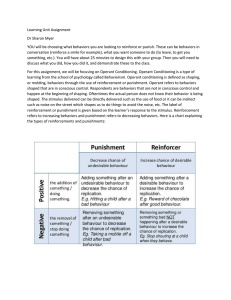
Learning Unit Assignment Dr Sharon Myer YOU will be choosing
... discuss what you did, how you did it, and demonstrate these to the class. For this assignment, we will be focusing on Operant Conditioning. Operant Conditioning is a type of learning from the school of psychology called Behaviorism. Operant conditioning is defined as shaping, or molding, behaviors t ...
... discuss what you did, how you did it, and demonstrate these to the class. For this assignment, we will be focusing on Operant Conditioning. Operant Conditioning is a type of learning from the school of psychology called Behaviorism. Operant conditioning is defined as shaping, or molding, behaviors t ...
Learning Theories - School of Computing
... “Psychology as the behaviorist views it is a purely objective experimental branch of natural science. Its theoretical goal is the prediction and control of behavior. Introspection forms no essential part of its methods, nor is the scientific value of its data dependent upon the readiness with which ...
... “Psychology as the behaviorist views it is a purely objective experimental branch of natural science. Its theoretical goal is the prediction and control of behavior. Introspection forms no essential part of its methods, nor is the scientific value of its data dependent upon the readiness with which ...
Adaptive Behavior in Autonomous Individuals
... 1828) suggested that bumps of the skull represented mental abilities. His theory, though incorrect, nevertheless proposed that different mental abilities were modular. Studying the mind (intelligence) from the perspective of information processing (Cognitive Psychology) . Studying intelligence from ...
... 1828) suggested that bumps of the skull represented mental abilities. His theory, though incorrect, nevertheless proposed that different mental abilities were modular. Studying the mind (intelligence) from the perspective of information processing (Cognitive Psychology) . Studying intelligence from ...
Ch. 19 S. 4 Cognitive Therapy and Behavior Therapy
... The two most widely used cognitive therapy methods are rational-emotive therapy and psychiatrist Aaron Beck’s model of therapy, sometimes called cognitive restructuring therapy. ...
... The two most widely used cognitive therapy methods are rational-emotive therapy and psychiatrist Aaron Beck’s model of therapy, sometimes called cognitive restructuring therapy. ...
Basic Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences
... • An innate reflex response elicited by an unconditioned stimulus (UCS) ...
... • An innate reflex response elicited by an unconditioned stimulus (UCS) ...
Answers To Test Yourself Questions
... Extinction is achieved in classical conditioning by omission of the UCS which precedes the UCR; extinction is achieved in operant conditioning by the omission of the consequence which follows the response. ...
... Extinction is achieved in classical conditioning by omission of the UCS which precedes the UCR; extinction is achieved in operant conditioning by the omission of the consequence which follows the response. ...
Reinforcement
... Learning: the process of acquiring new and relatively enduring information or behaviors • Does NOT include temporary changes due to disease, fatigue, injury, maturation, or drugs, since these do NOT qualify as learning even though they can alter behavior Crash Course Psychology: Episode 11, Learning ...
... Learning: the process of acquiring new and relatively enduring information or behaviors • Does NOT include temporary changes due to disease, fatigue, injury, maturation, or drugs, since these do NOT qualify as learning even though they can alter behavior Crash Course Psychology: Episode 11, Learning ...
Social Learning Theory
... Attributional style of depressed person: He/she attributes bad events to causes that are internal, stable, and global. Good results are believed to result from situational, unstable, and specific causes (e.g., luck). Attributional style of ‘non-depressed” person: He/she takes a bright view of good ...
... Attributional style of depressed person: He/she attributes bad events to causes that are internal, stable, and global. Good results are believed to result from situational, unstable, and specific causes (e.g., luck). Attributional style of ‘non-depressed” person: He/she takes a bright view of good ...
SOC 4108 2.16.14 Theories of Use
... interaction with others. 3 Variants: • Becker’s Learning Theory: Individuals learn to become drug users through watching others administer the drug properly, and by learning to associate the effects with pleasure. • Differential Association – Edwin Sutherland – We learn behavior from people who have ...
... interaction with others. 3 Variants: • Becker’s Learning Theory: Individuals learn to become drug users through watching others administer the drug properly, and by learning to associate the effects with pleasure. • Differential Association – Edwin Sutherland – We learn behavior from people who have ...
cognition notes learning, memory, problem solving
... • Long-Term Memory: It is estimated that the average adult has 1 billion bit of information in memory and the capacity for a thousand to a million times more…essentially LTM is limitless. • Where are they? o Memories do not reside in a single place. o Most recent research suggests memories form at t ...
... • Long-Term Memory: It is estimated that the average adult has 1 billion bit of information in memory and the capacity for a thousand to a million times more…essentially LTM is limitless. • Where are they? o Memories do not reside in a single place. o Most recent research suggests memories form at t ...
Behaviorism as a Theory of Personality: A Critical Look
... Inability to explain the development of human language. Although Skinner's ideas on operant conditioning are able to explain phobias and neurosis, they are sadly lacking in applicability to the more complex human behaviors of language and memory. The theory's inability to explain the language phenom ...
... Inability to explain the development of human language. Although Skinner's ideas on operant conditioning are able to explain phobias and neurosis, they are sadly lacking in applicability to the more complex human behaviors of language and memory. The theory's inability to explain the language phenom ...
Why do people use drugs?
... There are perceptual constancies that create perceptual stability. There are perceptual constancies that create perceptual stability. Three dimensional world can be created in a two dimensional retinal image Perception of Motion *** The Role of experience and culture affects perception F ...
... There are perceptual constancies that create perceptual stability. There are perceptual constancies that create perceptual stability. Three dimensional world can be created in a two dimensional retinal image Perception of Motion *** The Role of experience and culture affects perception F ...
Psychology – Dr. Saman – Lecture 2
... Smelling a grilled steak can produce salivation The reflexive stimulus (UCS) and response (UCR) are unconditioned The neutral stimulus is referred to as the conditioned stimulus (CS) In classical conditioning, the CS is repeatedly paired with the reflexive stimulus (UCS) Conditioning is best when th ...
... Smelling a grilled steak can produce salivation The reflexive stimulus (UCS) and response (UCR) are unconditioned The neutral stimulus is referred to as the conditioned stimulus (CS) In classical conditioning, the CS is repeatedly paired with the reflexive stimulus (UCS) Conditioning is best when th ...
Chemistry Problem Solving Drill
... It is operant conditioning that involves an act operating on the environment to produce rewarding or punishing stimuli. Through classical (Pavlovian) conditioning, an organism associates different stimuli that it does not control. Through operant conditioning, the organism associates its behaviors w ...
... It is operant conditioning that involves an act operating on the environment to produce rewarding or punishing stimuli. Through classical (Pavlovian) conditioning, an organism associates different stimuli that it does not control. Through operant conditioning, the organism associates its behaviors w ...
Chapter 3
... Operant Conditioning – (instrumental conditioning) people learn to perform behaviors that produce A. Operant Conditioning – consequences affect future behavior 1. Positive Reinforcement – 2. Negative Reinforcement – 3. Punishment – 4. Extinction – B. Shaping 1. Free product (followed by behavior of ...
... Operant Conditioning – (instrumental conditioning) people learn to perform behaviors that produce A. Operant Conditioning – consequences affect future behavior 1. Positive Reinforcement – 2. Negative Reinforcement – 3. Punishment – 4. Extinction – B. Shaping 1. Free product (followed by behavior of ...
Spacing Effect Practice document
... Short term memory, also known as __________________ , has a general limit of ______ items plus or minus two. Long term memory _____________________: Leading theory on long-term memory that neural connections gradually strengthen through rehearsal (repeated use) Flash-bulb memory: (Define) Type ...
... Short term memory, also known as __________________ , has a general limit of ______ items plus or minus two. Long term memory _____________________: Leading theory on long-term memory that neural connections gradually strengthen through rehearsal (repeated use) Flash-bulb memory: (Define) Type ...
ppt_ch10
... Behavior may not be as stable across time and situations as assumed by trait theorists ...
... Behavior may not be as stable across time and situations as assumed by trait theorists ...
n e w s a n d ...
... course, psychology (Fig. 1). These fields have approached this issue in different ways and each can inform and motivate future directions in motor control. In psychology, reward and punishment have long been recognized as instrumental for learning. As early as 1898, Edward Thorndike’s law of effect ...
... course, psychology (Fig. 1). These fields have approached this issue in different ways and each can inform and motivate future directions in motor control. In psychology, reward and punishment have long been recognized as instrumental for learning. As early as 1898, Edward Thorndike’s law of effect ...
Word
... Here are some questions to help you review. Use them to organize your notes and focus on important concepts. Review Guide for lecture 1 – Mark Cooper Know the reasons we study animal behavior. Know the different early periods of history. (cave drawings, Aristotle, Native Americans), Know the three f ...
... Here are some questions to help you review. Use them to organize your notes and focus on important concepts. Review Guide for lecture 1 – Mark Cooper Know the reasons we study animal behavior. Know the different early periods of history. (cave drawings, Aristotle, Native Americans), Know the three f ...
Learning - Villanova University
... - baby learns that crying leads to reward (daddy comes) - to make matters worse, dad only breaks down sometime (partial reinforcement) ...
... - baby learns that crying leads to reward (daddy comes) - to make matters worse, dad only breaks down sometime (partial reinforcement) ...
AP PSYCHOLOGY Review for the AP Exam Chapter 5-
... information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events Bottom-Up Processing *analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain’s integration of sensory information Top-Down Processing *information processing guided by higher-level mental processes *as when we const ...
... information, enabling us to recognize meaningful objects and events Bottom-Up Processing *analysis that begins with the sense receptors and works up to the brain’s integration of sensory information Top-Down Processing *information processing guided by higher-level mental processes *as when we const ...
Operant Conditioning - Henderson State University
... Evidence of cognitive processes during operant learning comes from rats during maze exploration, where they navigate it without an obvious reward. Rats seem to develop cognitive maps or mental representation of the layout of the maze (environment). ...
... Evidence of cognitive processes during operant learning comes from rats during maze exploration, where they navigate it without an obvious reward. Rats seem to develop cognitive maps or mental representation of the layout of the maze (environment). ...
Presentation
... Practice: The repetition of a task. It is best to practice over a period of time, than to practice all at once. ...
... Practice: The repetition of a task. It is best to practice over a period of time, than to practice all at once. ...
Psychological behaviorism

Psychological behaviorism is a form of behaviorism - a major theory within psychology which holds that behaviors are learned through positive and negative reinforcements. The theory recommends that psychological concepts (such as personality, learning and emotion) are to be explained in terms of observable behaviors that respond to stimulus. Behaviorism was first developed by John B. Watson (1912), who coined the term ""behaviorism,"" and then B.F. Skinner who developed what is known as ""radical behaviorism."" Watson and Skinner rejected the idea that psychological data could be obtained through introspection or by an attempt to describe consciousness; all psychological data, in their view, was to be derived from the observation of outward behavior. Recently, Arthur W. Staats has proposed a psychological behaviorism - a ""paradigmatic behaviorist theory"" which argues that personality consists of a set of learned behavioral patterns, acquired through the interaction between an individual's biology, environment, cognition, and emotion. Holth also critically reviews psychological behaviorism as a ""path to the grand reunification of psychology and behavior analysis"".Psychological behaviorism’s theory of personality represents one of psychological behaviorism’s central differences from the preceding behaviorism’s; the other parts of the broader approach as they relate to each other will be summarized in the paradigm sections























