Carbohydrates - Ukiah Adult School
... how energy from carbohydrates, proteins, and fats is extracted and used. encompasses the processes of anabolism and catabolism that occur continuously as the body uses energy to synthesize compounds or extracts energy from the breakdown of nutrients from food or body ...
... how energy from carbohydrates, proteins, and fats is extracted and used. encompasses the processes of anabolism and catabolism that occur continuously as the body uses energy to synthesize compounds or extracts energy from the breakdown of nutrients from food or body ...
Absorption in the small intestine
... thick network of blood capillaries and small lymphatics. • The basal side of the cell rests on a very thin basement membrane, which is close to the basement membrane of the underlying capillary. ...
... thick network of blood capillaries and small lymphatics. • The basal side of the cell rests on a very thin basement membrane, which is close to the basement membrane of the underlying capillary. ...
28 Gluconeogenesis In animals, glucose is required by the brain
... circulating levels of glucose, additional glucose must be released from the liver. The liver has some glucose stored in the form of glycogen but these stores only last for about 12 hours in the absence of dietary glucose. Considerably before the glucose stores have been consumed, the organism must b ...
... circulating levels of glucose, additional glucose must be released from the liver. The liver has some glucose stored in the form of glycogen but these stores only last for about 12 hours in the absence of dietary glucose. Considerably before the glucose stores have been consumed, the organism must b ...
Chapter 3: The Chemistry of Organic Molecules
... • Carbohydrates: polymer = polysaccharide monomer= monosaccharide • Proteins: polymer= polypeptide monomer= amino acid • Nucleic acids: polymer= nucleic acid Monomer= nucleotide ...
... • Carbohydrates: polymer = polysaccharide monomer= monosaccharide • Proteins: polymer= polypeptide monomer= amino acid • Nucleic acids: polymer= nucleic acid Monomer= nucleotide ...
Metabolism of Glucose C6H12O6+6O2 1 unit of Glucose 38 ATP
... In exercise, first you burn off muscle glycogen, then liver glycogen, then lipid. If you only exercise In Diabetes, the cells cannot use glucose for energy. Only lipids. It depends on lipids, but the the Fatty Acids produce much more acetyl-CoA that kreb cycle cannot handle. This results in an accu ...
... In exercise, first you burn off muscle glycogen, then liver glycogen, then lipid. If you only exercise In Diabetes, the cells cannot use glucose for energy. Only lipids. It depends on lipids, but the the Fatty Acids produce much more acetyl-CoA that kreb cycle cannot handle. This results in an accu ...
How much ATP is produced in this cycle?
... NADP+ picks up two high-energy electrons, along with a hydrogen ion (H+). It is then converted into NADPH. The NADPH can then carry the high-energy electrons to be used in chemical reactions elsewhere in the cell. ...
... NADP+ picks up two high-energy electrons, along with a hydrogen ion (H+). It is then converted into NADPH. The NADPH can then carry the high-energy electrons to be used in chemical reactions elsewhere in the cell. ...
Chapter 27 Reproductive Endocrinology
... E from ETC used to pump H across membrane concentration gradient = potential E movt of H releases E ADP + P + E ATP ...
... E from ETC used to pump H across membrane concentration gradient = potential E movt of H releases E ADP + P + E ATP ...
Chapter 3: The Chemistry of Organic Molecules
... • Carbohydrates: polymer = polysaccharide monomer= monosaccharide • Proteins: polymer= polypeptide monomer= amino acid • Nucleic acids: polymer= nucleic acid Monomer= nucleotide ...
... • Carbohydrates: polymer = polysaccharide monomer= monosaccharide • Proteins: polymer= polypeptide monomer= amino acid • Nucleic acids: polymer= nucleic acid Monomer= nucleotide ...
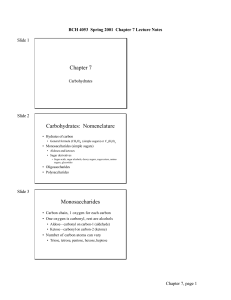
Chapter 7 Carbohydrates: Nomenclature Monosaccharides
... non-hydrogen atoms on the ring are in the equatorial position. That makes beta glucose more stable than alpha glucose, and the equilibrium mixture of the two contains more beta than alpha. Note we most commonly find glucose and other aldohexoses in the pyranose ring form, while fructose, a keto hexo ...
... non-hydrogen atoms on the ring are in the equatorial position. That makes beta glucose more stable than alpha glucose, and the equilibrium mixture of the two contains more beta than alpha. Note we most commonly find glucose and other aldohexoses in the pyranose ring form, while fructose, a keto hexo ...
Document
... Fermentation is used outside of the presence of oxygen. It is a series of reactions that convert NADH (from glycolysis) back into NAD+,allowing glycolysis to keep producing a small amount of ATP ...
... Fermentation is used outside of the presence of oxygen. It is a series of reactions that convert NADH (from glycolysis) back into NAD+,allowing glycolysis to keep producing a small amount of ATP ...
Homeostasis: Functions of the liver - mf011
... When the body has excess glucose, glycogenesis is the synthesis of glycogen from glucose that is stimulated in the presence of the pancreatic hormone insulin. Prevention of glucose from falling below the crucial level is performed by a process called glycogenolysis. Glycogenolysis is the catab ...
... When the body has excess glucose, glycogenesis is the synthesis of glycogen from glucose that is stimulated in the presence of the pancreatic hormone insulin. Prevention of glucose from falling below the crucial level is performed by a process called glycogenolysis. Glycogenolysis is the catab ...
Cellular Respiration Review Sheet
... 2. A cracker was burned and caused the temperature of 500g of water to increase by 4C. How many calories of energy were released from the cracker? How many kilocalories? 3. What does ATP stand for? What is the function of ATP? How does a cell make ATP? 4. What is the overall chemical equation for c ...
... 2. A cracker was burned and caused the temperature of 500g of water to increase by 4C. How many calories of energy were released from the cracker? How many kilocalories? 3. What does ATP stand for? What is the function of ATP? How does a cell make ATP? 4. What is the overall chemical equation for c ...
Principles of BIOCHEMISTRY
... • Muscles lack pyruvate dehydrogenase and cannot produce ethanol from pyruvate • Muscle lactate dehydrogenase converts pyruvate to lactate • This reaction regenerates NAD+ for use by glyceraldehyde 3phosphate dehydrogenase in glycolysis • Lactate formed in skeletal muscles during exercise is transpo ...
... • Muscles lack pyruvate dehydrogenase and cannot produce ethanol from pyruvate • Muscle lactate dehydrogenase converts pyruvate to lactate • This reaction regenerates NAD+ for use by glyceraldehyde 3phosphate dehydrogenase in glycolysis • Lactate formed in skeletal muscles during exercise is transpo ...
Biochemistry - El Camino College
... 1. ___________ - storage form of glucose in animals; stored in our ______ and muscle cells, broken down to glucose when needed 2. __________ - storage form of glucose in plants; stored in starch granules in plant cells, digested to __________ in our bodies 3. ___________ - main component of plant ce ...
... 1. ___________ - storage form of glucose in animals; stored in our ______ and muscle cells, broken down to glucose when needed 2. __________ - storage form of glucose in plants; stored in starch granules in plant cells, digested to __________ in our bodies 3. ___________ - main component of plant ce ...
Biological Chemistry
... molecules) covalently bonded together 1. ___________ - storage form of glucose in animals; stored in our ______ and muscle cells, broken down to glucose when needed 2. _______ (amylose) - storage form of glucose in plants; stored in starch granules in plant cells, digested to _______ in our bodies 3 ...
... molecules) covalently bonded together 1. ___________ - storage form of glucose in animals; stored in our ______ and muscle cells, broken down to glucose when needed 2. _______ (amylose) - storage form of glucose in plants; stored in starch granules in plant cells, digested to _______ in our bodies 3 ...
Synthesis of Fats, Proteins, and Carbohydrates Lab
... d. When a fat is made, 3 water molecules are also made (this is called a condensation reaction). Make the 3 water molecules by cutting out and gluing together the one H-H-H piece with three O-H pieces. Make sure to glue this piece onto the same sheet as the fat. e. Label your paper “Fat or Lipid” 3. ...
... d. When a fat is made, 3 water molecules are also made (this is called a condensation reaction). Make the 3 water molecules by cutting out and gluing together the one H-H-H piece with three O-H pieces. Make sure to glue this piece onto the same sheet as the fat. e. Label your paper “Fat or Lipid” 3. ...
Cellular Respiration
... • The mitochondria are the engines of our cells where sugar is burned for fuel and the exhaust is CO2 and H2O. ...
... • The mitochondria are the engines of our cells where sugar is burned for fuel and the exhaust is CO2 and H2O. ...
Chapter 5 - Ellis Benjamin
... molecule transfers P to ADP • Does not require oxygen (anaerobic) • Net gain of 2 ATPs • Results in 2 pyruvate and 2 NADH molecules per glucose that goes through glycolysis ...
... molecule transfers P to ADP • Does not require oxygen (anaerobic) • Net gain of 2 ATPs • Results in 2 pyruvate and 2 NADH molecules per glucose that goes through glycolysis ...
Ch 19 - Chemistry Courses: About
... • Looks allosteric, but this is monomeric enzyme • May be due to conformational change upon product release— stays in active state at high concentration of glucose ...
... • Looks allosteric, but this is monomeric enzyme • May be due to conformational change upon product release— stays in active state at high concentration of glucose ...
1.3.7 Metabolic Role of Biomolecules
... Metabolic = metabolism = all the chemical reactions in a cell Role = function/job or position/involvement Biomolecules = carbohydrates, fats, proteins Metabolic Role of Biomolecules = the function / job / involvement of carbohydrates, fats, proteins in the chemical reactions in cells making various ...
... Metabolic = metabolism = all the chemical reactions in a cell Role = function/job or position/involvement Biomolecules = carbohydrates, fats, proteins Metabolic Role of Biomolecules = the function / job / involvement of carbohydrates, fats, proteins in the chemical reactions in cells making various ...
Describe how cells are used in the production of
... • In the first stage glucose is broken down into pyruvic acid. • First stage is called glycolysis. • 2 molecules of ATP formed in the first stage. • Oxygen in not required for this stage. (maximum of two) • In this second stage pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide and water. • Second stag ...
... • In the first stage glucose is broken down into pyruvic acid. • First stage is called glycolysis. • 2 molecules of ATP formed in the first stage. • Oxygen in not required for this stage. (maximum of two) • In this second stage pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide and water. • Second stag ...
Chapter 9.5 and 9.6
... The cell doesn’t waste energy making more of a particular substance than it needs. The most common mechanism for this control is feedback inhibition: the end product of the anabolic pathway inhibits the enzyme that catalyzes an early step of the pathway Cellular respiration is controlled by all ...
... The cell doesn’t waste energy making more of a particular substance than it needs. The most common mechanism for this control is feedback inhibition: the end product of the anabolic pathway inhibits the enzyme that catalyzes an early step of the pathway Cellular respiration is controlled by all ...
CHO PPT
... SPARE THE USE OF PROTEINS FOR ENERGY:-when carbohydrates are not sufficient in our body to provide energy,protein breakdowwn itself to fullfill the requirement of carbohydrates HELPING IN PREVENTING KETOSIS:-In the absence of adequate cho large amount of ketone bodies are produced.The accumulation o ...
... SPARE THE USE OF PROTEINS FOR ENERGY:-when carbohydrates are not sufficient in our body to provide energy,protein breakdowwn itself to fullfill the requirement of carbohydrates HELPING IN PREVENTING KETOSIS:-In the absence of adequate cho large amount of ketone bodies are produced.The accumulation o ...
Extension worksheet – Option C - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... the active site to change so that the substrate cannot bind to it. Such inhibitors, if they bind reversibly, can act in end-product inhibition of metabolic reactions. End-product inhibition is an example of negative feedback. a ...
... the active site to change so that the substrate cannot bind to it. Such inhibitors, if they bind reversibly, can act in end-product inhibition of metabolic reactions. End-product inhibition is an example of negative feedback. a ...
Glucose

Glucose is a sugar with the molecular formula C6H12O6. The name ""glucose"" (/ˈɡluːkoʊs/) comes from the Greek word γλευκος, meaning ""sweet wine, must"". The suffix ""-ose"" is a chemical classifier, denoting a carbohydrate. It is also known as dextrose or grape sugar. With 6 carbon atoms, it is classed as a hexose, a sub-category of monosaccharides. α-D-glucose is one of the 16 aldose stereoisomers. The D-isomer (D-glucose) occurs widely in nature, but the L-isomer (L-glucose) does not. Glucose is made during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight. The reverse of the photosynthesis reaction, which releases this energy, is a very important source of power for cellular respiration. Glucose is stored as a polymer, in plants as starch and in animals as glycogen.