Exhibition of Undergraduate Research and Creative
... Apoptotic cell death is crucial for the normal development of animals. Apoptosis is a form of programmed cell death in which cell death is precisely regulated by a genetic program. Drosophila melanogaster has been extensively used as a model system to study the molecular bases of apoptosis. Reaper ( ...
... Apoptotic cell death is crucial for the normal development of animals. Apoptosis is a form of programmed cell death in which cell death is precisely regulated by a genetic program. Drosophila melanogaster has been extensively used as a model system to study the molecular bases of apoptosis. Reaper ( ...
The Major Transitions in Evolution
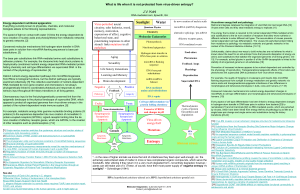
... prolonging vegetative development. b, Exposure to a long period of cold (that is, vernalization) results in the expression of VIN3 (red), which initiates repression of FLC transcription, and the binding of the PcG protein VRN2, as well as VRN1 and LHP1 (blue). In this process, chromatin at FLC is ep ...
... prolonging vegetative development. b, Exposure to a long period of cold (that is, vernalization) results in the expression of VIN3 (red), which initiates repression of FLC transcription, and the binding of the PcG protein VRN2, as well as VRN1 and LHP1 (blue). In this process, chromatin at FLC is ep ...
The Major Transitions in Evolution
... prolonging vegetative development. b, Exposure to a long period of cold (that is, vernalization) results in the expression of VIN3 (red), which initiates repression of FLC transcription, and the binding of the PcG protein VRN2, as well as VRN1 and LHP1 (blue). In this process, chromatin at FLC is ep ...
... prolonging vegetative development. b, Exposure to a long period of cold (that is, vernalization) results in the expression of VIN3 (red), which initiates repression of FLC transcription, and the binding of the PcG protein VRN2, as well as VRN1 and LHP1 (blue). In this process, chromatin at FLC is ep ...
2b Unit 5 Cell cycle notes
... o DNA is ____________________________ before division to insure that each daughter cell gets one complete set of genetic information o Problem of DNA overload and nutrient/waste exchange is solved. ...
... o DNA is ____________________________ before division to insure that each daughter cell gets one complete set of genetic information o Problem of DNA overload and nutrient/waste exchange is solved. ...
Epigenetic regulation of gene transcription. Publications
... The fundamental subunit of chromatin is the nucleosome, which consists of DNA wrapped around an octamer of four core histone proteins (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). Chromatin packages DNA within the cell and is repressive to any process which requires access to the DNA including DNA repair, replication, rec ...
... The fundamental subunit of chromatin is the nucleosome, which consists of DNA wrapped around an octamer of four core histone proteins (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). Chromatin packages DNA within the cell and is repressive to any process which requires access to the DNA including DNA repair, replication, rec ...
Leukaemia Section t(8;12)(q24;q22) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Iwai K, Hirata K, Ishida T, Takeuchi S, Hirase T, Rikitake Y, Kojima Y, Inoue N, Kawashima S, Yokoyama M. An antiproliferative gene BTG1 regulates angiogenesis in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004 Apr 9;316(3):628-35. ...
... Iwai K, Hirata K, Ishida T, Takeuchi S, Hirase T, Rikitake Y, Kojima Y, Inoue N, Kawashima S, Yokoyama M. An antiproliferative gene BTG1 regulates angiogenesis in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004 Apr 9;316(3):628-35. ...
Making Transgenic Plants and Animals
... progeny will be brown (which is dominant), indicating fertilization with a germ-line cell (gamete) that ultimately came from a KO-ES cell. Only about 50% of the brown progeny mice, however, will have the KO allele, because the transgenic ES cell that underwent meiosis to produce the germ-line cell w ...
... progeny will be brown (which is dominant), indicating fertilization with a germ-line cell (gamete) that ultimately came from a KO-ES cell. Only about 50% of the brown progeny mice, however, will have the KO allele, because the transgenic ES cell that underwent meiosis to produce the germ-line cell w ...
Sunlight Water Entropy
... adhesion proteins. For example, the ribosome links heat shock proteins to biophysically constrained nutrient energy-dependent RNA-mediated protein folding chemistry and cell type differentiation via supercoiled DNA in the context of the physiology of reproduction. [4] Distinct nutrient energy-depend ...
... adhesion proteins. For example, the ribosome links heat shock proteins to biophysically constrained nutrient energy-dependent RNA-mediated protein folding chemistry and cell type differentiation via supercoiled DNA in the context of the physiology of reproduction. [4] Distinct nutrient energy-depend ...
Laboratory of Insect Genetics and Biosciences (IGB) Dept. Biology
... I am sending you herewith enclosed the revised version of the review entitled “Cytosine methylation in insects: new routes for the comprehension of insect complexity” which we would like to submit for publication to the special issue “Chromatin and Epigenetics” of AIMS Biophysics. In the present ver ...
... I am sending you herewith enclosed the revised version of the review entitled “Cytosine methylation in insects: new routes for the comprehension of insect complexity” which we would like to submit for publication to the special issue “Chromatin and Epigenetics” of AIMS Biophysics. In the present ver ...
Chapter 21 The Genetic Control of Animal Development
... Combinatorial assembly of these allows production of 2,112,000 different antibodies. Even more antibodies are possible due to variation in recombination sites and hypermutability of the variable regions. ...
... Combinatorial assembly of these allows production of 2,112,000 different antibodies. Even more antibodies are possible due to variation in recombination sites and hypermutability of the variable regions. ...
Genetics and Genetic Engineering
... used to cut the DNA at specific sites cut ends of plasmid rings can accept pieces of DNA from other organisms ...
... used to cut the DNA at specific sites cut ends of plasmid rings can accept pieces of DNA from other organisms ...
Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology
... host cell (bacterium, yeast, or other cell), restriction enzymes (endonucleases), DNA ligase. Gene therapy: The treatment of certain diseases by introducing specific engineered genes in a patients cells. Vector: Is what is needed to carry the gene into the host cell; plasmids are often used as vecto ...
... host cell (bacterium, yeast, or other cell), restriction enzymes (endonucleases), DNA ligase. Gene therapy: The treatment of certain diseases by introducing specific engineered genes in a patients cells. Vector: Is what is needed to carry the gene into the host cell; plasmids are often used as vecto ...
THE ORGANIZATION AND CONTROL OF EUKARYOTIC GENOMES
... • Repressible enzymes usually used when cell makes something (ex. tryptophan) • Inducible enzymes usually used when cell breaks something down (ex. lactose) ...
... • Repressible enzymes usually used when cell makes something (ex. tryptophan) • Inducible enzymes usually used when cell breaks something down (ex. lactose) ...
Chapter 8
... Directions: Write questions and answer on a separate sheet of paper. Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs. a) histone, nonhistone b) chromatid, centromere c) sex chromosome, autosome d) diploid cell, haploid cell ...
... Directions: Write questions and answer on a separate sheet of paper. Distinguish between the terms in each of the following pairs. a) histone, nonhistone b) chromatid, centromere c) sex chromosome, autosome d) diploid cell, haploid cell ...
- Cal State LA - Instructional Web Server
... City of Hope Dr. Steven Smith Dr. Kristofer Munson Dr. Jarrod Clark Dr. Taras Schevchuck ...
... City of Hope Dr. Steven Smith Dr. Kristofer Munson Dr. Jarrod Clark Dr. Taras Schevchuck ...
Biology Fall 2013 Final Review
... 38. Describe the process of DNA replication (don’t forget about the enzymes involved!) ...
... 38. Describe the process of DNA replication (don’t forget about the enzymes involved!) ...
AMWA Plenary Session report
... Functionally, there are several types of stem cells with different capacities that give rise to differentiated cell types. The rule of thumb is that the more different cell types that a stem cell can give rise to, the earlier it comes in the lineage process—thus, totipotent stem cells can give rise ...
... Functionally, there are several types of stem cells with different capacities that give rise to differentiated cell types. The rule of thumb is that the more different cell types that a stem cell can give rise to, the earlier it comes in the lineage process—thus, totipotent stem cells can give rise ...
Mitosis
... held together by hydrogen bonds – Hydrogen bonds between two strands are easily broken ...
... held together by hydrogen bonds – Hydrogen bonds between two strands are easily broken ...
Introduction to the Cell Cycle Learning Objectives DNA
... held together by hydrogen bonds – Hydrogen bonds between two strands are easily broken – Each single strand then serves as template for new strand Where do the nucleotides to build new DNA come from? ...
... held together by hydrogen bonds – Hydrogen bonds between two strands are easily broken – Each single strand then serves as template for new strand Where do the nucleotides to build new DNA come from? ...
Grade 9 Science - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 2 single-stranded chromosomes at the end of each cell. The cell membrane begins to pinch together and new nuclear membranes form. There are 2 double stranded chromosomes at each end of the cell. There are 2 cells. In each, Double stranded chromosomes are pulled apart into singles stranded chromosome ...
... 2 single-stranded chromosomes at the end of each cell. The cell membrane begins to pinch together and new nuclear membranes form. There are 2 double stranded chromosomes at each end of the cell. There are 2 cells. In each, Double stranded chromosomes are pulled apart into singles stranded chromosome ...
MITOSIS COLORING HOMEWORK
... Cell division includes a very important process called MITOSIS where the nucleus creates a copy of all of its DNA so that each new cell is an exact copy of the parent cell and contains the exact same number of chromosomes. The cell cycle has five phases, but mitosis (nuclear) division occurs in four ...
... Cell division includes a very important process called MITOSIS where the nucleus creates a copy of all of its DNA so that each new cell is an exact copy of the parent cell and contains the exact same number of chromosomes. The cell cycle has five phases, but mitosis (nuclear) division occurs in four ...
File - Enders Science Page
... Match the Statements on the left with the correct Phase on the right. Each Phase may be used more than once. Statement ...
... Match the Statements on the left with the correct Phase on the right. Each Phase may be used more than once. Statement ...