Vision I
... Photoreceptor cells of the retina; maximally sensitive to one of three different wavelengths of light and hence encodes color vision. ...
... Photoreceptor cells of the retina; maximally sensitive to one of three different wavelengths of light and hence encodes color vision. ...
Orexin-A excites rat lateral vestibular nucleus neurons and improves
... lateral hypothalamic area and perifornical area. Lack of orexin neurons causes narcolepsy-cataplexy, which is characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, premature transitions to REM sleep, and sudden skeletal muscle weakness without impairment of consciousness. However, most studies so far on th ...
... lateral hypothalamic area and perifornical area. Lack of orexin neurons causes narcolepsy-cataplexy, which is characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, premature transitions to REM sleep, and sudden skeletal muscle weakness without impairment of consciousness. However, most studies so far on th ...
Lecture 2
... “As the entomologist chasing butterflies of bright colors, my attention was seeking in the garden of gray matter, those cells of delicate and elegant forms, the mysterious butterflies of the soul, whose ...
... “As the entomologist chasing butterflies of bright colors, my attention was seeking in the garden of gray matter, those cells of delicate and elegant forms, the mysterious butterflies of the soul, whose ...
A1992HX83800001
... between the action of polarizing current and different cations on impulse conduc1 tion in nerve fibers. The beauty of the analysis impressed me very much, and, although for many years after graduation I was engaged in spinal cord physiology, I always felt a motivation to switch to more simple system ...
... between the action of polarizing current and different cations on impulse conduc1 tion in nerve fibers. The beauty of the analysis impressed me very much, and, although for many years after graduation I was engaged in spinal cord physiology, I always felt a motivation to switch to more simple system ...
2.2 Electrical Communication Study Guide by Hisrich
... 2.2 Electrical Communication Study Guide by Hisrich 2.2.a How does communication happen within the body? Electrical Signals Nervous System ...
... 2.2 Electrical Communication Study Guide by Hisrich 2.2.a How does communication happen within the body? Electrical Signals Nervous System ...
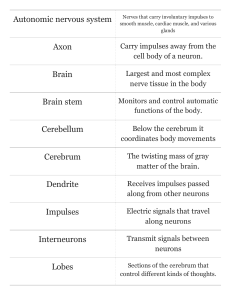
three basic functions of the nervous system
... 2. Motor neurons – transmit impulses away from the spinal cord and brain to muscles and tissue - also called efferent neurons 3. Interneurons – conduct impulses from sensory neurons to motor neurons S.A.M.E. Sensory = Afferent Motor = Efferent ...
... 2. Motor neurons – transmit impulses away from the spinal cord and brain to muscles and tissue - also called efferent neurons 3. Interneurons – conduct impulses from sensory neurons to motor neurons S.A.M.E. Sensory = Afferent Motor = Efferent ...
For electrical signaling
... At gap junctions, cells approach within about 3.5 nm of each other, rather than the 20 to 40 nm distance that separates cells at chemical synapses Postsynaptic potential in electrical synapses is not caused by the opening of ion channels by chemical transmitters, but by direct electrical coupling be ...
... At gap junctions, cells approach within about 3.5 nm of each other, rather than the 20 to 40 nm distance that separates cells at chemical synapses Postsynaptic potential in electrical synapses is not caused by the opening of ion channels by chemical transmitters, but by direct electrical coupling be ...
LSUHSC N C E
... “Brain Waves and Immune Genes in the Brain Wiring” Connections in the adult CNS are highly precise. In the visual system, retinal ganglion cells connect to target LGN neurons in adjacent, non-overlapping eye-specific layers. During development, retinal inputs are intermixed and the layers emerge as ...
... “Brain Waves and Immune Genes in the Brain Wiring” Connections in the adult CNS are highly precise. In the visual system, retinal ganglion cells connect to target LGN neurons in adjacent, non-overlapping eye-specific layers. During development, retinal inputs are intermixed and the layers emerge as ...
Nervous System - Lemon Bay High School
... The Nervous System works with the Endocrine System to provide electrical and chemical control of ALL body processes. ...
... The Nervous System works with the Endocrine System to provide electrical and chemical control of ALL body processes. ...
read more
... et al. 2013. Specifically, we postulate that the connectivity and dynamics of neurons in OI are optimized to represent eye movement signals using a linear decoder (analogous to a dendritic summation). The resulting spiking network replicates key properties of the OI, such as the typical distribution ...
... et al. 2013. Specifically, we postulate that the connectivity and dynamics of neurons in OI are optimized to represent eye movement signals using a linear decoder (analogous to a dendritic summation). The resulting spiking network replicates key properties of the OI, such as the typical distribution ...
Neurology - wsscience
... Chemical synapses differ from electric synapses because chemical synapses: Contain integral proteins Involve a neurotransmitter Involve direct physical contact between cells Propagate action potentials quickly and efficiently ...
... Chemical synapses differ from electric synapses because chemical synapses: Contain integral proteins Involve a neurotransmitter Involve direct physical contact between cells Propagate action potentials quickly and efficiently ...
Neural Crest
... • Homing of peripheral neurons and their supportive cells might be dictated by a delicate equilibrium between the multiple actions of stimulatory and inhibitory molecules, which is modulated further by defined responses of the dispersing cells to these ECM components during their successive phases ...
... • Homing of peripheral neurons and their supportive cells might be dictated by a delicate equilibrium between the multiple actions of stimulatory and inhibitory molecules, which is modulated further by defined responses of the dispersing cells to these ECM components during their successive phases ...
Document
... • SSRIs for short. SSRIs act on a specific chemical within the brain known as serotonin. This is one of several chemicals used to send messages from one nerve cell to another. ...
... • SSRIs for short. SSRIs act on a specific chemical within the brain known as serotonin. This is one of several chemicals used to send messages from one nerve cell to another. ...
Ch_09_Nervous_System_A_
... • SSRIs for short. SSRIs act on a specific chemical within the brain known as serotonin. This is one of several chemicals used to send messages from one nerve cell to another. ...
... • SSRIs for short. SSRIs act on a specific chemical within the brain known as serotonin. This is one of several chemicals used to send messages from one nerve cell to another. ...
Relationship between mutation and resistance to fluoroquinolones
... motifs in their basic components, the amino acids, or structures that are formed due to specific interactions between the amino acids. Characteristically, the bHLH proteins feature a stretch of basic amino acids (which can be charged positively) and two sections that are organized as helices and are ...
... motifs in their basic components, the amino acids, or structures that are formed due to specific interactions between the amino acids. Characteristically, the bHLH proteins feature a stretch of basic amino acids (which can be charged positively) and two sections that are organized as helices and are ...
Ch 8 Neurons and Network properties part-1
... Now let’s try to think about a living excitable cell… ...
... Now let’s try to think about a living excitable cell… ...
Channelrhodopsin

Channelrhodopsins are a subfamily of retinylidene proteins (rhodopsins) that function as light-gated ion channels. They serve as sensory photoreceptors in unicellular green algae, controlling phototaxis: movement in response to light. Expressed in cells of other organisms, they enable light to control electrical excitability, intracellular acidity, calcium influx, and other cellular processes. Channelrhodopsin-1 (ChR1) and Channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) from the model organism Chlamydomonas reinhardtii are the first discovered channelrhodopsins. Variants have been cloned from other algal species, and more are expected.