Notes
... front to back, it divides the body into ______ _____ ______sides transverse – refers to a cut that divides the body into _________ ____ ______ portions Coronal (frontal) – lengthwise plane running from side to side, it divides the body into front _________ _____ ___________ portions ...
... front to back, it divides the body into ______ _____ ______sides transverse – refers to a cut that divides the body into _________ ____ ______ portions Coronal (frontal) – lengthwise plane running from side to side, it divides the body into front _________ _____ ___________ portions ...
Notes-text only
... A frontal or coronal section divides the body (or organ) into anterior and posterior parts A transverse, or cross, section divides the body (or organ) into superior and inferior parts ...
... A frontal or coronal section divides the body (or organ) into anterior and posterior parts A transverse, or cross, section divides the body (or organ) into superior and inferior parts ...
10 great views inside the human body
... The renal arteries of the circulatory system deliver blood to the kidneys. The kidneys remove waste from the blood; this waste then passes into the renal pelvis and to the ureters. ...
... The renal arteries of the circulatory system deliver blood to the kidneys. The kidneys remove waste from the blood; this waste then passes into the renal pelvis and to the ureters. ...
Organ System Overview
... through the body from mouth to anus. The organs of the digestive system include the oral cavity (mouth), esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, and rectum. Their role is to break down food and deliver the products to the blood for dispersal to the body cells. The undigested food that remain ...
... through the body from mouth to anus. The organs of the digestive system include the oral cavity (mouth), esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, and rectum. Their role is to break down food and deliver the products to the blood for dispersal to the body cells. The undigested food that remain ...
Human Anatomy and Physiologych1newupdatefixed
... • The goal of most body systems is to __________________.These fragile ____________________ include the following: – 1-_______________---body takes in as food and chemical reactions release energy from it using O2.Carb’s are the main energy source…..Proteins provide nutrients and fats build cell str ...
... • The goal of most body systems is to __________________.These fragile ____________________ include the following: – 1-_______________---body takes in as food and chemical reactions release energy from it using O2.Carb’s are the main energy source…..Proteins provide nutrients and fats build cell str ...
Human Anatomy and Physiologych12014newupdatefixed
... • The goal of most body systems is to __________________.These fragile ____________________ include the following: – 1-_______________---body takes in as food and chemical reactions release energy from it using O2.Carb’s are the main energy source…..Proteins provide nutrients and fats build cell str ...
... • The goal of most body systems is to __________________.These fragile ____________________ include the following: – 1-_______________---body takes in as food and chemical reactions release energy from it using O2.Carb’s are the main energy source…..Proteins provide nutrients and fats build cell str ...
Organization of the Body
... 1. Right hypochondriac – right lobe of liver, gallbladder 2. Epigastric – right and left lobes of liver, stomach 3. Left hypochondriac – stomach, large intestine 4. Right lumbar – large and small intestine ...
... 1. Right hypochondriac – right lobe of liver, gallbladder 2. Epigastric – right and left lobes of liver, stomach 3. Left hypochondriac – stomach, large intestine 4. Right lumbar – large and small intestine ...
Medical Terminology - Porterville College
... – To convert food particles into simpler, molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body ...
... – To convert food particles into simpler, molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body ...
How do we see - Austin Community College
... _____ pineal gland (also called pineal body) (PIH nē-ahl OR PĪ-neahl) (This is a coneshaped gland located in the posterior portion of the roof of the diencephalon. Functions: secretes melatonin, promotes sleep, helps set the body’s biological clock and may be involved in mood and timing the onset of ...
... _____ pineal gland (also called pineal body) (PIH nē-ahl OR PĪ-neahl) (This is a coneshaped gland located in the posterior portion of the roof of the diencephalon. Functions: secretes melatonin, promotes sleep, helps set the body’s biological clock and may be involved in mood and timing the onset of ...
THE UNITY AND DIVERSITY OF LIFE
... • 1. Thoracic cavity – separated from rest of ventral cavity by diaphragm surrounded by ribs houses heart, lungs 2. Abdominopelvic a. abdominal – superior cavity houses stomach, liver, intestines b. Pelvic – inferior cavity houses reproductive organs, bladder, ...
... • 1. Thoracic cavity – separated from rest of ventral cavity by diaphragm surrounded by ribs houses heart, lungs 2. Abdominopelvic a. abdominal – superior cavity houses stomach, liver, intestines b. Pelvic – inferior cavity houses reproductive organs, bladder, ...
5-9_HypothalamicHormones_SzentgyorgyiR
... The function of the hypothalamic hormones The hypothalamus: The hypothalamus is a small but complex region of the brain located below the thalamus and right above the brain stem. It has links with both the nervous system as well as the endocrine system. Its main role is to maintain the internal bala ...
... The function of the hypothalamic hormones The hypothalamus: The hypothalamus is a small but complex region of the brain located below the thalamus and right above the brain stem. It has links with both the nervous system as well as the endocrine system. Its main role is to maintain the internal bala ...
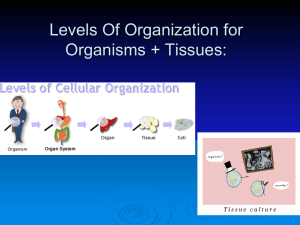
Levels Of Organization - Sterlingmontessoriscience
... Though all cells perform the processes that keep humans alive, they also have specialized functions as well. Examples may be nerve cells (neurons), blood cells, and bone cells. ...
... Though all cells perform the processes that keep humans alive, they also have specialized functions as well. Examples may be nerve cells (neurons), blood cells, and bone cells. ...
Introduction – Chapter I
... parietal pericardium – also surrounds heart pericardial cavity – potential space between 3. In abdominopelvic cavity: parietal peritoneum – lines wall of cavity “to the side” “stretch around” visceral peritoneium – covers organs peritoneal cavity – potential space within ...
... parietal pericardium – also surrounds heart pericardial cavity – potential space between 3. In abdominopelvic cavity: parietal peritoneum – lines wall of cavity “to the side” “stretch around” visceral peritoneium – covers organs peritoneal cavity – potential space within ...
Human Nervous System
... • There is a network of sensory neurons that transmit information from the sensory receptors in the body to the CNS. • There are also motor neurons that carry information from the CNS to the muscles that will carry out the action. (See Neuron powerpoint for more information about neurons) ...
... • There is a network of sensory neurons that transmit information from the sensory receptors in the body to the CNS. • There are also motor neurons that carry information from the CNS to the muscles that will carry out the action. (See Neuron powerpoint for more information about neurons) ...
Muscular System Rocks!
... is movement. Muscles are the only tissue in the body that has the ability to contract and therefore move the other parts of the body. The muscular systems second function: the maintenance of posture and body position. ...
... is movement. Muscles are the only tissue in the body that has the ability to contract and therefore move the other parts of the body. The muscular systems second function: the maintenance of posture and body position. ...
Advanced Human Anatomy Score: ____/10
... 1. Three fluid-filled channels in the inner ear; provide information about orientation to the brain to help maintain balance 2. Fluid found within the tympanic and vestibular canals of the cochlea 3. Malleus, incus, stapes; smallest bones of the human body located in the middle ear 5. Membrane cover ...
... 1. Three fluid-filled channels in the inner ear; provide information about orientation to the brain to help maintain balance 2. Fluid found within the tympanic and vestibular canals of the cochlea 3. Malleus, incus, stapes; smallest bones of the human body located in the middle ear 5. Membrane cover ...
The Human Body: Anatomical Regions, Directions, and Body
... • Transverse or horizontal (cross section) – divides the body into superior and inferior parts • Oblique section – cuts made diagonally ...
... • Transverse or horizontal (cross section) – divides the body into superior and inferior parts • Oblique section – cuts made diagonally ...
ch1-notes - WordPress.com
... Chapter 1 – The Human Organism Anatomy Focuses on the structure of the body Latin for “dissect” or “cut up” Covers a wide range of studies including: Structure of body parts Microscopic organization Development processes There are two different approaches to anatomy Systemic - organization of the bo ...
... Chapter 1 – The Human Organism Anatomy Focuses on the structure of the body Latin for “dissect” or “cut up” Covers a wide range of studies including: Structure of body parts Microscopic organization Development processes There are two different approaches to anatomy Systemic - organization of the bo ...
Certificate in Human Biology
... how they interact with each other, as well as the tissues that form them. It does not consider how parts of the body function; what they do, this is the field of physiology. Anatomy is and was the starting point of scientific investigation of the human body. Without an understanding of structure we ...
... how they interact with each other, as well as the tissues that form them. It does not consider how parts of the body function; what they do, this is the field of physiology. Anatomy is and was the starting point of scientific investigation of the human body. Without an understanding of structure we ...
Anatomy and Physiology Notes
... • formed by skull – vertebral or spinal canal • contains the spinal cord • formed by vertebral column Meninges line dorsal body cavity ...
... • formed by skull – vertebral or spinal canal • contains the spinal cord • formed by vertebral column Meninges line dorsal body cavity ...
Intro to Human Body
... o Thoracic Cavity: above diaphragm o Abdominopelvic Cavity: below diaphragm ● Diaphragm = large, dome-shaped muscle ● Organs called viscera ...
... o Thoracic Cavity: above diaphragm o Abdominopelvic Cavity: below diaphragm ● Diaphragm = large, dome-shaped muscle ● Organs called viscera ...
Head and neck anatomy

This article describes the anatomy of the head and neck of the human body, including the brain, bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, glands, nose, mouth, teeth, tongue, and throat.