Carbohydrate metabolism
... •Epinephrine stimulates α1 adrenergic receptors in liver → activation of phospholipase-C which hydrolyses phosphatidyl inositol into 1,2 diacylglycerol and inositol triphosphate → release Ca++ from its intracellular stores into the cytoplasm raising the intracytoplasmic concentration of Ca++ which r ...
... •Epinephrine stimulates α1 adrenergic receptors in liver → activation of phospholipase-C which hydrolyses phosphatidyl inositol into 1,2 diacylglycerol and inositol triphosphate → release Ca++ from its intracellular stores into the cytoplasm raising the intracytoplasmic concentration of Ca++ which r ...
UNIVERSITI PENDIOIKAN SULTAN lORIS
... produce a 6 carbon molecule, which is then split in two. After phosphorylation and reduction, what more ...
... produce a 6 carbon molecule, which is then split in two. After phosphorylation and reduction, what more ...
BI 200 - Exam #2
... 23. In eukaryotic mitochondria enzymes of the Krebs cycle are found in the _________ and components of the electron transport chain are associated with the ____________. a. cristae; matrix b. cytoplasm; cristae c. matrix; cristae d. none of the above – eukaryotes don’t have mitochondria 24. In chem ...
... 23. In eukaryotic mitochondria enzymes of the Krebs cycle are found in the _________ and components of the electron transport chain are associated with the ____________. a. cristae; matrix b. cytoplasm; cristae c. matrix; cristae d. none of the above – eukaryotes don’t have mitochondria 24. In chem ...
Practice Exam #2.1 - Montana State University Billings
... C. by connections to cholesterol D. by hydrophobic interactions E. proteins are not held in the plasma membrane and are free to leave the membrane at will 89. Which of the following does not occur during glycolysis? A. sugar splitting B. carbon dioxide release D. ATP production E. Glucose priming ...
... C. by connections to cholesterol D. by hydrophobic interactions E. proteins are not held in the plasma membrane and are free to leave the membrane at will 89. Which of the following does not occur during glycolysis? A. sugar splitting B. carbon dioxide release D. ATP production E. Glucose priming ...
03 - summer worksheet
... B. Circle and identify all of the functional groups seen in this ATP molecule shown below. (note: ATP is an incredibly important energy molecule that we will talk about a lot in this class. Take a couple of minutes to get to know it….). ...
... B. Circle and identify all of the functional groups seen in this ATP molecule shown below. (note: ATP is an incredibly important energy molecule that we will talk about a lot in this class. Take a couple of minutes to get to know it….). ...
CHEMISTRY OF FOOD FERMENTATION
... Fermentation is a form of anaerobic digestion that generates adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by the process of substrate-level phosphorylation. The energy for generating ATP comes from the oxidation of organic compounds, such as carbohydrates. In contrast, during respiration the energy for ATP formatio ...
... Fermentation is a form of anaerobic digestion that generates adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by the process of substrate-level phosphorylation. The energy for generating ATP comes from the oxidation of organic compounds, such as carbohydrates. In contrast, during respiration the energy for ATP formatio ...
BOTANY DEPARTMENT - university of nairobi staff profiles
... Define homeostatis, differentiate between Homoeotherms and Poikilotherms Distinguish different modes autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition Understand anaerobic and aerobic metabolism and its importance A good understanding of biological reductive and oxidative reactions. Evaluate the function of A ...
... Define homeostatis, differentiate between Homoeotherms and Poikilotherms Distinguish different modes autotrophic and heterotrophic nutrition Understand anaerobic and aerobic metabolism and its importance A good understanding of biological reductive and oxidative reactions. Evaluate the function of A ...
Cellular Respiration - Spokane Public Schools
... + about 32 or 34 ATP by oxidative phosphorylation, depending on which shuttle transports electrons from NADH in cytosol ...
... + about 32 or 34 ATP by oxidative phosphorylation, depending on which shuttle transports electrons from NADH in cytosol ...
Chapter Two Crossword Puzzle 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
... 5. Biological molecules contain very large molecules, therefore they are often called __________. 7. __________ group—consists of a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms 10. All biological reactions of this sort are mediated by __________, which speed up chemical reactions in cells 11. The bui ...
... 5. Biological molecules contain very large molecules, therefore they are often called __________. 7. __________ group—consists of a phosphorus atom bonded to four oxygen atoms 10. All biological reactions of this sort are mediated by __________, which speed up chemical reactions in cells 11. The bui ...
Cellular Respiration - MF011 General Biology 2 (May 2011 Semester)
... respiration and related pathways Aerobic ...
... respiration and related pathways Aerobic ...
Citric Acid Cycle
... Low levels of ADP, Pi, oxygen, and NADH that decrease electron transport activity. ...
... Low levels of ADP, Pi, oxygen, and NADH that decrease electron transport activity. ...
Muscle
... the Keq for metabolic sequence • The energy release accompanying ATP hydrolysis is transmitted to the unfavorable reaction so that the overall free energy for the coupled process is negative (favorable) – DG0’ for ATP hydrolysis is a large negative number – ATP changes the Keq by a factor of 108 (p6 ...
... the Keq for metabolic sequence • The energy release accompanying ATP hydrolysis is transmitted to the unfavorable reaction so that the overall free energy for the coupled process is negative (favorable) – DG0’ for ATP hydrolysis is a large negative number – ATP changes the Keq by a factor of 108 (p6 ...
Anaerobic Respiration
... • The process of lactic acid fermentation replaces the Krebs Cycle & the ETC so that the cell can have a continual source of energy, even in the absence of oxygen. • However this shift is only temporary and cells need oxygen for sustained activity. ...
... • The process of lactic acid fermentation replaces the Krebs Cycle & the ETC so that the cell can have a continual source of energy, even in the absence of oxygen. • However this shift is only temporary and cells need oxygen for sustained activity. ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5/e
... Oxidation of Propionyl-CoA Most dietary fatty acids are even-numbered ...
... Oxidation of Propionyl-CoA Most dietary fatty acids are even-numbered ...
Cellular Respiration
... + about 32 or 34 ATP by oxidative phosphorylation, depending on which shuttle transports electrons from NADH in cytosol ...
... + about 32 or 34 ATP by oxidative phosphorylation, depending on which shuttle transports electrons from NADH in cytosol ...
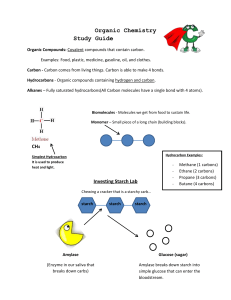
Organic Chemistry Study Guide Organic Compounds: Covalent
... biopolymers, or large biomolecules, essential for all known forms of life. Nucleic acids, which include DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid), are made from monomers known as nucleotides. ...
... biopolymers, or large biomolecules, essential for all known forms of life. Nucleic acids, which include DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid), are made from monomers known as nucleotides. ...
Metabolism Chp 7
... Energy from catabolism is used to attach phosphate group onto ADP to make ATP then when energy is needed: breaking apart ATP releases energy that can be used to build another compound Updated S’08 ...
... Energy from catabolism is used to attach phosphate group onto ADP to make ATP then when energy is needed: breaking apart ATP releases energy that can be used to build another compound Updated S’08 ...
Chapter 2 ppt
... composed of 2 or more different elements combined. • When elements combine they do so to gain stability. • They can share electrons with another element or compound and give away electrons ...
... composed of 2 or more different elements combined. • When elements combine they do so to gain stability. • They can share electrons with another element or compound and give away electrons ...
ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN (student)
... So what’s the deal with ATP?? • C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36 ATP • We need to produce 36 ATP in Cell. Resp. • After 3 stages, we have only produced 6 ATP through substrate-level oxidation • Thus, there are 30 ATP left to create – We produce the remaining 30 ATP through oxidative phosphorylation ...
... So what’s the deal with ATP?? • C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O + 36 ATP • We need to produce 36 ATP in Cell. Resp. • After 3 stages, we have only produced 6 ATP through substrate-level oxidation • Thus, there are 30 ATP left to create – We produce the remaining 30 ATP through oxidative phosphorylation ...
Supplemental notes in pdf
... fusion reactions on the sun to prevent (for as long as possible) reaching equilibrium with the environment; a high entropy state called death. Reaction coupling permits energetically unfavorable reactions to be more favorable in the context of a pathway. Coupling ATP hydrolysis to a phosphoryl trans ...
... fusion reactions on the sun to prevent (for as long as possible) reaching equilibrium with the environment; a high entropy state called death. Reaction coupling permits energetically unfavorable reactions to be more favorable in the context of a pathway. Coupling ATP hydrolysis to a phosphoryl trans ...
Launch Activity
... this is very soluble and toxic, so is not around for long! It is then combined with CO2 using ATP to produce UREA (CO(NH2)2 this occurs in the ornithine cycle. ...
... this is very soluble and toxic, so is not around for long! It is then combined with CO2 using ATP to produce UREA (CO(NH2)2 this occurs in the ornithine cycle. ...
Paracoccus denitrificans
... one of three energy sources •the sun •reduced organic compounds •reduced inorganic compounds •the chemical energy obtained can be used to do work Figure 9.1 ...
... one of three energy sources •the sun •reduced organic compounds •reduced inorganic compounds •the chemical energy obtained can be used to do work Figure 9.1 ...
Metabolism II
... • Lipolysis – breakdown of lipids for entry into TCA cycle • Triglycerides are predominant lipid in body used for energy • Stored in adipose tissue • Glycerol backbone & 3 fatty acids The first step in lipid metabolism is the hydrolysis of the lipid in the cytoplasm to produce glycerol and fatty aci ...
... • Lipolysis – breakdown of lipids for entry into TCA cycle • Triglycerides are predominant lipid in body used for energy • Stored in adipose tissue • Glycerol backbone & 3 fatty acids The first step in lipid metabolism is the hydrolysis of the lipid in the cytoplasm to produce glycerol and fatty aci ...
File
... 18) The free energy for the oxidation of glucose to CO2 and water is -686 kcal/mol and the free energy for the reduction of NAD+ to NADH is +53 kcal/mol. Why are only two molecules of NADH formed during glycolysis when it appears that as many as a dozen could be formed? A) Most of the free energy av ...
... 18) The free energy for the oxidation of glucose to CO2 and water is -686 kcal/mol and the free energy for the reduction of NAD+ to NADH is +53 kcal/mol. Why are only two molecules of NADH formed during glycolysis when it appears that as many as a dozen could be formed? A) Most of the free energy av ...
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).Glycolysis is a determined sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The intermediates provide entry points to glycolysis. For example, most monosaccharides, such as fructose and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form fat.Glycolysis is an oxygen independent metabolic pathway, meaning that it does not use molecular oxygen (i.e. atmospheric oxygen) for any of its reactions. However the products of glycolysis (pyruvate and NADH + H+) are sometimes disposed of using atmospheric oxygen. When molecular oxygen is used in the disposal of the products of glycolysis the process is usually referred to as aerobic, whereas if the disposal uses no oxygen the process is said to be anaerobic. Thus, glycolysis occurs, with variations, in nearly all organisms, both aerobic and anaerobic. The wide occurrence of glycolysis indicates that it is one of the most ancient metabolic pathways. Indeed, the reactions that constitute glycolysis and its parallel pathway, the pentose phosphate pathway, occur metal-catalyzed under the oxygen-free conditions of the Archean oceans, also in the absence of enzymes. Glycolysis could thus have originated from chemical constraints of the prebiotic world.Glycolysis occurs in most organisms in the cytosol of the cell. The most common type of glycolysis is the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas (EMP pathway), which was discovered by Gustav Embden, Otto Meyerhof, and Jakub Karol Parnas. Glycolysis also refers to other pathways, such as the Entner–Doudoroff pathway and various heterofermentative and homofermentative pathways. However, the discussion here will be limited to the Embden–Meyerhof–Parnas pathway.The entire glycolysis pathway can be separated into two phases: The Preparatory Phase – in which ATP is consumed and is hence also known as the investment phase The Pay Off Phase – in which ATP is produced.↑ ↑ 2.0 2.1 ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑