Topic 1
... Metamorphosis - biological process by which an animal physically develops after birth or hatching that involves a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Various insects, amphibians, molluscs, crustaceans, Cnidarians, echinoder ...
... Metamorphosis - biological process by which an animal physically develops after birth or hatching that involves a conspicuous and relatively abrupt change in the animal's body structure through cell growth and differentiation. Various insects, amphibians, molluscs, crustaceans, Cnidarians, echinoder ...
Cell Structure and Function Student Notes
... • ___________ unicellular organisms and all multicellular organisms. • Cells that contain membrane bound __________. • The DNA is separated from the rest of the cell by a nucleus. • Much ______ than Prokaryotic cells. ...
... • ___________ unicellular organisms and all multicellular organisms. • Cells that contain membrane bound __________. • The DNA is separated from the rest of the cell by a nucleus. • Much ______ than Prokaryotic cells. ...
Chapter 6 and 9 - Wando High School
... 29. If a heterozygous organism (Rr) produces gametes, what are the chances that the gamete will have the dominant allele? 30. In humans, there is a gene that controls formation (or lack thereof) of muscles in the tongue that allow people with those muscles to roll their tongues, while people who lac ...
... 29. If a heterozygous organism (Rr) produces gametes, what are the chances that the gamete will have the dominant allele? 30. In humans, there is a gene that controls formation (or lack thereof) of muscles in the tongue that allow people with those muscles to roll their tongues, while people who lac ...
gene therapy - Thalassemia.com
... stem cells to become a permanent source of blood cells that grow and produce new cells with the functioning copy of the gene. ...
... stem cells to become a permanent source of blood cells that grow and produce new cells with the functioning copy of the gene. ...
Chromosomes
... • A single recognition site for the restriction enzyme AluI located near the middle of the Alu element. • Alu elements are found only in primates. • Human chromosomes contain about 1,000,000 Alu copies (10% of the total genome). • Alu is a "jumping gene" – a transposable DNA sequence that "reproduce ...
... • A single recognition site for the restriction enzyme AluI located near the middle of the Alu element. • Alu elements are found only in primates. • Human chromosomes contain about 1,000,000 Alu copies (10% of the total genome). • Alu is a "jumping gene" – a transposable DNA sequence that "reproduce ...
PPT lecture slides
... exhibited a defect in motility, suggesting that RhoB has a role in this process that is conditional on cell stress • FOG-2, in addition to GATA-4, has a role in early gonadal development and sexual differentiation, and FOG-1 at later fetal stages, while GATA-1 executes its action postnatally ...
... exhibited a defect in motility, suggesting that RhoB has a role in this process that is conditional on cell stress • FOG-2, in addition to GATA-4, has a role in early gonadal development and sexual differentiation, and FOG-1 at later fetal stages, while GATA-1 executes its action postnatally ...
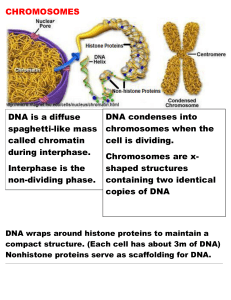
Chromosomes Notes
... spaghetti-like mass called chromatin during interphase. Interphase is the non-dividing phase. ...
... spaghetti-like mass called chromatin during interphase. Interphase is the non-dividing phase. ...
gene expression
... Composed of DNA and proteins called histones Nucloesome – DNA wrapped around a histone Forms looped domains Heterochromatin – highly compacted DNA so generally is not transcribed ...
... Composed of DNA and proteins called histones Nucloesome – DNA wrapped around a histone Forms looped domains Heterochromatin – highly compacted DNA so generally is not transcribed ...
Mitosis EXTRA CREDIT Study Guide
... 1. What happens to the ratio of volume to surface area, as a cells’ size increases? 2. Why are cells small? 3. Which cell would produce more waste: cell with a volume of 10cm3, or one with a surface area of 10cm2? Explain ...
... 1. What happens to the ratio of volume to surface area, as a cells’ size increases? 2. Why are cells small? 3. Which cell would produce more waste: cell with a volume of 10cm3, or one with a surface area of 10cm2? Explain ...
Cloning
... You might not believe it, but there are human clones among us right now. They weren't made in a lab, though: they're identical twins, created naturally. Mrs. Degl ...
... You might not believe it, but there are human clones among us right now. They weren't made in a lab, though: they're identical twins, created naturally. Mrs. Degl ...
Unit I Objectives
... 33. What is sickle cell disease? What gene is mutated? Is this inherited as a recessive, or a dominant trait? Why is sickle cell disease said to be an example of “pleiotropy”? 34. Why are skin color, intelligence, and height examples of polygenes? What type of curve suggests that a trait is inherite ...
... 33. What is sickle cell disease? What gene is mutated? Is this inherited as a recessive, or a dominant trait? Why is sickle cell disease said to be an example of “pleiotropy”? 34. Why are skin color, intelligence, and height examples of polygenes? What type of curve suggests that a trait is inherite ...
Biol115_2014_Lecture 12_Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
... To initiate transcription, eukaryotic RNA polymerase requires the assistance of proteins called transcription factors! ...
... To initiate transcription, eukaryotic RNA polymerase requires the assistance of proteins called transcription factors! ...
Editor(s): Laura Hoopes | http://www.nature.com/scitable/topic/gene
... But how, then, do eukaryotic genes manage to escape this silencing? This is where the histone code comes into play. This code includes modifications of the histones' positively charged amino acids to create some domains in which DNA is more open and others in which it is very tightly bound up. DNA m ...
... But how, then, do eukaryotic genes manage to escape this silencing? This is where the histone code comes into play. This code includes modifications of the histones' positively charged amino acids to create some domains in which DNA is more open and others in which it is very tightly bound up. DNA m ...
Sam Rhine Outline - Spring Branch ISD
... Forest University. If you want to use antibodies to stop leukemia caused by cancer stem cells you might want to do your residency in oncology at Stanford University. Keep your ‘antennae out’ during the four years of medical school - determine who is doing what you want to pursue for a career - and g ...
... Forest University. If you want to use antibodies to stop leukemia caused by cancer stem cells you might want to do your residency in oncology at Stanford University. Keep your ‘antennae out’ during the four years of medical school - determine who is doing what you want to pursue for a career - and g ...
TRANSPONSONS or TRANSPOSABLE ELEMENTS
... The RNAi machinery cuts up the dsRNA of the TE Fragile X syndrome is characterized by a triplet CCG repeat that is present in the 5’ untranslated region that expands in affected individuals. When this triplet repeat expands beyond a certain length the gene is silenced due to cytosine methylation of ...
... The RNAi machinery cuts up the dsRNA of the TE Fragile X syndrome is characterized by a triplet CCG repeat that is present in the 5’ untranslated region that expands in affected individuals. When this triplet repeat expands beyond a certain length the gene is silenced due to cytosine methylation of ...
CHAPTER 18 REGULATION OF GENE EXPRESSION I. Student
... Students may find it hard to grasp the idea of epigenetic inheritance. They may not understand how modifications to the chromosome that do not alter the sequence of bases can still be passed on to subsequent generations of offspring. ...
... Students may find it hard to grasp the idea of epigenetic inheritance. They may not understand how modifications to the chromosome that do not alter the sequence of bases can still be passed on to subsequent generations of offspring. ...
WARNING:
... Sexual Reproduction – the form of reproduction in which cells from two parents unite to form a zygote Meiosis – the process that reduces the number of chromosomes in reproductive cells Life Cycle – the series of distinct stages of life that most organisms grow and mature through Direct Development – ...
... Sexual Reproduction – the form of reproduction in which cells from two parents unite to form a zygote Meiosis – the process that reduces the number of chromosomes in reproductive cells Life Cycle – the series of distinct stages of life that most organisms grow and mature through Direct Development – ...
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression
... gives chromatin a looser structure transcription proteins have access to genes may be involved in transcription factors attaching to promoter site ...
... gives chromatin a looser structure transcription proteins have access to genes may be involved in transcription factors attaching to promoter site ...
Control of Development File
... Activity 3.15b How Cells become specialised • As cells become more differentiated , their structure becomes specialised; they have a restricted range of functions , or just one particular function . The proteins synthesised by the cell determines its structure and function. For instance, a ciliated ...
... Activity 3.15b How Cells become specialised • As cells become more differentiated , their structure becomes specialised; they have a restricted range of functions , or just one particular function . The proteins synthesised by the cell determines its structure and function. For instance, a ciliated ...
First Semester Final Exam Study Guide
... - Use the textbook, your notes, a friend (donʼt just copy), other science books, and the internet to answer these questions. - The answers can be in picture or graph form. You do not need complete sentences. - The answers should be on a separate piece of paper. - You should be done with this study g ...
... - Use the textbook, your notes, a friend (donʼt just copy), other science books, and the internet to answer these questions. - The answers can be in picture or graph form. You do not need complete sentences. - The answers should be on a separate piece of paper. - You should be done with this study g ...
Abstract book - SciLifeLab Science Summit 2016
... Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology & Molecular Cell Biology and ...
... Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology & Molecular Cell Biology and ...
Prokaryotes
... exact characterisitcs of the parent cell. (In fact, the cell essentially replicates itself according to its own DNA and then divides itself from the newly created cell.) Since the Prokaryotes exhibit this asexual behavior as opposed to sexual behavior, where a recombination of chromosones occur to f ...
... exact characterisitcs of the parent cell. (In fact, the cell essentially replicates itself according to its own DNA and then divides itself from the newly created cell.) Since the Prokaryotes exhibit this asexual behavior as opposed to sexual behavior, where a recombination of chromosones occur to f ...