Respiration, Circulation, & Execretion
... • Pulse: surge of blood through an artery; measured in beats per minute; average is between 60-80 bpm • Heart rate is set by the pacemaker: bundle of nerve cells located at the top of right atrium • ECG: electrocardiogram measures electrical signals • Blood pressure: force blood exerts on blood vess ...
... • Pulse: surge of blood through an artery; measured in beats per minute; average is between 60-80 bpm • Heart rate is set by the pacemaker: bundle of nerve cells located at the top of right atrium • ECG: electrocardiogram measures electrical signals • Blood pressure: force blood exerts on blood vess ...
Document
... 2. The skin gets rid of wastes when you perspire. Perspiration = liquid waste consisting of water and salts. 3.The kidneys = maintain a proper balance of water and minerals. The kidneys, remove excess water, salts, and urea from the blood. This fluid is called urine. ...
... 2. The skin gets rid of wastes when you perspire. Perspiration = liquid waste consisting of water and salts. 3.The kidneys = maintain a proper balance of water and minerals. The kidneys, remove excess water, salts, and urea from the blood. This fluid is called urine. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - The Amazing Circulatory System
... • A heart attack stops blood taking oxygen to the brain • The heart is positioned behind the ribcage and between the lungs • Red blood cells live about 4 months • There are about 5 million red blood cells in a droplet of blood • All the chambers in the heart have valves that control the blood flow ...
... • A heart attack stops blood taking oxygen to the brain • The heart is positioned behind the ribcage and between the lungs • Red blood cells live about 4 months • There are about 5 million red blood cells in a droplet of blood • All the chambers in the heart have valves that control the blood flow ...
Circulatory System Review
... Which component in blood is directly related to hemophilia? Why? (1) Compare and contrast RBC and WBC in terms of a) cell structure and b) function. (2) Compare and contrast arteries and veins in terms of a) type of blood they carry and b) the direction of blood flow with respect to heart. (2) 8. Wh ...
... Which component in blood is directly related to hemophilia? Why? (1) Compare and contrast RBC and WBC in terms of a) cell structure and b) function. (2) Compare and contrast arteries and veins in terms of a) type of blood they carry and b) the direction of blood flow with respect to heart. (2) 8. Wh ...
Jenga Review Questions What organ pumps the blood? What type
... 29. What tissue connects muscles to bones? 30. What part of the bone makes blood cells? 31. What tissue connects bone to bone? 32. What tissue is found in the joints of the body to help cushion bones? 33. List 3 of the 5 functions of the Skeletal System? 34. What two systems work with the skeletal s ...
... 29. What tissue connects muscles to bones? 30. What part of the bone makes blood cells? 31. What tissue connects bone to bone? 32. What tissue is found in the joints of the body to help cushion bones? 33. List 3 of the 5 functions of the Skeletal System? 34. What two systems work with the skeletal s ...
Circulatory system webquest - School District of La Crosse
... 8. Describe the role of platelet cells in the blood? ...
... 8. Describe the role of platelet cells in the blood? ...
code blue vocabulary
... Spinal cord: made up of millions of nerves, it receives and relays information from all areas of the body Neurons: millions of cells that make up nerves Nerves: send messages throughout the body Axon: the long trunk of a nerve Dendrites: the smaller branches of a nerve Synapses: small spaces between ...
... Spinal cord: made up of millions of nerves, it receives and relays information from all areas of the body Neurons: millions of cells that make up nerves Nerves: send messages throughout the body Axon: the long trunk of a nerve Dendrites: the smaller branches of a nerve Synapses: small spaces between ...
File
... • The circulatory system is a transport system that uses blood to carry nutrients and oxygen to the cells of the body. – It also carries waste products such as carbon dioxide away from the cells. – The circulatory system transports chemical messages between cells and different parts of the body. – I ...
... • The circulatory system is a transport system that uses blood to carry nutrients and oxygen to the cells of the body. – It also carries waste products such as carbon dioxide away from the cells. – The circulatory system transports chemical messages between cells and different parts of the body. – I ...
Test Review Key
... stimulates increased breathing. Increased breathing helps remove carbon dioxide from the blood, returning blood pH to normal levels. N 16. If blood temperature rises too high, specialized neurons in the hypothalamus of the brain sense the change. These neurons signal other nerve centers, which in tu ...
... stimulates increased breathing. Increased breathing helps remove carbon dioxide from the blood, returning blood pH to normal levels. N 16. If blood temperature rises too high, specialized neurons in the hypothalamus of the brain sense the change. These neurons signal other nerve centers, which in tu ...
Chapter 9 Homeostasis
... Occurs at the surface where body comes into contact with the external environment Exchange of thermal energy occurs through 1 of 4 mechanisms ...
... Occurs at the surface where body comes into contact with the external environment Exchange of thermal energy occurs through 1 of 4 mechanisms ...
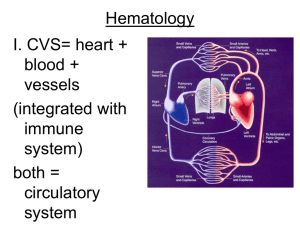
Hematology
... VIII. Recyclying RBCs –p. 632 1. RBCs become become engulfed by phagocytes of liver, spleen and bone marrow. - alpha and beta chains broken down into amino acids and metabolized or released into bl. -heme stripped of its iron and becomes biliverdin (green) 2 . biliverdin becomes bilirubin (yellow) ...
... VIII. Recyclying RBCs –p. 632 1. RBCs become become engulfed by phagocytes of liver, spleen and bone marrow. - alpha and beta chains broken down into amino acids and metabolized or released into bl. -heme stripped of its iron and becomes biliverdin (green) 2 . biliverdin becomes bilirubin (yellow) ...
1 - School-Portal.co.uk
... movement and keep warm – i.e. in barns. 9. What measures are being employed to try to conserve the ocean’s fish stocks? Setting quotas and net size restrictions 10. What is mycoprotein and how is it produced? Protein produced by fungus Fusarium suitable for vegetarians. Grown on glucose syrup in aer ...
... movement and keep warm – i.e. in barns. 9. What measures are being employed to try to conserve the ocean’s fish stocks? Setting quotas and net size restrictions 10. What is mycoprotein and how is it produced? Protein produced by fungus Fusarium suitable for vegetarians. Grown on glucose syrup in aer ...
Chapter 16 Circulation Section 2 Blood and Lymph
... • Fluid inside the lymphatic system • It consists of water and dissolved materials such as glucose • I also contains white blood cells that have left the capillaries ...
... • Fluid inside the lymphatic system • It consists of water and dissolved materials such as glucose • I also contains white blood cells that have left the capillaries ...
Quiz 4 1407 - HCC Learning Web
... A) the building blocks from which they are synthesized B) their solubility in cell membranes C) their requirement for travel through the bloodstream D) their reliance on signal transduction in the cell 36) Which of the following are similar in structure to cholesterol? A) leptin and serotonin B) lut ...
... A) the building blocks from which they are synthesized B) their solubility in cell membranes C) their requirement for travel through the bloodstream D) their reliance on signal transduction in the cell 36) Which of the following are similar in structure to cholesterol? A) leptin and serotonin B) lut ...
EXCHANGE IN MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS
... • LUNGS (SEE P.2 DIAGRAM) • MIXING OF OXYGEN RICH AND OXYGEN POOR AIR • NOSE/MOUTHTRACHEABRON CHI • ALVEOLI (CAVITIES CONTAINING CAPILLARIES) • THESE ALVEOLI PROVIDE A LARGE SURFACE AREA TO EXCHANGE OXYGEN AND CARBON DIOXIDE • (de-oxygenated blood is pumped through the pulmonary arteries to the l ...
... • LUNGS (SEE P.2 DIAGRAM) • MIXING OF OXYGEN RICH AND OXYGEN POOR AIR • NOSE/MOUTHTRACHEABRON CHI • ALVEOLI (CAVITIES CONTAINING CAPILLARIES) • THESE ALVEOLI PROVIDE A LARGE SURFACE AREA TO EXCHANGE OXYGEN AND CARBON DIOXIDE • (de-oxygenated blood is pumped through the pulmonary arteries to the l ...
Blood Chapter
... not returned to the capillary. The excess tissue fluid is picked up by the lymph capillaries and is returned to the systemic venous blood at the subclavianvein. ...
... not returned to the capillary. The excess tissue fluid is picked up by the lymph capillaries and is returned to the systemic venous blood at the subclavianvein. ...
Animal System Review Key
... stimulates increased breathing. Increased breathing helps remove carbon dioxide from the blood, returning blood pH to normal levels. N 16. If blood temperature rises too high, specialized neurons in the hypothalamus of the brain sense the change. These neurons signal other nerve centers, which in tu ...
... stimulates increased breathing. Increased breathing helps remove carbon dioxide from the blood, returning blood pH to normal levels. N 16. If blood temperature rises too high, specialized neurons in the hypothalamus of the brain sense the change. These neurons signal other nerve centers, which in tu ...
Hemo the Magnificent
... gives off nutrients and oxygen takes away wastes (garbage) and carbon dioxide cells are generally no more than two cells away from a capillary Red blood cells pass through in single file RBC passage is controlled by a gatekeeper, a round muscle called a sphincter muscle ...
... gives off nutrients and oxygen takes away wastes (garbage) and carbon dioxide cells are generally no more than two cells away from a capillary Red blood cells pass through in single file RBC passage is controlled by a gatekeeper, a round muscle called a sphincter muscle ...
Wellness – Human Body Systems Date ______ Name The 11
... ____________ - small flap that closes over the opening of the respiratory system when swallowing, preventing food from entering the airway ____________ - muscular tube connecting the mouth to the stomach ____________ - produces bile, a substance that helps break down fats ____________ - stores bile ...
... ____________ - small flap that closes over the opening of the respiratory system when swallowing, preventing food from entering the airway ____________ - muscular tube connecting the mouth to the stomach ____________ - produces bile, a substance that helps break down fats ____________ - stores bile ...
Assessment Questions for each Essential Question
... Using the figure above, suggest what would happen if the order of events of the cardiac cycle ...
... Using the figure above, suggest what would happen if the order of events of the cardiac cycle ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.