Ch 48: Nervous System – part 1
... How do action potentials “travel” along an axon? the strong depolarization of one action potential assures that the neighboring region of the neuron will be depolarized above threshold, triggering a new action potential, and so on… SYNAPSE: junction between a neuron and another cell; found betwe ...
... How do action potentials “travel” along an axon? the strong depolarization of one action potential assures that the neighboring region of the neuron will be depolarized above threshold, triggering a new action potential, and so on… SYNAPSE: junction between a neuron and another cell; found betwe ...
(Early Period) - Connectionism
... networks are simplified models of the brain composed of large numbers of units (the analogs of neurons) together with weights that measure the strength of connections between the units. A glance at its history: ● The 1940s: it was pioneered by neurophysiologist Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts. The ...
... networks are simplified models of the brain composed of large numbers of units (the analogs of neurons) together with weights that measure the strength of connections between the units. A glance at its history: ● The 1940s: it was pioneered by neurophysiologist Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts. The ...
Handout - Science in the News
... Ion: Electrically charged molecule. Ion channel: Openings in the membrane that surround all cells to allow and control the flow of ions. The membrane is otherwise impermeable to ions. Membrane voltage: Electrical force due to the imbalance of ions inside and outside of a neuron. This voltage is affe ...
... Ion: Electrically charged molecule. Ion channel: Openings in the membrane that surround all cells to allow and control the flow of ions. The membrane is otherwise impermeable to ions. Membrane voltage: Electrical force due to the imbalance of ions inside and outside of a neuron. This voltage is affe ...
Nervous Tissue
... Tumors can arise from all four types of glia, and these tend to grow rapidly and destroy nearby regions of the brain or spinal cord Tumors can also arise from satellite cells or Schwann cells, compressing and destroying the neurons they surround ...
... Tumors can arise from all four types of glia, and these tend to grow rapidly and destroy nearby regions of the brain or spinal cord Tumors can also arise from satellite cells or Schwann cells, compressing and destroying the neurons they surround ...
Psychiatry`s age of enlightenment
... however, achievement of this goal has been limited by a lack of neuromodulatory tools capable of targeting distinct populations of neurons, based on either genetic identity or circuit connectivity, in behaving animals with the temporal precision required for causality testing. Such a tool would fina ...
... however, achievement of this goal has been limited by a lack of neuromodulatory tools capable of targeting distinct populations of neurons, based on either genetic identity or circuit connectivity, in behaving animals with the temporal precision required for causality testing. Such a tool would fina ...
Edvard Moser
... components to be detected in this internal map was the grid cell. Grid cells fire electric impulses when animals are at particular locations that together tile the environment in a periodic hexagonal pattern, like in a Chinese checkerboard. The circuit was soon found to include also other functional ...
... components to be detected in this internal map was the grid cell. Grid cells fire electric impulses when animals are at particular locations that together tile the environment in a periodic hexagonal pattern, like in a Chinese checkerboard. The circuit was soon found to include also other functional ...
Chapter 9 Nerves
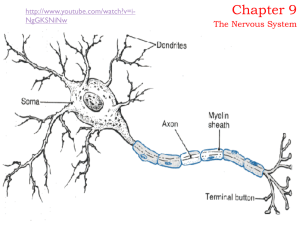
... Dendrites and the cell body provide receptive surfaces A single AXON arises from the cell body and may be enclosed in a myelin sheath and a neurilemma. ...
... Dendrites and the cell body provide receptive surfaces A single AXON arises from the cell body and may be enclosed in a myelin sheath and a neurilemma. ...
Exam 2-SG suggested answers (2010)
... obviously better. Start with “piece of furniture” as the general category, then get more specific. a. A complex cell is a neuron in the visual cortex that responds to oriented bars or edges but doesn’t have distinct “on” and “off” areas when mapped by spots of light. b. All-trans retinal is the isom ...
... obviously better. Start with “piece of furniture” as the general category, then get more specific. a. A complex cell is a neuron in the visual cortex that responds to oriented bars or edges but doesn’t have distinct “on” and “off” areas when mapped by spots of light. b. All-trans retinal is the isom ...
20150210_RAVI_Lecture
... need to precisely control activity in one cell type while leaving the others unaltered. Crick later speculated in lectures that light might be a relevant control tool, but without a concept for how this could be done.’ Neuron 71, July 14, 2011 ...
... need to precisely control activity in one cell type while leaving the others unaltered. Crick later speculated in lectures that light might be a relevant control tool, but without a concept for how this could be done.’ Neuron 71, July 14, 2011 ...
The Nervous System
... Functions of astrocytes: 1. Connect neurons to capillaries. This makes up the “blood-brain barrier”. 2. Maintain the the electrochemical environment ...
... Functions of astrocytes: 1. Connect neurons to capillaries. This makes up the “blood-brain barrier”. 2. Maintain the the electrochemical environment ...
Nerve cord
... “Nerve net”: Simplest nervous system are a netlike arrangement of neurons throughout the body “Nerve cord”: Most complex have a nerve cord and a brain ...
... “Nerve net”: Simplest nervous system are a netlike arrangement of neurons throughout the body “Nerve cord”: Most complex have a nerve cord and a brain ...
the nervous system
... How does it do it? • Cells carry messages from one part of the body to another • The messages in the nervous system are electrical signals called impulses • The cells that transmit the impulses are called neurons – Made of: • Dendrite • Axon • Myelin Sheath ...
... How does it do it? • Cells carry messages from one part of the body to another • The messages in the nervous system are electrical signals called impulses • The cells that transmit the impulses are called neurons – Made of: • Dendrite • Axon • Myelin Sheath ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... 1. The parts of the vertebrate eye include the sclera, the choroids, and the retina. The sclera includes the white of the eye and the cornea. The choroid includes blood vessels, lens, iris, and pupil. The retina is a layer of photoreceptors at the back of the eye. Most of the eye’s volume is filled ...
... 1. The parts of the vertebrate eye include the sclera, the choroids, and the retina. The sclera includes the white of the eye and the cornea. The choroid includes blood vessels, lens, iris, and pupil. The retina is a layer of photoreceptors at the back of the eye. Most of the eye’s volume is filled ...
Optogenetics and the Circuit Dynamics of Psychiatric
... of Psychiatric Disease Optogenetics is a method for delivering millisecondprecision control (for activation or inhibition) to targeted cells using light within freely behaving mammals.1 The components of this method, as practiced today, involve (1) lasers and fiber optics for light delivery into the ...
... of Psychiatric Disease Optogenetics is a method for delivering millisecondprecision control (for activation or inhibition) to targeted cells using light within freely behaving mammals.1 The components of this method, as practiced today, involve (1) lasers and fiber optics for light delivery into the ...
Slide ()
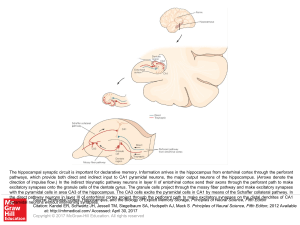
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Slide ()
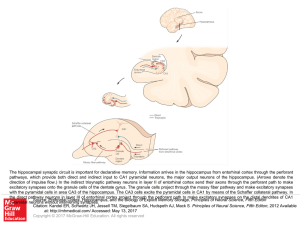
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
... The hippocampal synaptic circuit is important for declarative memory. Information arrives in the hippocampus from entorhinal cortex through the perforant pathways, which provide both direct and indirect input to CA1 pyramidal neurons, the major output neurons of the hippocampus. (Arrows denote the d ...
Name
... _____ 5. Neuron, serving as part of the conduction pathway between sensory and motor neurons _____ 6. Gaps in the myelin sheath _____ 7. Collection of nerve cell bodies found outside the CNS _____ 8. Neuron that conducts impulses away from the CNS to muscles and glands _____ 9. Sensory receptors fou ...
... _____ 5. Neuron, serving as part of the conduction pathway between sensory and motor neurons _____ 6. Gaps in the myelin sheath _____ 7. Collection of nerve cell bodies found outside the CNS _____ 8. Neuron that conducts impulses away from the CNS to muscles and glands _____ 9. Sensory receptors fou ...
Neuroscience - Instructional Resources
... Before birth, a baby’s neurons increase in number at an astonishing rate increasing the size of the brain. They are not fully equipped, properly positioned, or completely functioning. 30,000 neurons would fit in the space the size of a pinhead. At birth, the brain’s cerebral cortex has 100 billion n ...
... Before birth, a baby’s neurons increase in number at an astonishing rate increasing the size of the brain. They are not fully equipped, properly positioned, or completely functioning. 30,000 neurons would fit in the space the size of a pinhead. At birth, the brain’s cerebral cortex has 100 billion n ...
Recent advances in ocular drug delivery
... Creation and use of materials and devices at the size scale of intracellular structures and molecules, and involves systems and constructs in the order of <100 nm. General principles: 1- Bio-mimicry: direct molecules to the proper cells 2- Pseudo-intelligence 3- Feedback control: control dosage prec ...
... Creation and use of materials and devices at the size scale of intracellular structures and molecules, and involves systems and constructs in the order of <100 nm. General principles: 1- Bio-mimicry: direct molecules to the proper cells 2- Pseudo-intelligence 3- Feedback control: control dosage prec ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior: The Neuron
... • The arrival of an action potential at an axon’s terminal buttons triggers the release of neurotransmitters- chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another. • The chemicals are stored in small sacs called synaptic vesicles. • Once released, the neurotransmitters diffuse across the s ...
... • The arrival of an action potential at an axon’s terminal buttons triggers the release of neurotransmitters- chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another. • The chemicals are stored in small sacs called synaptic vesicles. • Once released, the neurotransmitters diffuse across the s ...
Slide ()
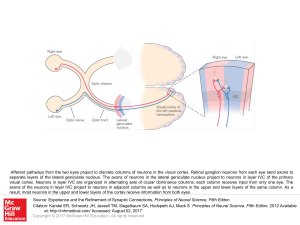
... visual cortex. Neurons in layer IVC are organized in alternating sets of ocular dominance columns; each column receives input from only one eye. The axons of the neurons in layer IVC project to neurons in adjacent columns as well as to neurons in the upper and lower layers of the same column. As a r ...
... visual cortex. Neurons in layer IVC are organized in alternating sets of ocular dominance columns; each column receives input from only one eye. The axons of the neurons in layer IVC project to neurons in adjacent columns as well as to neurons in the upper and lower layers of the same column. As a r ...
PR_161115_Inaktive_Gehirnzellen_E
... Many things we think we know about the world have their origin in popular culture, not science. The most well-known false ‘fact’ about the brain is the misconception that we only use ten percent of the brain’s overall capacity. This so-called ’ten percent myth’, while accepted as such by neuroscient ...
... Many things we think we know about the world have their origin in popular culture, not science. The most well-known false ‘fact’ about the brain is the misconception that we only use ten percent of the brain’s overall capacity. This so-called ’ten percent myth’, while accepted as such by neuroscient ...
Biology General Knowledge 3 iQuiz
... vessels has lost a lot of its oxygen, urea and some water? ...
... vessels has lost a lot of its oxygen, urea and some water? ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.