specimen jar craft - National Wildlife Federation
... The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain, even if diffuse neural tissue is present. It is located in the head, usually ...
... The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, adult sea squirts and starfish do not have a brain, even if diffuse neural tissue is present. It is located in the head, usually ...
Chapter 2: Brain Development
... • Most embryonic cells are pluripotent stem cells • A variety of chemicals signal cells to turn into specialized cells • Ectodermal cells are inhibited by molecules, signalling a development into neural cells and not skin cells • After neural cell determination: ...
... • Most embryonic cells are pluripotent stem cells • A variety of chemicals signal cells to turn into specialized cells • Ectodermal cells are inhibited by molecules, signalling a development into neural cells and not skin cells • After neural cell determination: ...
Slide ()
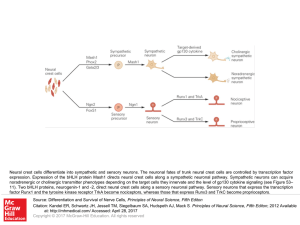
... Neural crest cells differentiate into sympathetic and sensory neurons. The neuronal fates of trunk neural crest cells are controlled by transcription factor expression. Expression of the bHLH protein Mash1 directs neural crest cells along a sympathetic neuronal pathway. Sympathetic neurons can acqui ...
... Neural crest cells differentiate into sympathetic and sensory neurons. The neuronal fates of trunk neural crest cells are controlled by transcription factor expression. Expression of the bHLH protein Mash1 directs neural crest cells along a sympathetic neuronal pathway. Sympathetic neurons can acqui ...
Using Breakthroughs in Visual Neuroscience to
... close to that of humans, what we learn through ethical studies of nonhuman primates brings us closer to human medical applications. Studies using an array of electrodes implanted in the brain show that monkeys can use their visual system to control an artificial limb remotely, by mental control alon ...
... close to that of humans, what we learn through ethical studies of nonhuman primates brings us closer to human medical applications. Studies using an array of electrodes implanted in the brain show that monkeys can use their visual system to control an artificial limb remotely, by mental control alon ...
Optogenetics
... Chronic pain. Electrical stimulation methods include local peripheral nerve stimulation, local cranial nerve stimulation and 'subthreshold' motor cortex stimulation. Reasonable optogenic approaches might include NpHR-mediated inhibition of specific pain fibres or foci, sparing other fibre types. ChR ...
... Chronic pain. Electrical stimulation methods include local peripheral nerve stimulation, local cranial nerve stimulation and 'subthreshold' motor cortex stimulation. Reasonable optogenic approaches might include NpHR-mediated inhibition of specific pain fibres or foci, sparing other fibre types. ChR ...
Directed Differentiation of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem
... Genetic epilepsy with febrile seizures plus (GEFS+) is an autosomal dominant disorder that can be caused by many different point mutations in the Nav1.1 voltage-gated sodium channel. Our lab has used a Drosophila K1270T knock-in model and discovered a conditional gain-of-function alteration in sodiu ...
... Genetic epilepsy with febrile seizures plus (GEFS+) is an autosomal dominant disorder that can be caused by many different point mutations in the Nav1.1 voltage-gated sodium channel. Our lab has used a Drosophila K1270T knock-in model and discovered a conditional gain-of-function alteration in sodiu ...
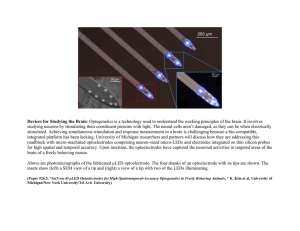
26-5 Devices for Studying the Brain
... Devices for Studying the Brain: Optogenetics is a technology used to understand the working principles of the brain. It involves studying neurons by stimulating their constituent proteins with light. The neural cells aren’t damaged, as they can be when electrically stimulated. Achieving simultaneous ...
... Devices for Studying the Brain: Optogenetics is a technology used to understand the working principles of the brain. It involves studying neurons by stimulating their constituent proteins with light. The neural cells aren’t damaged, as they can be when electrically stimulated. Achieving simultaneous ...
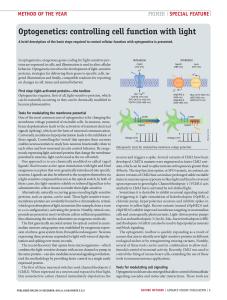
Optogenetics: controlling cell function with light
... each other and how neuronal circuits control behavior. By exogenously expressing light-activated proteins that change the membrane potential in neurons, light can be used as the on-off switch. One approach is to use chemically modified so-called ‘caged ligands’ that become active upon stimulation wi ...
... each other and how neuronal circuits control behavior. By exogenously expressing light-activated proteins that change the membrane potential in neurons, light can be used as the on-off switch. One approach is to use chemically modified so-called ‘caged ligands’ that become active upon stimulation wi ...
Slide
... Overview of the visual system as related to visual prostheses. In most retinal dystrophies, the first order photoreceptor neurons (rods and cones) are lost. Thus, second order neurons (bipolar cells) are the earliest viable target, typically for subretinal and suprachoroidal devices. Epiretinal devi ...
... Overview of the visual system as related to visual prostheses. In most retinal dystrophies, the first order photoreceptor neurons (rods and cones) are lost. Thus, second order neurons (bipolar cells) are the earliest viable target, typically for subretinal and suprachoroidal devices. Epiretinal devi ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.