1-nervous_system
... Myelin sheath—insulation—speeds up impulse Nodes of Ranvier--speeds up impulse ...
... Myelin sheath—insulation—speeds up impulse Nodes of Ranvier--speeds up impulse ...
Quiz - Web Adventures
... a) Observe how frog hearts work b) Re-create Nobel Prize experiments c) Test how insulin binds to blood cells d) Understand how opioids work in the brain 6) Feelings of pleasure are triggered in the brain’s Reward Pathway by: a) Insulin b) Endogenous opioids c) NSAIDs d) Estrogen 7) Neurons transmit ...
... a) Observe how frog hearts work b) Re-create Nobel Prize experiments c) Test how insulin binds to blood cells d) Understand how opioids work in the brain 6) Feelings of pleasure are triggered in the brain’s Reward Pathway by: a) Insulin b) Endogenous opioids c) NSAIDs d) Estrogen 7) Neurons transmit ...
Neurons - Transcript - the Cassiopeia Project
... symphonies... is not the product of simple cellular interactions. And yet it might be...because everything that humans do (or think or feel) is the result of the basic units of brain structure - the neurons. The human brain contains more than a hundred billion neurons. Just like a single ant could n ...
... symphonies... is not the product of simple cellular interactions. And yet it might be...because everything that humans do (or think or feel) is the result of the basic units of brain structure - the neurons. The human brain contains more than a hundred billion neurons. Just like a single ant could n ...
ppt - Le Moyne College
... Structures of Animal Cells Structure of a Neuron Variation Among Neurons Glia (Glial Cells) ...
... Structures of Animal Cells Structure of a Neuron Variation Among Neurons Glia (Glial Cells) ...
Nervous System II: Development & Plasticity
... II • Oligodendrocytes: few tree cells. (Gk) type of neuroglia which myelinate axons in the Central Nervous System (CNS). • Neurons: are nerve cells electrically excitable cells that process and transmit information. ...
... II • Oligodendrocytes: few tree cells. (Gk) type of neuroglia which myelinate axons in the Central Nervous System (CNS). • Neurons: are nerve cells electrically excitable cells that process and transmit information. ...
Chapter 13
... The following terms are freely used in your text book. Make sure you know what they mean, how they are used, and how to use them. When an example is given, make sure you can describe and recall it. If a picture is provided, know what the structure looks like and where it is located. If a diagram des ...
... The following terms are freely used in your text book. Make sure you know what they mean, how they are used, and how to use them. When an example is given, make sure you can describe and recall it. If a picture is provided, know what the structure looks like and where it is located. If a diagram des ...
Structure of a Neuron
... 3. Dendrite: receives impulses from other neurons and carries them toward the cell body ...
... 3. Dendrite: receives impulses from other neurons and carries them toward the cell body ...
Slide ()
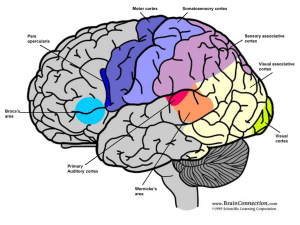
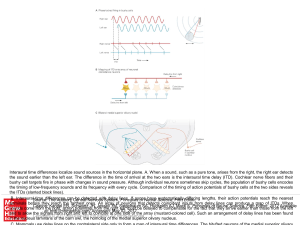
... Interaural time differences localize sound sources in the horizontal plane. A. When a sound, such as a pure tone, arises from the right, the right ear detects the sound earlier than the left ear. The difference in the time of arrival at the two ears is the interaural time delay (ITD). Cochlear nerve ...
... Interaural time differences localize sound sources in the horizontal plane. A. When a sound, such as a pure tone, arises from the right, the right ear detects the sound earlier than the left ear. The difference in the time of arrival at the two ears is the interaural time delay (ITD). Cochlear nerve ...
Action Potential Neurons at Work
... The sodium potassium pump continually pumps 3 sodium ions outside and 2 K+ inside to keep the outside more positive and the inside more negative. ...
... The sodium potassium pump continually pumps 3 sodium ions outside and 2 K+ inside to keep the outside more positive and the inside more negative. ...
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... – Electrical signaling – Cell-to-cell signaling during development ...
... – Electrical signaling – Cell-to-cell signaling during development ...
Mirror Neurons & You
... certain signal behaviors Examples: tool use, communication-pretty much all aspects of what we ...
... certain signal behaviors Examples: tool use, communication-pretty much all aspects of what we ...
cell division. - cis myp science
... A centriole is a small set of microtubules arranged in a specific way. When two centrioles are found next to each other, they are usually at right angles. The centrioles are found in pairs and move towards the poles (opposite ends) of the nucleus when it is time for cell division. ...
... A centriole is a small set of microtubules arranged in a specific way. When two centrioles are found next to each other, they are usually at right angles. The centrioles are found in pairs and move towards the poles (opposite ends) of the nucleus when it is time for cell division. ...
Nervous Tissue
... What is the main function of this tissue? Transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effectors that control their activity ...
... What is the main function of this tissue? Transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effectors that control their activity ...
Hippocampus+and+Neurons+Final+Draft
... place cells: that is, they fire bursts of action potentials when the animal passes through a specific part of its environment. Hippocampal place cells interact extensively with head direction cells, whose activity acts as an inertial compass, and with grid cells in the neighboring entorhinal cortex. ...
... place cells: that is, they fire bursts of action potentials when the animal passes through a specific part of its environment. Hippocampal place cells interact extensively with head direction cells, whose activity acts as an inertial compass, and with grid cells in the neighboring entorhinal cortex. ...
The Nervous System- Nervous Tissue
... Functional classification based on type of information & direction of information transmission: • Sensory (afferent) neurons – • transmit sensory information from receptors of PNS towards ...
... Functional classification based on type of information & direction of information transmission: • Sensory (afferent) neurons – • transmit sensory information from receptors of PNS towards ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.