BEHAVIORISM
... (“A—sound—will lead to B—food”) Operant conditioning (E.L. Thorndike, B.F. Skinner): Successful or punishing result (law of cause-effect) rather leads to complex/artificial behavior adoption (learning or avoidance)=> Walden Two, a behaviorallyengineered Utopia Even after extinction of positive reinf ...
... (“A—sound—will lead to B—food”) Operant conditioning (E.L. Thorndike, B.F. Skinner): Successful or punishing result (law of cause-effect) rather leads to complex/artificial behavior adoption (learning or avoidance)=> Walden Two, a behaviorallyengineered Utopia Even after extinction of positive reinf ...
Behaviorism and Cogntivism
... This philosophy has been adopted by corporate training because it is grounded in psychological principles that efficiently produce overt, observable, and measurable outcomes, which are popular in corporate environments that are also focused on measurable results. Behaviorist adult education lend ...
... This philosophy has been adopted by corporate training because it is grounded in psychological principles that efficiently produce overt, observable, and measurable outcomes, which are popular in corporate environments that are also focused on measurable results. Behaviorist adult education lend ...
Noorudean tohmeh
... called radical behaviorism, and founded his own school of experimental research psychology. ...
... called radical behaviorism, and founded his own school of experimental research psychology. ...
Learning - springpsychology
... Transfer in psychology= change in learning in one situation due to prior learning in another situation, the transfer can be positive or negative Chemical influences in learning = The TOTE= to carry on someone’s back or someone’s arms, to carry some thing The TOTE model=leaning and motivation a metho ...
... Transfer in psychology= change in learning in one situation due to prior learning in another situation, the transfer can be positive or negative Chemical influences in learning = The TOTE= to carry on someone’s back or someone’s arms, to carry some thing The TOTE model=leaning and motivation a metho ...
Behaviorism - N. Schollmeier`s Educational Research
... A “skinner box” is coined after B.F. Skinner, in which a rat is placed into a cage. This cage has a button in which the rat would eventually bump into while randomly running around and in turn release a food pellet. The “buttonpressing” behavior then increases due to the positive reinforcer (the foo ...
... A “skinner box” is coined after B.F. Skinner, in which a rat is placed into a cage. This cage has a button in which the rat would eventually bump into while randomly running around and in turn release a food pellet. The “buttonpressing” behavior then increases due to the positive reinforcer (the foo ...
AP Psychology Crib Notes
... satisfy a hierarchy of motives toward self-actualization Cognitive: people are rational and want to predict and control their world, personal constructs help in this process Biological: biological factors such as body type or genetics ...
... satisfy a hierarchy of motives toward self-actualization Cognitive: people are rational and want to predict and control their world, personal constructs help in this process Biological: biological factors such as body type or genetics ...
Brief_overview_of_theorists_by_Professor_Johnston
... Improving the human condition—societal purposes and individual purposes Teacher-directed Continuity Interaction Learning is active Children should be involved in real-life tasks ...
... Improving the human condition—societal purposes and individual purposes Teacher-directed Continuity Interaction Learning is active Children should be involved in real-life tasks ...
Major Theories of Literacy Learning and
... Whole Language Approach: Children’s Interests are Important (Developing a Love for Reading (Marie Clay, Kenneth & Yetta Goodman) ...
... Whole Language Approach: Children’s Interests are Important (Developing a Love for Reading (Marie Clay, Kenneth & Yetta Goodman) ...
Emily Pannkuk EDUC Chapter 6 Quotes and Comments INTASC
... 1. “Behaviorism is a theory that explains learning in terms of observable behaviors and how they’re influenced by stimuli from the environment. It defines learning as a relatively enduring change in observable behavior that occurs as a result of experience (Schunk, 2004; B.F. Skinner, 1953).” Pg 164 ...
... 1. “Behaviorism is a theory that explains learning in terms of observable behaviors and how they’re influenced by stimuli from the environment. It defines learning as a relatively enduring change in observable behavior that occurs as a result of experience (Schunk, 2004; B.F. Skinner, 1953).” Pg 164 ...
OTHER THEORIES OF PERSONALITY BEHAVIORISM AND
... Determinism: What we think are choices that we make are the consequence of antecedents that we do not realize have ...
... Determinism: What we think are choices that we make are the consequence of antecedents that we do not realize have ...
Lecture 3 - Learning to make your brain happy
... 3. All associations are not equivalent: (e.g. Taste Aversion) Preparedness (revisited) 4. Timing is critical The Operant Conditioning paradigm Remember the Law of Effect Superstitious behavior Positive reinforcement ...
... 3. All associations are not equivalent: (e.g. Taste Aversion) Preparedness (revisited) 4. Timing is critical The Operant Conditioning paradigm Remember the Law of Effect Superstitious behavior Positive reinforcement ...
Overview of the Behaviorist Approach
... • (-) The approach is seen as mechanistic. Human beings are complex animals, we feel emotions, we live in complex societies etc. To see humans as functioning in a mechanistic manner is to over-simplify human behavior. • (-) It excludes innate factors. We now know that genetic factors do play an enor ...
... • (-) The approach is seen as mechanistic. Human beings are complex animals, we feel emotions, we live in complex societies etc. To see humans as functioning in a mechanistic manner is to over-simplify human behavior. • (-) It excludes innate factors. We now know that genetic factors do play an enor ...
Behaviorist Theory
... Ivan Pavlov's model of classical conditioning based off one's personality and characteristics. (Schunk, 2012, p. 72) B.F. Skinner tested Watson's theories which he was able to associate with behaviorism. Skinner ...
... Ivan Pavlov's model of classical conditioning based off one's personality and characteristics. (Schunk, 2012, p. 72) B.F. Skinner tested Watson's theories which he was able to associate with behaviorism. Skinner ...
Learning Theories
... http://www.usask.ca/education/coursework/802papers/mergel/brenda.htm Outline of Educational Learning Theories and Theorists. (n.d.). Educational Learning Theories and Theorists. Retrieved June 25, 2011 from ...
... http://www.usask.ca/education/coursework/802papers/mergel/brenda.htm Outline of Educational Learning Theories and Theorists. (n.d.). Educational Learning Theories and Theorists. Retrieved June 25, 2011 from ...
Behavioral Learning Theory
... Before learning about this theory I did not know about all these key words that are affiliated with this one theory. Behaviorism is a learning theory that only focuses on objectively visible behaviors and discounts any independent activities of the mind. Behavior theorists define learning as nothing ...
... Before learning about this theory I did not know about all these key words that are affiliated with this one theory. Behaviorism is a learning theory that only focuses on objectively visible behaviors and discounts any independent activities of the mind. Behavior theorists define learning as nothing ...
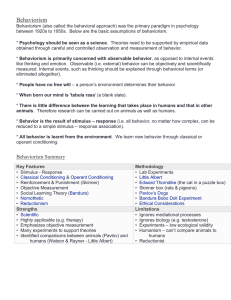
Behaviorism
... * Psychology should be seen as a science. Theories need to be supported by empirical data obtained through careful and controlled observation and measurement of behavior. * Behaviorism is primarily concerned with observable behavior, as opposed to internal events like thinking and emotion. Observabl ...
... * Psychology should be seen as a science. Theories need to be supported by empirical data obtained through careful and controlled observation and measurement of behavior. * Behaviorism is primarily concerned with observable behavior, as opposed to internal events like thinking and emotion. Observabl ...
Module 27 Notes Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning A type
... A type of associative learning (like classical conditioning). Type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforce or diminished if followed by a punisher. The likelihood of a behavior’s occurrence is linked to the response (consequence) that behavior receives o Reward ...
... A type of associative learning (like classical conditioning). Type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforce or diminished if followed by a punisher. The likelihood of a behavior’s occurrence is linked to the response (consequence) that behavior receives o Reward ...
Psychological behaviorism

Psychological behaviorism is a form of behaviorism - a major theory within psychology which holds that behaviors are learned through positive and negative reinforcements. The theory recommends that psychological concepts (such as personality, learning and emotion) are to be explained in terms of observable behaviors that respond to stimulus. Behaviorism was first developed by John B. Watson (1912), who coined the term ""behaviorism,"" and then B.F. Skinner who developed what is known as ""radical behaviorism."" Watson and Skinner rejected the idea that psychological data could be obtained through introspection or by an attempt to describe consciousness; all psychological data, in their view, was to be derived from the observation of outward behavior. Recently, Arthur W. Staats has proposed a psychological behaviorism - a ""paradigmatic behaviorist theory"" which argues that personality consists of a set of learned behavioral patterns, acquired through the interaction between an individual's biology, environment, cognition, and emotion. Holth also critically reviews psychological behaviorism as a ""path to the grand reunification of psychology and behavior analysis"".Psychological behaviorism’s theory of personality represents one of psychological behaviorism’s central differences from the preceding behaviorism’s; the other parts of the broader approach as they relate to each other will be summarized in the paradigm sections