ______________, and it is protected by the bones of the spine. It transmits messages between the brain and the muscles and the ______ ...
02biologya
... • Axon terminals release neurotransmitter. • Neurotransmitter enters synaptic gap. • Neurotransmitter binds to receptors that it fits. ...
... • Axon terminals release neurotransmitter. • Neurotransmitter enters synaptic gap. • Neurotransmitter binds to receptors that it fits. ...
Neurons and Glial Cells
... have. Research performed during the last few decades indicates that neurogenesis, the birth of new neurons, continues into adulthood. Neurogenesis was rst discovered in songbirds that produce new neurons while learning songs. For mammals, new neurons also play an important role in learning: about 1 ...
... have. Research performed during the last few decades indicates that neurogenesis, the birth of new neurons, continues into adulthood. Neurogenesis was rst discovered in songbirds that produce new neurons while learning songs. For mammals, new neurons also play an important role in learning: about 1 ...
Final Exam Review Part II 1) The entire nervous system is divided
... B) Send signals rapidly between body parts C) Produce major body fluids such as plasma and interstitial tissue fluid D) Detect sense stimuli 5) The cell type that carries out all the basic functions of the nervous system is the A) Neuroglia B) Neuron C) Adipocyte D) Schwann cell 6) The numerous, sma ...
... B) Send signals rapidly between body parts C) Produce major body fluids such as plasma and interstitial tissue fluid D) Detect sense stimuli 5) The cell type that carries out all the basic functions of the nervous system is the A) Neuroglia B) Neuron C) Adipocyte D) Schwann cell 6) The numerous, sma ...
AAAS Summary
... neuronal activity. Four separate classes of drugs (NMDA glutamate antagonists, GABAmimetics, sodium channel blockers, and alcohol) have been shown to trigger neuroapoptosis in the developing animal brain. The activity level of a neuron is determined by the amount of excitatory versus inhibitory tran ...
... neuronal activity. Four separate classes of drugs (NMDA glutamate antagonists, GABAmimetics, sodium channel blockers, and alcohol) have been shown to trigger neuroapoptosis in the developing animal brain. The activity level of a neuron is determined by the amount of excitatory versus inhibitory tran ...
Chapter 6
... c. This amino acid neurotransmitter acts as excitatory signals, activating NMethyl-d–aspartate (NMDA) receptors which have been implicated in learning and memory. Overstimulation by this neurotransmitter of NMDA receptors, however, can cause nerve cell damage or cell death. d. This catecholamine neu ...
... c. This amino acid neurotransmitter acts as excitatory signals, activating NMethyl-d–aspartate (NMDA) receptors which have been implicated in learning and memory. Overstimulation by this neurotransmitter of NMDA receptors, however, can cause nerve cell damage or cell death. d. This catecholamine neu ...
Nervous System
... Synapse are joints where neurons meet. This a space that impulses must travel through to reach another neuron. Axodendritic synapse: Synapse b/w an axon and dendrite of another cell. Axosomic synapse: Synapses between, two axons (axoaxonic), or two dendrites (dendrodendritic), or a dendrite an ...
... Synapse are joints where neurons meet. This a space that impulses must travel through to reach another neuron. Axodendritic synapse: Synapse b/w an axon and dendrite of another cell. Axosomic synapse: Synapses between, two axons (axoaxonic), or two dendrites (dendrodendritic), or a dendrite an ...
vision part VII_2
... 1. Hue means the wave length e.g. red light (wavelength 723-647 nm), green light (575-492 nm), and blue light (492-450 nm). 2. Intensity or saturation means the purity of the colour i.e. it is pure or mixed with other colours 3. Brightness means the amount of light in the colour ...
... 1. Hue means the wave length e.g. red light (wavelength 723-647 nm), green light (575-492 nm), and blue light (492-450 nm). 2. Intensity or saturation means the purity of the colour i.e. it is pure or mixed with other colours 3. Brightness means the amount of light in the colour ...
Invertebrate nervous systems:
... Briefly, the modifications were these:1.The hindbrain became divided into a ventral portion, called the medulla oblongata, a dorsal portion, the cerebellum, and the anterior pons. The medulla became specialized as a control center for some autonomic and somatic pathways concerned with vital function ...
... Briefly, the modifications were these:1.The hindbrain became divided into a ventral portion, called the medulla oblongata, a dorsal portion, the cerebellum, and the anterior pons. The medulla became specialized as a control center for some autonomic and somatic pathways concerned with vital function ...
ppt - University of Rochester
... stronger than Earth's magnetic field) The only things it can measure are changes in the magnetic properties of things inside the magnet: in this case, your head When neurons are active, they make electrical activity, which in turns creates tiny magnetic fields BUT far too small for MRI to measure (1 ...
... stronger than Earth's magnetic field) The only things it can measure are changes in the magnetic properties of things inside the magnet: in this case, your head When neurons are active, they make electrical activity, which in turns creates tiny magnetic fields BUT far too small for MRI to measure (1 ...
The Nervous System
... radiaJon is read by a scanner and superimposed on a picture of the brain • FuncJonal magneJc resonance imaging (fMRI) -‐ blood oxygenated level dependent (BOLD) response reflects the fact that blood in ...
... radiaJon is read by a scanner and superimposed on a picture of the brain • FuncJonal magneJc resonance imaging (fMRI) -‐ blood oxygenated level dependent (BOLD) response reflects the fact that blood in ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.