Artery
... Key Concepts Arteries When blood leaves the heart, it travels through arteries. The walls of arteries are generally very thick. In fact, artery walls consist of three cell layers. Capillaries In the capillaries, materials are exchanged between the blood and the body’s cells. Capillary walls are onl ...
... Key Concepts Arteries When blood leaves the heart, it travels through arteries. The walls of arteries are generally very thick. In fact, artery walls consist of three cell layers. Capillaries In the capillaries, materials are exchanged between the blood and the body’s cells. Capillary walls are onl ...
Anatomy Joke - Mr. Bell`s Anatomy and Physiology
... Regulation of body temperature First point of contact with the environment ...
... Regulation of body temperature First point of contact with the environment ...
Lesson 5 Animal Systems
... Nutrient and O-rich blood is delivered to the body’s cells Blood travels through blood vessels Blood reaches tiny vessels called capillaries Dissolved nutrients and O can pass through their thin walls and enter the cells Cells past waste materials back through the capillaries and into the blood O-po ...
... Nutrient and O-rich blood is delivered to the body’s cells Blood travels through blood vessels Blood reaches tiny vessels called capillaries Dissolved nutrients and O can pass through their thin walls and enter the cells Cells past waste materials back through the capillaries and into the blood O-po ...
Third Nine Weeks Exam Study Guide Skeletal System- (pg 474-481)
... liver_-G , Pancreas-C 14What structure(s) enable(s) the small intestine to absorb large amounts of nutrients? Villi 15.. Which process takes place in the large intestine? .Water is absorbed, Vitamin K is produced ...
... liver_-G , Pancreas-C 14What structure(s) enable(s) the small intestine to absorb large amounts of nutrients? Villi 15.. Which process takes place in the large intestine? .Water is absorbed, Vitamin K is produced ...
File
... Analyzing Urine • Urine can be tested to detect number of diseases. • High levels of glucose may indicate diabetes. • High levels of protein (blood) is a sign that the kidneys are not functioning properly. ...
... Analyzing Urine • Urine can be tested to detect number of diseases. • High levels of glucose may indicate diabetes. • High levels of protein (blood) is a sign that the kidneys are not functioning properly. ...
Name: Date: Period:_____ Final Review: Study Guide # 4 TOPICS
... should be easy to locate in your notebook! 2. Next, scan the objectives for the topic you are about to study in order to get a sense of what you should be focusing your time and energy on. 3. Start mastering each objective by answering the associated review questions right on this sheet. 4. After yo ...
... should be easy to locate in your notebook! 2. Next, scan the objectives for the topic you are about to study in order to get a sense of what you should be focusing your time and energy on. 3. Start mastering each objective by answering the associated review questions right on this sheet. 4. After yo ...
Integration of the Urinary System
... activates a hormonal pathway that increases blood pressure. When oxygen levels in body tissues decrease, the kidneys secrete the hormone erythropoietin. Erythropoietin stimulates the bone marrow to increase production of red blood cells. The kidneys regulate ion concentrations in blood plasma by re ...
... activates a hormonal pathway that increases blood pressure. When oxygen levels in body tissues decrease, the kidneys secrete the hormone erythropoietin. Erythropoietin stimulates the bone marrow to increase production of red blood cells. The kidneys regulate ion concentrations in blood plasma by re ...
Ecology
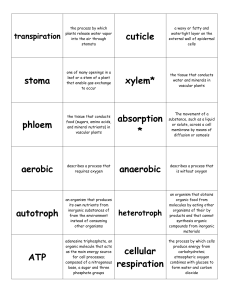
... an organism that produces its own nutrients from inorganic substances of from the environment instead of consuming other organisms ...
... an organism that produces its own nutrients from inorganic substances of from the environment instead of consuming other organisms ...
Circulatory System
... supply of oxygen and drop off the carbon dioxide. F. The blood now has a supply of oxygen and flows to the top left chamber. G. It then passes through a valve to the lower left chamber. H. The blood is then pumped to all parts of the body. VII. Blood A. About half of blood is liquid (PLASMA), which ...
... supply of oxygen and drop off the carbon dioxide. F. The blood now has a supply of oxygen and flows to the top left chamber. G. It then passes through a valve to the lower left chamber. H. The blood is then pumped to all parts of the body. VII. Blood A. About half of blood is liquid (PLASMA), which ...
The Circulatory System
... white blood cells help the body fight off germs. Platelets form plugs (scabs) that stop us from bleeding to death. ...
... white blood cells help the body fight off germs. Platelets form plugs (scabs) that stop us from bleeding to death. ...
Circulatory system.pps
... in it goessystem into the separated circulatory is very heartto and throughexcept the heart’s various processes, similar humans, they have a three chamber oxygen laden blood forcedof toblood all of to theoccur. cells heart which allows theismixing needinghave its nutrients. The oxygen poor blood Hum ...
... in it goessystem into the separated circulatory is very heartto and throughexcept the heart’s various processes, similar humans, they have a three chamber oxygen laden blood forcedof toblood all of to theoccur. cells heart which allows theismixing needinghave its nutrients. The oxygen poor blood Hum ...
View PDF
... - Fluid in body continuous with outside so both layers bathed in fluid. Fig. 42.3: - In multicellular organisms diffusion distance too big for efficient exchange of nutrients and waste therefore develop a circulatory system. Have fluid ( blood), tubes ( blood vessels) and pump ( heart). a) Open: -I ...
... - Fluid in body continuous with outside so both layers bathed in fluid. Fig. 42.3: - In multicellular organisms diffusion distance too big for efficient exchange of nutrients and waste therefore develop a circulatory system. Have fluid ( blood), tubes ( blood vessels) and pump ( heart). a) Open: -I ...
Name - dublin.k12.ca.us
... everyday activities. We inhale air using our respiratory system. The oxygen then moves into blood, which is part of the __________________ system. Conversely, we produce carbon dioxide within our bodies. This “waste” is moved from cells in the body to our lungs through the circulatory system (blood) ...
... everyday activities. We inhale air using our respiratory system. The oxygen then moves into blood, which is part of the __________________ system. Conversely, we produce carbon dioxide within our bodies. This “waste” is moved from cells in the body to our lungs through the circulatory system (blood) ...
Excretion - Ardsley Schools
... • Regulates the makeup of body fluid • Detoxification: Liver detoxifies the blood • Removes harmful substances: bacteria, certain drugs, hormones, from the blood • Liver changes these substances into less harmful ones • Inactive forms are returned to the blood and excreted via the kidneys ...
... • Regulates the makeup of body fluid • Detoxification: Liver detoxifies the blood • Removes harmful substances: bacteria, certain drugs, hormones, from the blood • Liver changes these substances into less harmful ones • Inactive forms are returned to the blood and excreted via the kidneys ...
excretion questions with answers
... Carbon dioxide, urea, uric acid, spent hormones, excess water and salts (any four) have to be excreted from the body. 2 Name three organs which have an excretory function. (3) The kidneys, lungs and liver have an excretory function. 3 Supply the missing words in the following paragraph: Blood is tak ...
... Carbon dioxide, urea, uric acid, spent hormones, excess water and salts (any four) have to be excreted from the body. 2 Name three organs which have an excretory function. (3) The kidneys, lungs and liver have an excretory function. 3 Supply the missing words in the following paragraph: Blood is tak ...
DiagnosticTest
... d. A cellulose membrane Items 2 and 3 refer to the following diagrams of specialized cells in the body. ...
... d. A cellulose membrane Items 2 and 3 refer to the following diagrams of specialized cells in the body. ...
Human Body Systems – Level 1
... -- white blood cells function in the immune system -- platelets help in blood clotting ...
... -- white blood cells function in the immune system -- platelets help in blood clotting ...
Chapter 12 - Unit 4
... All cells of the body have the same basic need for energy, nutrients and oxygen to carry our their functions. All cells also need to remove wastes. Body systems work together to provide cells with what they need. ...
... All cells of the body have the same basic need for energy, nutrients and oxygen to carry our their functions. All cells also need to remove wastes. Body systems work together to provide cells with what they need. ...
Regulation- Excretory System PPT PreAP
... Nervous & Excretory Systems • Regulation within animal systems requires maintaining homeostasis- the ability of the body or a cell to seek and maintain a stable internal environment when dealing with external changes • There are several organ systems that work together to maintain an organism’s inte ...
... Nervous & Excretory Systems • Regulation within animal systems requires maintaining homeostasis- the ability of the body or a cell to seek and maintain a stable internal environment when dealing with external changes • There are several organ systems that work together to maintain an organism’s inte ...
Circulatory System - Ms. Emery's AP Biology
... atmosphere to the bloodstream and release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere. • Deoxygenated blood through pulmonary artery to lungs. Oxygenated by air-filled sacs (alveoli), blood returns to heart through pulmonary veins. ...
... atmosphere to the bloodstream and release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere. • Deoxygenated blood through pulmonary artery to lungs. Oxygenated by air-filled sacs (alveoli), blood returns to heart through pulmonary veins. ...
Body Systems Work Together
... stimulus in the body, and signaling a response, like sugar level, water level, calcium level, growth, or sleep. ...
... stimulus in the body, and signaling a response, like sugar level, water level, calcium level, growth, or sleep. ...
Anatomy and Physiology
... a calorie (cal) is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1g of water through 1°C a kilocalorie (kcal) is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1kg of water through 1°C. The kilocalorie is the unit used to measure the energy value of foods ...
... a calorie (cal) is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1g of water through 1°C a kilocalorie (kcal) is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1kg of water through 1°C. The kilocalorie is the unit used to measure the energy value of foods ...
Chapter 17 Review
... Explain the different types of blood. Blood type: determined by the type of antigen present on the red blood cell (Type A, B, AB, and O) Antigen: protein or carbohydrate that acts as a signal enabling the body to recognize foreign substances A blood = A antigen and B antibodies B blood = B antigen a ...
... Explain the different types of blood. Blood type: determined by the type of antigen present on the red blood cell (Type A, B, AB, and O) Antigen: protein or carbohydrate that acts as a signal enabling the body to recognize foreign substances A blood = A antigen and B antibodies B blood = B antigen a ...
Systems Study Questions
... 75. mouth, epiglottis, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus 76. mouth, epiglottis, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, blood, cells 77. kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra 78. right atrium, right ventricle, artery, lungs, vein, left atrium, left ventricle, aorta, cells, v ...
... 75. mouth, epiglottis, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, anus 76. mouth, epiglottis, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, blood, cells 77. kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, urethra 78. right atrium, right ventricle, artery, lungs, vein, left atrium, left ventricle, aorta, cells, v ...
Homeostasis

Homeostasis or homoeostasis (homeo- + -stasis) is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH). It is a process that maintains the stability of the human body's internal environment in response to changes in external conditions.The concept was described by French physiologist Claude Bernard in 1865 and the word was coined by Walter Bradford Cannon in 1926. Although the term was originally used to refer to processes within living organisms, it is frequently applied to automatic control systems such as thermostats. Homeostasis requires a sensor to detect changes in the condition to be regulated, an effector mechanism that can vary that condition, and a negative feedback connection between the two.