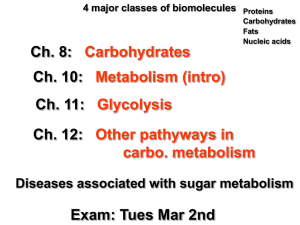
Cellular Respiration
... making it NADH (remaining proton dissolves) • NAD+ is oxidized form • NADH is reduced form • NAD+ reduction occurs in one reaction in glycolysis, during the pyruvate oxidation step (stage 2) and in three reactions of the Krebs cycle. ...
... making it NADH (remaining proton dissolves) • NAD+ is oxidized form • NADH is reduced form • NAD+ reduction occurs in one reaction in glycolysis, during the pyruvate oxidation step (stage 2) and in three reactions of the Krebs cycle. ...
Chapter 7 Review Name: Date: Question Answer Process that
... 24. The Krebs cycle occurs in the __ 25. Oxygen, electrons and protons form ___ 26. Aerobic respiration produces a total of ___ ATP. Fermentation produces a total of ___ ATP 27. The enzyme that forms ATP is called __ 28. Cellular respiration is ___% efficient in the conversion of the energy in gluco ...
... 24. The Krebs cycle occurs in the __ 25. Oxygen, electrons and protons form ___ 26. Aerobic respiration produces a total of ___ ATP. Fermentation produces a total of ___ ATP 27. The enzyme that forms ATP is called __ 28. Cellular respiration is ___% efficient in the conversion of the energy in gluco ...
File
... disrupt them. In the first diagram, show how the processes work normally. Trace movement of an electron with an orange arrow, movement of H+ ions (active transport and chemiosmosis) with black arrows, and formation of ATP with a pink arrow. In the second diagram, draw arrows showing the movement of ...
... disrupt them. In the first diagram, show how the processes work normally. Trace movement of an electron with an orange arrow, movement of H+ ions (active transport and chemiosmosis) with black arrows, and formation of ATP with a pink arrow. In the second diagram, draw arrows showing the movement of ...
SBI4U: Respiration and Photosynthesis Test
... 2). Describe the meaning of the term chemiosmosis and its role in the production of energy for the cell. [3] 3). Cellular respiration is controlled by feedback loops. Explain what this means, using an ...
... 2). Describe the meaning of the term chemiosmosis and its role in the production of energy for the cell. [3] 3). Cellular respiration is controlled by feedback loops. Explain what this means, using an ...
Slide 1
... Reducing and Non-reducing • Since mono- and disaccharides are hemiacetals they have a reactive carbonyl that can be oxidized. • Linear polymer usually one reducing end (free anomeric carbon), one non-reducing end, and all internal monosaccharides are acetals that are not in equilibrium with open cha ...
... Reducing and Non-reducing • Since mono- and disaccharides are hemiacetals they have a reactive carbonyl that can be oxidized. • Linear polymer usually one reducing end (free anomeric carbon), one non-reducing end, and all internal monosaccharides are acetals that are not in equilibrium with open cha ...
notes for cell resp - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... A. AcetylCoA enters the cycle and combines with oxaloacetate to form a six carbon citrate (citric acid) B. Rearrangement of the molecule yield NADH and CO2 C. Loss of the CoA drives GDP to GTP which drives ADP to ATP D. FAD is reduced to FADH2 E. More rearrangements produce NADH and oxaloacetate F. ...
... A. AcetylCoA enters the cycle and combines with oxaloacetate to form a six carbon citrate (citric acid) B. Rearrangement of the molecule yield NADH and CO2 C. Loss of the CoA drives GDP to GTP which drives ADP to ATP D. FAD is reduced to FADH2 E. More rearrangements produce NADH and oxaloacetate F. ...
BIOB111 - Tutorial activity for Session 21
... Then discuss the importance of reduced coenzymes (NADH and FADH2) that are formed in certain steps - and how they are used to produce energy in the form of ATP. ...
... Then discuss the importance of reduced coenzymes (NADH and FADH2) that are formed in certain steps - and how they are used to produce energy in the form of ATP. ...
Plasma Membrane Transporter Protein Mutations
... and results in the accumulation of nontransported glucose in the intestinal lumen and refractory diarrhea secondary to its osmotic effects. Direct evidence for genetic control of intestinal glucose transport in humans was obtained by in vitro studies of jejunal biopsy material from families in which ...
... and results in the accumulation of nontransported glucose in the intestinal lumen and refractory diarrhea secondary to its osmotic effects. Direct evidence for genetic control of intestinal glucose transport in humans was obtained by in vitro studies of jejunal biopsy material from families in which ...
see previous week 3 link
... • Citric acid cycle – a cyclical series of oxidation reactions that give off CO2 and produce one ATP per cycle; occurs twice per glucose molecule • Electron transport system – a series of carriers that accept electrons removed from glucose and pass them from one carrier to the next until the final ...
... • Citric acid cycle – a cyclical series of oxidation reactions that give off CO2 and produce one ATP per cycle; occurs twice per glucose molecule • Electron transport system – a series of carriers that accept electrons removed from glucose and pass them from one carrier to the next until the final ...
Endocrinology – glucose homeostasis
... Functions • Insulin is a hormone of plenty. It enhances the conversion of circulating pools of glucose, amino acids and FFAs into stored glycogen, protein and adipose tissue. • On carbohydrate metabolism, it has two main functions. First, it reduces the rate of release of glucose from the liver. It ...
... Functions • Insulin is a hormone of plenty. It enhances the conversion of circulating pools of glucose, amino acids and FFAs into stored glycogen, protein and adipose tissue. • On carbohydrate metabolism, it has two main functions. First, it reduces the rate of release of glucose from the liver. It ...
Practice Paper 1 - Australian Pharmacy Council
... Due to the frequent changes to the scope and content within the practice of pharmacy in Australia, the APC does not guarantee that the information in this paper is accurate or relevant once published publicly. The actual KAPS Examination is delivered by computer and candidates should visit the APC w ...
... Due to the frequent changes to the scope and content within the practice of pharmacy in Australia, the APC does not guarantee that the information in this paper is accurate or relevant once published publicly. The actual KAPS Examination is delivered by computer and candidates should visit the APC w ...
Chapter 7 Carbohydrates: Nomenclature Monosaccharides
... non-hydrogen atoms on the ring are in the equatorial position. That makes beta glucose more stable than alpha glucose, and the equilibrium mixture of the two contains more beta than alpha. Note we most commonly find glucose and other aldohexoses in the pyranose ring form, while fructose, a keto hexo ...
... non-hydrogen atoms on the ring are in the equatorial position. That makes beta glucose more stable than alpha glucose, and the equilibrium mixture of the two contains more beta than alpha. Note we most commonly find glucose and other aldohexoses in the pyranose ring form, while fructose, a keto hexo ...
Catabolic Pathways and Glycolysis
... Catabolic Pathways and Glycolysis • The ability to do that work depends on catabolic process that harvest the potential energy found in organic molecules. The 2 catabolic processes that occur in organisms are fermentation (breakdown without O2)and cellular respiration (breakdown with O2). ...
... Catabolic Pathways and Glycolysis • The ability to do that work depends on catabolic process that harvest the potential energy found in organic molecules. The 2 catabolic processes that occur in organisms are fermentation (breakdown without O2)and cellular respiration (breakdown with O2). ...
METABOLIC COMPARTMENTATION
... • The complete oxidation of glucose to carbon dioxide directly yields 2 ATP, 2 GTP, 10 NADH and 2 FADH. Depending on the assumptions used with respect to electron shuttle and ATP yield this could be the equivalent of 30 to 38 ATP molecules per molecule of glucose oxidized to carbon dioxide. Whatever ...
... • The complete oxidation of glucose to carbon dioxide directly yields 2 ATP, 2 GTP, 10 NADH and 2 FADH. Depending on the assumptions used with respect to electron shuttle and ATP yield this could be the equivalent of 30 to 38 ATP molecules per molecule of glucose oxidized to carbon dioxide. Whatever ...
Chapter 2- Biological Molecules Answers 36. c. the pentose sugar
... they do not mix. The oil molecules tend to clump together rather than mix with the water. This is because oil molecules are nonpolar and therefore hydrophobic (water-fearing). ...
... they do not mix. The oil molecules tend to clump together rather than mix with the water. This is because oil molecules are nonpolar and therefore hydrophobic (water-fearing). ...
AP BIOLOGY Chapter 4 - Livonia Public Schools
... Denaturing in proteins is due to the disruption of peptide bonds False; 1° remains intact but hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds and disulfide bridges in 2° & 3°are disrupted ...
... Denaturing in proteins is due to the disruption of peptide bonds False; 1° remains intact but hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds and disulfide bridges in 2° & 3°are disrupted ...
nutritional terminology
... Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide. An electron carrier; derivative of niacin - vitamin B3. ...
... Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide. An electron carrier; derivative of niacin - vitamin B3. ...
Glycogen Metabolism
... fourth glucose from α (16) branch point The transferase transfers 3 glucose residues from a 4-residue limit branch to the end of another branch, diminishing the limit branch to a single glucose residue . The α(16) glucosidase then catalyzes hydrolysis of the α(16) linkage by adding H2O, yielding ...
... fourth glucose from α (16) branch point The transferase transfers 3 glucose residues from a 4-residue limit branch to the end of another branch, diminishing the limit branch to a single glucose residue . The α(16) glucosidase then catalyzes hydrolysis of the α(16) linkage by adding H2O, yielding ...
File
... respiration. Oxygen enters the body when an organism breathes. Glucose enters the body when an organism eats. The Products What does the cell produce? The main product of cellular respiration is ATP. Waste products include carbon dioxide and water. Carbon dioxide is transported from your mitochondri ...
... respiration. Oxygen enters the body when an organism breathes. Glucose enters the body when an organism eats. The Products What does the cell produce? The main product of cellular respiration is ATP. Waste products include carbon dioxide and water. Carbon dioxide is transported from your mitochondri ...
E - ČVUT
... distances between NH and CO groups in the backbone of a particular protein. Hydrogen and oxygen in these polar groups are attracted by the van der Waals force, by the hydrogen ...
... distances between NH and CO groups in the backbone of a particular protein. Hydrogen and oxygen in these polar groups are attracted by the van der Waals force, by the hydrogen ...
Biomolecules
... • May contain different types of monosaccharides • They can be very large molecules ...
... • May contain different types of monosaccharides • They can be very large molecules ...
I - Decatur ISD
... A. Special proteins that speed chemical reactions 1. Chemical reactions require a certain _______________ to get started. 2. Enzymes decrease this energy, making reactions occur faster. B. Lock-and-Key Model 1. Enzymes are not used up by the reaction, but each can only work on one reaction ...
... A. Special proteins that speed chemical reactions 1. Chemical reactions require a certain _______________ to get started. 2. Enzymes decrease this energy, making reactions occur faster. B. Lock-and-Key Model 1. Enzymes are not used up by the reaction, but each can only work on one reaction ...
Light Independent
... - Uses ATP from light reaction and carbon dioxide from the air to make glucose. - Called the Calvin Cycle ...
... - Uses ATP from light reaction and carbon dioxide from the air to make glucose. - Called the Calvin Cycle ...
Glucose

Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. The name ""glucose"" (/ˈɡluːkoʊs/) comes from the Greek word γλευκος, meaning ""sweet wine, must"". The suffix ""-ose"" is a chemical classifier, denoting a carbohydrate. It is also known as dextrose or grape sugar. With 6 carbon atoms, it is classed as a hexose, a sub-category of monosaccharides. α-D-glucose is one of the 16 aldose stereoisomers. The D-isomer (D-glucose) occurs widely in nature, but the L-isomer (L-glucose) does not. Glucose is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. The reverse of the photosynthesis reaction, which releases this energy, is a very important source of power for cellular respiration. Glucose is stored as a polymer, in plants as starch and in animals as glycogen.