Myers Module Twenty One
... after a response, strengthens the response. Negative reinforcement is any stimulus that when removed after a response, strengthens the response. Note: negative reinforcement is not punishment. Primary reinforcer: an innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need. Eg: foo ...
... after a response, strengthens the response. Negative reinforcement is any stimulus that when removed after a response, strengthens the response. Note: negative reinforcement is not punishment. Primary reinforcer: an innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need. Eg: foo ...
Document
... 1. A _________________________ is something that produces a reaction. 2. Classical _________________________ is a simple form of learning in which one stimulus comes to call forth the response that is usually associated with a different stimulus. 3. Russian physiologist Ivan ____________________ dis ...
... 1. A _________________________ is something that produces a reaction. 2. Classical _________________________ is a simple form of learning in which one stimulus comes to call forth the response that is usually associated with a different stimulus. 3. Russian physiologist Ivan ____________________ dis ...
Operant Conditioning Notes File
... Shaping and Chaining • One can reinforce a responses and continue to do so until desire response is met • This technique is used to teach animals tricks ...
... Shaping and Chaining • One can reinforce a responses and continue to do so until desire response is met • This technique is used to teach animals tricks ...
Operant Conditioning
... Operant conditioning uses operant or voluntary behavior Ask: Is the behavior something the animal can control? Does the animal have a choice in how to behave? ...
... Operant conditioning uses operant or voluntary behavior Ask: Is the behavior something the animal can control? Does the animal have a choice in how to behave? ...
OperateConditioning
... - learned behavior to a conditioned stimulus that occurs after a relationship has been created between CS and US (CR). • For example – you know class is over when the bell rings. ...
... - learned behavior to a conditioned stimulus that occurs after a relationship has been created between CS and US (CR). • For example – you know class is over when the bell rings. ...
Assumptions of Behaviorism
... A prompt of cue that comes before a behavior that results in the correct behavior being elicited. ...
... A prompt of cue that comes before a behavior that results in the correct behavior being elicited. ...
X-Period/Learning Test
... Famous behaviorist Skinner box ALL behavior relates to external rewards ...
... Famous behaviorist Skinner box ALL behavior relates to external rewards ...
LEARNING
... • Extinction -- eliminating the response • Generalization -- extending the response to similar stimuli • Discrimination -- limiting the response to a specific stimulus • Higher order conditioning -- extending the response to remote conditioned stimuli ...
... • Extinction -- eliminating the response • Generalization -- extending the response to similar stimuli • Discrimination -- limiting the response to a specific stimulus • Higher order conditioning -- extending the response to remote conditioned stimuli ...
Learning
... • Responses are unconditioned reflexes (UR) brought about by an unconditioned stimulus (US). • We pair the conditioned stimulus (CS) with the US so that the UR is brought about by the CS, at which point we say it is a conditioned response (CR) ...
... • Responses are unconditioned reflexes (UR) brought about by an unconditioned stimulus (US). • We pair the conditioned stimulus (CS) with the US so that the UR is brought about by the CS, at which point we say it is a conditioned response (CR) ...
Operant Conditioning Notes (teacher version)
... consequences becomes more likely; behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely. Skinner Box – a chamber containing a bar that an animal can manipulate to obtain a food or water reinforcer; devices are attached to record the animal’s rate of bar pressing. ...
... consequences becomes more likely; behaviors followed by unfavorable consequences become less likely. Skinner Box – a chamber containing a bar that an animal can manipulate to obtain a food or water reinforcer; devices are attached to record the animal’s rate of bar pressing. ...
Name - Mr. Kern
... 5. Form of learning based on the consequences of actions. _______________________ 6. When a conditioned response stops occurring. _______________________ 7. Stimulus that causes an automatic response. ________________________________ 8. Stimulus that encourages a behavior by meeting an organism’s ba ...
... 5. Form of learning based on the consequences of actions. _______________________ 6. When a conditioned response stops occurring. _______________________ 7. Stimulus that causes an automatic response. ________________________________ 8. Stimulus that encourages a behavior by meeting an organism’s ba ...
STUDY GUIDE Module 15 Define: Taste Aversion Spontaneous
... when an organism produces the same response to similar stimuli. ...
... when an organism produces the same response to similar stimuli. ...
A.P. Psychology 6 - Vocabulary Terms
... For this Unit, you will be responsible for understanding the following terms. You will be required to identify most of these terms on the Matching section of this unit’s Quiz. You will also be required to explain, describe, and give example for some of these terms on the Identification section. ...
... For this Unit, you will be responsible for understanding the following terms. You will be required to identify most of these terms on the Matching section of this unit’s Quiz. You will also be required to explain, describe, and give example for some of these terms on the Identification section. ...
Learning
... An unconditioned stimulus (UCS) triggers… An unconditioned response (UCR) in a person or other animal ...
... An unconditioned stimulus (UCS) triggers… An unconditioned response (UCR) in a person or other animal ...
Learning
... An unconditioned stimulus (UCS) triggers… An unconditioned response (UCR) in a person or other animal ...
... An unconditioned stimulus (UCS) triggers… An unconditioned response (UCR) in a person or other animal ...
Operant Conditioning
... Subjects of operant conditioning associate behaviors with their consequences. They are more likely to repeat rewarded (reinforced) behaviors and less likely to repeat punished behaviors. ...
... Subjects of operant conditioning associate behaviors with their consequences. They are more likely to repeat rewarded (reinforced) behaviors and less likely to repeat punished behaviors. ...
Crash Course #11 Learning
... Unconditioned or ________________________ response Describe the acquisition phase of conditioning: Conditioned or ____________________ response. Classical Conditioning: a type of ________________ in which one learns to link ______________ or more stimuli and anticipate events. B.F. ______________ an ...
... Unconditioned or ________________________ response Describe the acquisition phase of conditioning: Conditioned or ____________________ response. Classical Conditioning: a type of ________________ in which one learns to link ______________ or more stimuli and anticipate events. B.F. ______________ an ...
BEHAVIORISM
... (“A—sound—will lead to B—food”) Operant conditioning (E.L. Thorndike, B.F. Skinner): Successful or punishing result (law of cause-effect) rather leads to complex/artificial behavior adoption (learning or avoidance)=> Walden Two, a behaviorallyengineered Utopia Even after extinction of positive reinf ...
... (“A—sound—will lead to B—food”) Operant conditioning (E.L. Thorndike, B.F. Skinner): Successful or punishing result (law of cause-effect) rather leads to complex/artificial behavior adoption (learning or avoidance)=> Walden Two, a behaviorallyengineered Utopia Even after extinction of positive reinf ...
Module 27 Notes Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning A type
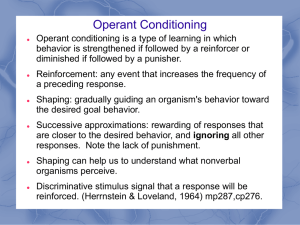
... Module 27 Notes Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning A type of associative learning (like classical conditioning). Type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforce or diminished if followed by a punisher. The likelihood of a behavior’s occurrence is linked to ...
... Module 27 Notes Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning A type of associative learning (like classical conditioning). Type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforce or diminished if followed by a punisher. The likelihood of a behavior’s occurrence is linked to ...
Name: Period: Learning Reading Guide 1. What is classical
... stimulus similar to the original CS without prior training with the second stimulus. 5. What is an example of spontaneous recovery? ...
... stimulus similar to the original CS without prior training with the second stimulus. 5. What is an example of spontaneous recovery? ...
Operant conditioning

Operant conditioning (also, “instrumental conditioning”) is a learning process in which behavior is sensitive to, or controlled by its consequences. For example, a child may learn to open a box to get the candy inside, or learn to avoid touching a hot stove. In contrast, classical conditioning causes a stimulus to signal a positive or negative consequence; the resulting behavior does not produce the consequence. For example, the sight of a colorful wrapper comes to signal ""candy"", causing a child to salivate, or the sound of a door slam comes to signal an angry parent, causing a child to tremble. The study of animal learning in the 20th century was dominated by the analysis of these two sorts of learning, and they are still at the core of behavior analysis.