Synapses formed by normal and abnormal hippocampal mossy fibers
... Following mossy cell degeneration, which results in the denervation of their target cells in the molecular layer, granule cells “sprout” new axon collaterals and extend them into the dentate inner molecular layer (Nadler et al. 1980; Laurberg and Zimmer 1981; Frotscher and Zimmer 1983; Sloviter et a ...
... Following mossy cell degeneration, which results in the denervation of their target cells in the molecular layer, granule cells “sprout” new axon collaterals and extend them into the dentate inner molecular layer (Nadler et al. 1980; Laurberg and Zimmer 1981; Frotscher and Zimmer 1983; Sloviter et a ...
Age-related naturally occurring depression of
... other two sides were made of transparent plastic. The floor was made of stainless steel rods connected to a shock delivery apparatus (Grid Floor Shocker, Coulbourn Instruments, Model E13-08). There was a loudspeaker to emit acoustic stimuli of known intensity, frequency, and duration. The apparatus w ...
... other two sides were made of transparent plastic. The floor was made of stainless steel rods connected to a shock delivery apparatus (Grid Floor Shocker, Coulbourn Instruments, Model E13-08). There was a loudspeaker to emit acoustic stimuli of known intensity, frequency, and duration. The apparatus w ...
spinal cord - Zanichelli
... potential In resting potential the axon is not conducting the impulse. Inside, the cell is negative at rest. The potential depends on the concentration of ions (Na+ and K+) in and out the membrane. [ Na+]out > [ Na+]in [ K+]in > [ K+]out Sylvia S. Mader Concepts of Biology © Zanichelli editore, 2012 ...
... potential In resting potential the axon is not conducting the impulse. Inside, the cell is negative at rest. The potential depends on the concentration of ions (Na+ and K+) in and out the membrane. [ Na+]out > [ Na+]in [ K+]in > [ K+]out Sylvia S. Mader Concepts of Biology © Zanichelli editore, 2012 ...
Dorsal spinal cord stimulation obtunds the capacity of intrathoracic
... caudal dorsal thorax. A four-pole lead (Octrode; Advanced Neuromodulation Systems, Plano, TX) was advanced rostrally in the epidural space to the T1–T4 spinal cord level, utilizing anterior-posterior fluoroscopy. The tip of the lead was positioned slightly to the left of midline, according to curren ...
... caudal dorsal thorax. A four-pole lead (Octrode; Advanced Neuromodulation Systems, Plano, TX) was advanced rostrally in the epidural space to the T1–T4 spinal cord level, utilizing anterior-posterior fluoroscopy. The tip of the lead was positioned slightly to the left of midline, according to curren ...
A simulation of parahippocampal and hippocampal structures guiding spatial navigation of
... Young et al., 1997). In particular, if cholinergic modulation is present, these cation currents are activated. Figure 3 shows the self-sustained spiking activity of a modeled neuron. The spiking of a neuron in response to sensory input causes calcium influx which further activates the current, causi ...
... Young et al., 1997). In particular, if cholinergic modulation is present, these cation currents are activated. Figure 3 shows the self-sustained spiking activity of a modeled neuron. The spiking of a neuron in response to sensory input causes calcium influx which further activates the current, causi ...
In LHRH neurons
... More recently, studies of GT-1 cells and LHRH neurons (from mouse olfactory placode) show that GABA actually stimulates LHRH release, as well as increasing intracellular Ca2+ oscillations and membrane ...
... More recently, studies of GT-1 cells and LHRH neurons (from mouse olfactory placode) show that GABA actually stimulates LHRH release, as well as increasing intracellular Ca2+ oscillations and membrane ...
Effect of Adrenalectomy on Miniature Inhibitory Postsynaptic
... cellbody as established during the recording session (see examples in Fig. 1, A--D). Since the intracellular dyes were found to influence the physiological properties of the cells, staining was only performed in a limited number of cells and not routinely applied. Only those neurons that could be id ...
... cellbody as established during the recording session (see examples in Fig. 1, A--D). Since the intracellular dyes were found to influence the physiological properties of the cells, staining was only performed in a limited number of cells and not routinely applied. Only those neurons that could be id ...
Prevalent Presence of Periodic Actin-spectrin-based
... patterns in dendrites; concordantly, quantitative autocorrelation analyses showed substantially lower average autocorrelation amplitudes in dendrites (Fig. 2J, K). Together, our data suggest that the MPS structure is prevalent in morphologically and functionally diverse excitatory and inhibitory neu ...
... patterns in dendrites; concordantly, quantitative autocorrelation analyses showed substantially lower average autocorrelation amplitudes in dendrites (Fig. 2J, K). Together, our data suggest that the MPS structure is prevalent in morphologically and functionally diverse excitatory and inhibitory neu ...
The Structure and Plasticity of the Proximal Axon of Hippocampal
... central nervous system (CNS), for instance cortical and hippocampal neurons. They possess several dendrites and one long axon projecting from the soma. In contrast, bipolar neurons (fig. 1B), which are sensory neurons (for instance retinal bipolar cells), have two processes arising from the cell bod ...
... central nervous system (CNS), for instance cortical and hippocampal neurons. They possess several dendrites and one long axon projecting from the soma. In contrast, bipolar neurons (fig. 1B), which are sensory neurons (for instance retinal bipolar cells), have two processes arising from the cell bod ...
The role of NADPH oxidase (NOX) enzymes in neurodegenerative
... functions by affecting a number of redox-sensitive intracellular signaling molecules, including phosphatases, transcription factors and ion channels, see Fig. 2. Both protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) and dualspecificity phosphatases (DSPs) are inactivated by ROS through reversible oxidation of cy ...
... functions by affecting a number of redox-sensitive intracellular signaling molecules, including phosphatases, transcription factors and ion channels, see Fig. 2. Both protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs) and dualspecificity phosphatases (DSPs) are inactivated by ROS through reversible oxidation of cy ...
Changes in Intracellular pH Associated with Glutamate Excitotoxicity
... However, other experiments have questioned the sole involvement of calcium, sinceneuronal death can occur without large deviations in [Ca*+], and high potassium or cyanide induced increasesin [Ca*+], do not produce toxicity (Michaels and Rothman, 1990; Dubinsky and Rothman, 1991). Intracellular acid ...
... However, other experiments have questioned the sole involvement of calcium, sinceneuronal death can occur without large deviations in [Ca*+], and high potassium or cyanide induced increasesin [Ca*+], do not produce toxicity (Michaels and Rothman, 1990; Dubinsky and Rothman, 1991). Intracellular acid ...
The Control of Rate and Timing of Spikes in the Deep Cerebellar
... DCN neurons is derived from cerebellar cortex via GABAA-type inhibitory Purkinje cell input (Billard et al., 1993). Purkinje cell synapses provide 73% of the total synapses to DCN neurons, and almost all somatic synapses of DCN neurons are inhibitory (Palkovits et al., 1977; De Zeeuw and Berrebi, 19 ...
... DCN neurons is derived from cerebellar cortex via GABAA-type inhibitory Purkinje cell input (Billard et al., 1993). Purkinje cell synapses provide 73% of the total synapses to DCN neurons, and almost all somatic synapses of DCN neurons are inhibitory (Palkovits et al., 1977; De Zeeuw and Berrebi, 19 ...
Synchronization of Fast (30-40 Hz)
... was verified on coronal or sagittal sections (80 pm) stained with thionine. Data analysis. Intracellular, extracellular, and field potentials were treated as time series and underwent time and spectral analyses. Timerelations between two channels were disclosed with cross-correlation functions (Bend ...
... was verified on coronal or sagittal sections (80 pm) stained with thionine. Data analysis. Intracellular, extracellular, and field potentials were treated as time series and underwent time and spectral analyses. Timerelations between two channels were disclosed with cross-correlation functions (Bend ...
General and cell type specific mechanisms target
... transgenes to visualize and study how PKD-2 is transported. PKD2::GFP transgenes fully rescue the male mating defect of pkd2(sy606) null mutants (Fig. 7), indicating that these transgenes are functional. PKD-2::GFP transgene expression patterns are consistent with previous anti-PKD-2 antibody staini ...
... transgenes to visualize and study how PKD-2 is transported. PKD2::GFP transgenes fully rescue the male mating defect of pkd2(sy606) null mutants (Fig. 7), indicating that these transgenes are functional. PKD-2::GFP transgene expression patterns are consistent with previous anti-PKD-2 antibody staini ...
Spike-timing dependent plasticity and the cognitive map
... between pre- and post-synaptic spiking, the change in the weight of a synapse (∆w) according to a standard implementation of additive STDP can be calculated using Eq. 2. The parameters A+ and A− correspond to the maximum possible change in the synaptic weight per spike pair, while τ+ and τ− denote t ...
... between pre- and post-synaptic spiking, the change in the weight of a synapse (∆w) according to a standard implementation of additive STDP can be calculated using Eq. 2. The parameters A+ and A− correspond to the maximum possible change in the synaptic weight per spike pair, while τ+ and τ− denote t ...
full text pdf
... Pruning: circuit specification and more Why do neurons build synapses or neurites just to degrade them again later on during development? For one, neurons (many billions in the mammalian brain) must make many highly specific synaptic connections (often thousands for a mammalian neuron in the brain). ...
... Pruning: circuit specification and more Why do neurons build synapses or neurites just to degrade them again later on during development? For one, neurons (many billions in the mammalian brain) must make many highly specific synaptic connections (often thousands for a mammalian neuron in the brain). ...
Electrophysiological evidence that noradrenergic neurons of the rat
... were made in KPBS 0.02 M at pH 7.4 except for the DAB. Controls in the absence of CTb or GAD antibodies and in the presence respectively of BSA or swine serum were routinely done. On sections submitted to the double immunohistochemical procedure without the presence of CTb antiserum, no blue-black g ...
... were made in KPBS 0.02 M at pH 7.4 except for the DAB. Controls in the absence of CTb or GAD antibodies and in the presence respectively of BSA or swine serum were routinely done. On sections submitted to the double immunohistochemical procedure without the presence of CTb antiserum, no blue-black g ...
Physiological Plasticity of Single Neurons in Auditory Cortex of the
... expressing each value as a percentage change from the average of the last five-trial block of the sensitization phase. The number of trials to criterion for pupillary conditioning was defined as five consecutive trials during the conditioning phase all of which had responses greater than the average ...
... expressing each value as a percentage change from the average of the last five-trial block of the sensitization phase. The number of trials to criterion for pupillary conditioning was defined as five consecutive trials during the conditioning phase all of which had responses greater than the average ...
Multiple dynamic representations in the motor cortex
... measures behavioural performance (d9 5 0, chance performance; d9 5 1.75, expert level (above the dashed line) approximately 80% correct trials). d, Whisker movement and forces. Top traces, trial showing whisker angle (grey) and set point (black). Middle traces, whisking amplitude (see Methods). Bott ...
... measures behavioural performance (d9 5 0, chance performance; d9 5 1.75, expert level (above the dashed line) approximately 80% correct trials). d, Whisker movement and forces. Top traces, trial showing whisker angle (grey) and set point (black). Middle traces, whisking amplitude (see Methods). Bott ...
Anatomical origins of the classical receptive field and modulatory
... even though neurons do not respond directly with action potentials to stimulation of the surround region alone (Blakemore and Tobin, 1972; Maffei and Fiorentini, 1976; Nelson and Frost, 1978; Alhnan et al., 1985; Gilbert and Wiesel, 1990; DeAngelis et al., 1994; Li and Li, 1994; Sillito et al., 199 ...
... even though neurons do not respond directly with action potentials to stimulation of the surround region alone (Blakemore and Tobin, 1972; Maffei and Fiorentini, 1976; Nelson and Frost, 1978; Alhnan et al., 1985; Gilbert and Wiesel, 1990; DeAngelis et al., 1994; Li and Li, 1994; Sillito et al., 199 ...
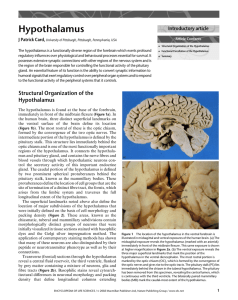
Hypothalamus
... However, the parvocellular neurons release their secretory products into fenestrated capillaries that drain into the long portal vessels that drain into the anterior lobe. The magnocellular neurons secrete either vasopressin or oxytocin, and are largely concentrated in the supraoptic (SON) and parav ...
... However, the parvocellular neurons release their secretory products into fenestrated capillaries that drain into the long portal vessels that drain into the anterior lobe. The magnocellular neurons secrete either vasopressin or oxytocin, and are largely concentrated in the supraoptic (SON) and parav ...
Synapse formation in developing neural circuits.
... Most of the subsequent synaptic studies in the nineteenth century and earlier half of the twentieth century also focused around the functionality of synapses, or synaptic transmission. It is therefore befitting that the actual term ‘‘synapse’’ was not coined by a neuroanatomist, but by a physiologis ...
... Most of the subsequent synaptic studies in the nineteenth century and earlier half of the twentieth century also focused around the functionality of synapses, or synaptic transmission. It is therefore befitting that the actual term ‘‘synapse’’ was not coined by a neuroanatomist, but by a physiologis ...
Passive Properties of Swimmeret Motor Neurons
... recorded with microelectrodes in the processes of swimmeret motor neurons in isolated abdominal nerve cord preparations. Membrane potentials had a median of 059 mV, with 25th and 75th percentiles of 066.0 and 053 mV. The median input resistance was 6.4 MV, with 25th and 75th percentiles of 3.4 and 1 ...
... recorded with microelectrodes in the processes of swimmeret motor neurons in isolated abdominal nerve cord preparations. Membrane potentials had a median of 059 mV, with 25th and 75th percentiles of 066.0 and 053 mV. The median input resistance was 6.4 MV, with 25th and 75th percentiles of 3.4 and 1 ...
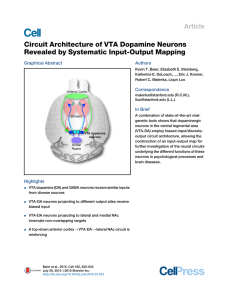
Circuit Architecture of VTA Dopamine Neurons Revealed by
... been comparatively evaluated at the whole-brain level. VTA-DA and VTA-GABA neurons have distinct firing patterns in vivo (Cohen et al., 2012), and their optogenetic activation produces opposing behavioral effects (Tsai et al., 2009; Tan et al., 2012). Thus, a systematic, comparative analysis of syna ...
... been comparatively evaluated at the whole-brain level. VTA-DA and VTA-GABA neurons have distinct firing patterns in vivo (Cohen et al., 2012), and their optogenetic activation produces opposing behavioral effects (Tsai et al., 2009; Tan et al., 2012). Thus, a systematic, comparative analysis of syna ...
The sacral autonomic outflow is sympathetic
... The peripheral targets of the sacral VM neurons are located in the pelvic plexus —which, in some species, such as the mouse, is condensed into a bona fide ganglion — and are considered, by definition, parasympathetic 15. Since a proportion of pelvic ganglionic neurons receive input from upper lumba ...
... The peripheral targets of the sacral VM neurons are located in the pelvic plexus —which, in some species, such as the mouse, is condensed into a bona fide ganglion — and are considered, by definition, parasympathetic 15. Since a proportion of pelvic ganglionic neurons receive input from upper lumba ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.