Afferent (Sensory) Division Part 1
... environment • Perception is the conscious interpretation of those stimuli ...
... environment • Perception is the conscious interpretation of those stimuli ...
Chapter 5: Learning
... Twitmeyer was examining the human knee jerk reflex at the same time Pavlov was studying salivation in dogs. UCS - hammer on knee UCR - Knee Jerk ...
... Twitmeyer was examining the human knee jerk reflex at the same time Pavlov was studying salivation in dogs. UCS - hammer on knee UCR - Knee Jerk ...
Zonk Rules - Blue Valley Schools
... 44. I once had a Chevy Citation which was a piece of crap car. It always broke down and never ran right. In fact it would stall at every stop sign (a real chich magnent). Since owning this Chevy, I have an aversion to Chevy cars and will never own one again. My aversion to Chevy cars is an example o ...
... 44. I once had a Chevy Citation which was a piece of crap car. It always broke down and never ran right. In fact it would stall at every stop sign (a real chich magnent). Since owning this Chevy, I have an aversion to Chevy cars and will never own one again. My aversion to Chevy cars is an example o ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY (7th Edition in Modules) David Myers
... 1. Former crack cocaine users should avoid cues (people, places) associated with previous drug use. 2. Through classical conditioning, a drug (plus its taste) that affects the immune response may cause the taste of the drug to invoke the immune response. (Ader 1985) ...
... 1. Former crack cocaine users should avoid cues (people, places) associated with previous drug use. 2. Through classical conditioning, a drug (plus its taste) that affects the immune response may cause the taste of the drug to invoke the immune response. (Ader 1985) ...
Growth and development
... Elicit inherent behavior Unconditioned stimulus, response Conditioned stimulus, response Operant conditioning Skinner Reinforcement, continuous, fixed, variable Positive or negative Observational and imitational ...
... Elicit inherent behavior Unconditioned stimulus, response Conditioned stimulus, response Operant conditioning Skinner Reinforcement, continuous, fixed, variable Positive or negative Observational and imitational ...
unit-4-sensation-perception-teacherblog
... For example, an individual fails to notice a difference between two images that are identical except for one change. The reasons these changes usually remain unnoticed by the observer include obstructions in the visual field, eye movements, a change of location, or a lack of attention. The bra ...
... For example, an individual fails to notice a difference between two images that are identical except for one change. The reasons these changes usually remain unnoticed by the observer include obstructions in the visual field, eye movements, a change of location, or a lack of attention. The bra ...
Experimenter
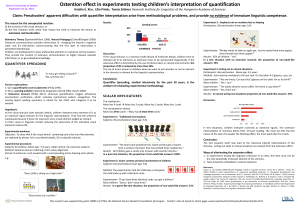
... Experimenter: " The adults deserve some coffee. Are there 2 cups there?” Most children: " Yes, there are.” ...
... Experimenter: " The adults deserve some coffee. Are there 2 cups there?” Most children: " Yes, there are.” ...
Chapter 1 Study Guide
... able to define and/or describe each item and read what the text has to say about each item. In other words, be familiar with the chapter section that introduces and discusses each item from the guide. ...
... able to define and/or describe each item and read what the text has to say about each item. In other words, be familiar with the chapter section that introduces and discusses each item from the guide. ...
Module 26: Classical Conditioning
... Habituation vs. Adaptation Adaptation is recoverable. Habituation is not. • Habituation – reduced sensitivity to a stimulus, even if the stimulus changes. • Our reaction is strong at first but not when the stimulus or something like it happens again. • A turtle draws its head back into its shell wh ...
... Habituation vs. Adaptation Adaptation is recoverable. Habituation is not. • Habituation – reduced sensitivity to a stimulus, even if the stimulus changes. • Our reaction is strong at first but not when the stimulus or something like it happens again. • A turtle draws its head back into its shell wh ...
Powerpoint Slides - Shannon Deets Counseling LLC
... bell after the dogs salivated they would not have become conditioned) » The CS and UCS must come very close together in time (Pavlov tried to stretch the time and saw no association) » The neutral stimulus must be paired with the UCS several times, often many times, before conditioning can take plac ...
... bell after the dogs salivated they would not have become conditioned) » The CS and UCS must come very close together in time (Pavlov tried to stretch the time and saw no association) » The neutral stimulus must be paired with the UCS several times, often many times, before conditioning can take plac ...
Kyle Muntzinger - Wright State University
... Student Activities • Bell and Straw Conditioning – Hands on experiment for the kids using the involuntary reaction of blinking. • Pairs of students will classically condition one another by using the bells and straws. ...
... Student Activities • Bell and Straw Conditioning – Hands on experiment for the kids using the involuntary reaction of blinking. • Pairs of students will classically condition one another by using the bells and straws. ...
Classical Conditioning Definition A form of associative learning
... 2. Put another way, this is how quickly one conditions (or learns) that the NS will always be paired with the US. Hence, they will provide the now conditioned response. 3. For instance, how long did it take for the dogs to learn that every time the metronome came out, that meant food was coming? Tha ...
... 2. Put another way, this is how quickly one conditions (or learns) that the NS will always be paired with the US. Hence, they will provide the now conditioned response. 3. For instance, how long did it take for the dogs to learn that every time the metronome came out, that meant food was coming? Tha ...
File
... Discrimination: the ability to distinguish between the conditioned stimulus (CS) and similar stimuli that are not ...
... Discrimination: the ability to distinguish between the conditioned stimulus (CS) and similar stimuli that are not ...
Solution 1
... 7. How can apparently nonlinear attentional modulation of a neural response arise from multiplicative modulation in an earlier area? Multiplicative modulation at one levels means an amplification or suppression of a neuron’s output. If a neuron is tuned to respond to a preferred region, then a multi ...
... 7. How can apparently nonlinear attentional modulation of a neural response arise from multiplicative modulation in an earlier area? Multiplicative modulation at one levels means an amplification or suppression of a neuron’s output. If a neuron is tuned to respond to a preferred region, then a multi ...
Psychology Final Exam
... 28. In John B. Watson and Rosalie Rayner's experiment, "Little Albert" began to fear all objects that were white and furry because of a. discrimination. c. generalization. b. systematic desensitization. d. all of the above. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- ...
... 28. In John B. Watson and Rosalie Rayner's experiment, "Little Albert" began to fear all objects that were white and furry because of a. discrimination. c. generalization. b. systematic desensitization. d. all of the above. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- ...
Sensation
... two stimuli required for detection 50% of the time, also called just noticeable difference (JND). For example, if you were asked to hold two objects of different weights, the just noticeable difference would be the minimum weight difference between the two that you could sense half of the time. ...
... two stimuli required for detection 50% of the time, also called just noticeable difference (JND). For example, if you were asked to hold two objects of different weights, the just noticeable difference would be the minimum weight difference between the two that you could sense half of the time. ...
learning - missstacy
... on the principle of extinction: Maury Flooding = a person is exposed to the (fearprovoking) harmless stimulus until the fear is extinguished Systematic desensitization = person is taught relaxation techniques & then exposed gradually to fearful stimulus ...
... on the principle of extinction: Maury Flooding = a person is exposed to the (fearprovoking) harmless stimulus until the fear is extinguished Systematic desensitization = person is taught relaxation techniques & then exposed gradually to fearful stimulus ...
Auditory: Stimulus Auditory
... • Receptors: Hair cells in the cochlea • Transduction: Physical opening of ion channels in the cochlea by the tectorial membrane • Afferent Signals: unevenly distributed to allow most signals for range of human speech • Pathway: contralateral to primary auditory cortex • CNS Areas: Primary in sup ...
... • Receptors: Hair cells in the cochlea • Transduction: Physical opening of ion channels in the cochlea by the tectorial membrane • Afferent Signals: unevenly distributed to allow most signals for range of human speech • Pathway: contralateral to primary auditory cortex • CNS Areas: Primary in sup ...
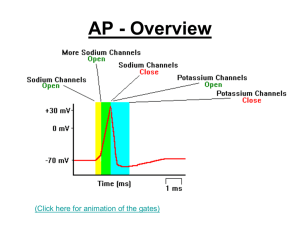
AP – All or nothing
... membrane, this is repolarisation • The membrane briefly becomes hyperpolarised (more negative on the inside than usual) • The Na+ / K+ channels close ...
... membrane, this is repolarisation • The membrane briefly becomes hyperpolarised (more negative on the inside than usual) • The Na+ / K+ channels close ...
PMHS - VitaAPPsych
... 7. The type of reinforcer that strengthens a response by reducing or removing an aversive (unpleasant) stimulus. ______________________ ________________________ 8. Learning that occurs, but is not apparent, until there is an incentive to demonstrate the learning. _______________________ ___________ ...
... 7. The type of reinforcer that strengthens a response by reducing or removing an aversive (unpleasant) stimulus. ______________________ ________________________ 8. Learning that occurs, but is not apparent, until there is an incentive to demonstrate the learning. _______________________ ___________ ...
Attending to Contrast
... basis of the psychological phenomena of visual attention. Desimone and colleagues have suggested that attention may increase the efficiency with which attended stimuli are encoded, while Maunsell and colleagues have argued that attention boosts the overall strength of neural signals without altering ...
... basis of the psychological phenomena of visual attention. Desimone and colleagues have suggested that attention may increase the efficiency with which attended stimuli are encoded, while Maunsell and colleagues have argued that attention boosts the overall strength of neural signals without altering ...