intro to anatomy activities
... 4. Label the anterior & posterior diagrams with body directional terms. Be creative and be sure to include: anterior, posterior, cranial, caudal, proximal, distal, superior, inferior, medial, lateral, ventral, dorsal, transverse, coronal, sagittal, frontal, midsagittal, 5. Label the body cavities: c ...
... 4. Label the anterior & posterior diagrams with body directional terms. Be creative and be sure to include: anterior, posterior, cranial, caudal, proximal, distal, superior, inferior, medial, lateral, ventral, dorsal, transverse, coronal, sagittal, frontal, midsagittal, 5. Label the body cavities: c ...
Introduction to Health Occupations Midterm Exam Study Guide
... Human cell reproduces, grows, repairs itself, uses oxygen and nutrients, digests food, eliminates waste, produces heat and energy, and is able to move around Cells combine to form tissue Ventral cavities of the body include the thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic cavities. Caudal means near the ...
... Human cell reproduces, grows, repairs itself, uses oxygen and nutrients, digests food, eliminates waste, produces heat and energy, and is able to move around Cells combine to form tissue Ventral cavities of the body include the thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic cavities. Caudal means near the ...
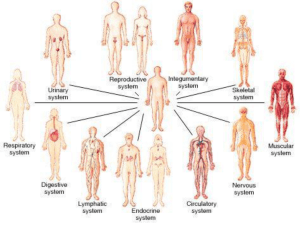
Body Systems
... ***Sagittal plane: divides body into right and left parts ***Coronal (frontal) plane: vertical cut at right angles to sagittal plane. Divides body into anterior & posterior (front & back) ***Transverse: horizontal cut that divides body into upper and lower parts ...
... ***Sagittal plane: divides body into right and left parts ***Coronal (frontal) plane: vertical cut at right angles to sagittal plane. Divides body into anterior & posterior (front & back) ***Transverse: horizontal cut that divides body into upper and lower parts ...
Principle Cavities of the Body
... tissue fluid back to the bloodstream and carries certain fatty substances away from the digestive organs and into the bloodstream. They defend the body against infections by removing disease-causing microorganisms and viruses from tissue fluid. ...
... tissue fluid back to the bloodstream and carries certain fatty substances away from the digestive organs and into the bloodstream. They defend the body against infections by removing disease-causing microorganisms and viruses from tissue fluid. ...
Exercise 2 body systems and muscles - PCC
... Nervous System • Structures: Brain, Spinal cord, peripheral nerves and sense organs. • Function: • Fast-acting control system of the body • Coordinates body regions, interprets environmental cues, and integrates information ...
... Nervous System • Structures: Brain, Spinal cord, peripheral nerves and sense organs. • Function: • Fast-acting control system of the body • Coordinates body regions, interprets environmental cues, and integrates information ...
First Human Body Test Review
... facing space, either outside or around internal space. EX: Forms many linings giving protection and containment on inside and outside of structures such as the skin, organs, and body cavities. • Connective – functions to bind and support other tissues. Cells in connective tissue are always surrounde ...
... facing space, either outside or around internal space. EX: Forms many linings giving protection and containment on inside and outside of structures such as the skin, organs, and body cavities. • Connective – functions to bind and support other tissues. Cells in connective tissue are always surrounde ...
The Human Body: Anatomical Regions, Directions, and Body Cavities
... and back of the body Medial, lateral, and intermediate – toward the midline, away from the midline, and between a more medial and lateral structure ...
... and back of the body Medial, lateral, and intermediate – toward the midline, away from the midline, and between a more medial and lateral structure ...
The Central Nervous System
... The Diencephalon or Interbrain o Sits on top of the brain stem and is enclosed by the cerebral hemispheres. o Composed of three main parts: Thalamus, epithalamus, and hypothalamus Thalamus- A relay station for impulses, allows us to recognize a sensation as pleasant or unpleasant, the impulse is e ...
... The Diencephalon or Interbrain o Sits on top of the brain stem and is enclosed by the cerebral hemispheres. o Composed of three main parts: Thalamus, epithalamus, and hypothalamus Thalamus- A relay station for impulses, allows us to recognize a sensation as pleasant or unpleasant, the impulse is e ...
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY INTRO NOTES
... B. Skeletal (bone, ligaments, and cartilage) support levers for muscles to attach protection mineral storage (calcium) blood production C. Muscular (skeletal muscles and associated tendons) movement/heat production maintaining posture facial expressions protection and support of ot ...
... B. Skeletal (bone, ligaments, and cartilage) support levers for muscles to attach protection mineral storage (calcium) blood production C. Muscular (skeletal muscles and associated tendons) movement/heat production maintaining posture facial expressions protection and support of ot ...
Tissue Types File
... o protection o movement (with muscles) o storage of minerals o hematopoiesis (blood formation) ...
... o protection o movement (with muscles) o storage of minerals o hematopoiesis (blood formation) ...
HERE
... Lymph nodes • Lymph nodes are filled with white blood cells. • Lymph nodes are located throughout the body and swell when you’re fighting an infection because they work harder and collect dead cells. • The main job of the lymph nodes is to filter the lymph (clear fluid that comes from tissues) by ...
... Lymph nodes • Lymph nodes are filled with white blood cells. • Lymph nodes are located throughout the body and swell when you’re fighting an infection because they work harder and collect dead cells. • The main job of the lymph nodes is to filter the lymph (clear fluid that comes from tissues) by ...
Anatomical Position NOTES
... Medial – “toward the body’s midline” Lateral – “away from the body’s midline” Proximal – “close to the point of attachment” Distal – “away from the point of attachment” Superficial (external) – “close to the body surface” Deep (internal) – “deep within the body” ...
... Medial – “toward the body’s midline” Lateral – “away from the body’s midline” Proximal – “close to the point of attachment” Distal – “away from the point of attachment” Superficial (external) – “close to the body surface” Deep (internal) – “deep within the body” ...
Skeletal, Muscular, Respiratory, Digestive and Urinary
... Define homeostasis - A state of balance List the three main functions of the skeletal system. 1. Serves as an anchor for all the body’s movement 2. Provides support 3. Protects soft organs inside of the body List the three main parts of bone and the functions of each. 1. Compact – hard layer of outs ...
... Define homeostasis - A state of balance List the three main functions of the skeletal system. 1. Serves as an anchor for all the body’s movement 2. Provides support 3. Protects soft organs inside of the body List the three main parts of bone and the functions of each. 1. Compact – hard layer of outs ...
Human Systems The Integumentary System protects the body from
... The Nervous System transmits signals throughout the body. It is defined by a cell known as a ____________ or nerve cell. ...
... The Nervous System transmits signals throughout the body. It is defined by a cell known as a ____________ or nerve cell. ...
HSI 1.01 Body Systems
... contains brain and spinal cord – the brain is in the CRANIAL CAVITY and the spinal cord is in the ...
... contains brain and spinal cord – the brain is in the CRANIAL CAVITY and the spinal cord is in the ...
Regional Terms in Anatomy
... SAGITTAL SECTION Cut lengthwise dividing into right and left parts ...
... SAGITTAL SECTION Cut lengthwise dividing into right and left parts ...
Post-test review - Plain Local Schools
... Capillaries – are the smallest ______, have _____ walls, which allow for? Heart diagram – 4 chambers, 4 valves, vena cavas, aorta, pulmonary arteries/veins Blood flow through the heart Lymphatic system – it transports excess fluid to the bloodstream, absorbs fats, and protects against disease-causin ...
... Capillaries – are the smallest ______, have _____ walls, which allow for? Heart diagram – 4 chambers, 4 valves, vena cavas, aorta, pulmonary arteries/veins Blood flow through the heart Lymphatic system – it transports excess fluid to the bloodstream, absorbs fats, and protects against disease-causin ...
Introduction to Anatomy
... Adeno- gland. Adenoid is a lymph gland found in the nasopharynx. Alba- white. Albinsm is the white appearance of skin lacking melanin. Algia- pain. Neuroalgia is a pain following the course of a nerve. Angi- vessel. Angioplasty is the repair of a blood vessel. Arthro- joint. Arthritis is the inflamm ...
... Adeno- gland. Adenoid is a lymph gland found in the nasopharynx. Alba- white. Albinsm is the white appearance of skin lacking melanin. Algia- pain. Neuroalgia is a pain following the course of a nerve. Angi- vessel. Angioplasty is the repair of a blood vessel. Arthro- joint. Arthritis is the inflamm ...
Anatomy 1
... Adeno- gland. Adenoid is a lymph gland found in the nasopharynx. Alba- white. Albinsm is the white appearance of skin lacking melanin. Algia- pain. Neuroalgia is a pain following the course of a nerve. Angi- vessel. Angioplasty is the repair of a blood vessel. Arthro- joint. Arthritis is the inflamm ...
... Adeno- gland. Adenoid is a lymph gland found in the nasopharynx. Alba- white. Albinsm is the white appearance of skin lacking melanin. Algia- pain. Neuroalgia is a pain following the course of a nerve. Angi- vessel. Angioplasty is the repair of a blood vessel. Arthro- joint. Arthritis is the inflamm ...
Human Anatomy
... o Gross anatomy is the study of structures that are visible to the naked eye Surface anatomy is limited to ________________ structures Radiologic anatomy is the study of internal structures, using Xrays, etc. o Microscopic anatomy is the study of the body under a microscope Histology is the st ...
... o Gross anatomy is the study of structures that are visible to the naked eye Surface anatomy is limited to ________________ structures Radiologic anatomy is the study of internal structures, using Xrays, etc. o Microscopic anatomy is the study of the body under a microscope Histology is the st ...
big ideas - Hobbs High School
... 1. General functions of the nervous system – action potential, sodium-potassium pump, etc. 2. Neuroglial Cells and their functions (Oligodendrocyte, astrocyte, microglial cells) 3. Anatomy of a neuron (axon, dendrite, etc.) 4. Number of cranial and spinal nerves 5. Synapses & Neurotransmitters 6. Me ...
... 1. General functions of the nervous system – action potential, sodium-potassium pump, etc. 2. Neuroglial Cells and their functions (Oligodendrocyte, astrocyte, microglial cells) 3. Anatomy of a neuron (axon, dendrite, etc.) 4. Number of cranial and spinal nerves 5. Synapses & Neurotransmitters 6. Me ...
Ativity 1, 2, 3 - PCC - Portland Community College
... • Structures: • Oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, gallbladder ...
... • Structures: • Oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, gallbladder ...
nervous system
... • The endocrine system is made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical substances produced in the body that regulate the activity of cells or organs – “chemical messengers”). These hormones regulate the body's growth, metabolism, and sexual development and function. The hormones ar ...
... • The endocrine system is made up of glands that produce and secrete hormones (chemical substances produced in the body that regulate the activity of cells or organs – “chemical messengers”). These hormones regulate the body's growth, metabolism, and sexual development and function. The hormones ar ...
The Endocrine System
... tissues or organs – called target cells or target tissues The target cell or target tissue has a specific proteins that allows the hormone to attach to ...
... tissues or organs – called target cells or target tissues The target cell or target tissue has a specific proteins that allows the hormone to attach to ...
Unit 1
... (ex) proton (ex) hydrogen atom (ex) water molecule (ex) DNA (ex) nucleus (ex) muscle cell (ex) connective tissue (ex) heart (ex) digestive system (ex) human ...
... (ex) proton (ex) hydrogen atom (ex) water molecule (ex) DNA (ex) nucleus (ex) muscle cell (ex) connective tissue (ex) heart (ex) digestive system (ex) human ...
Head and neck anatomy

This article describes the anatomy of the head and neck of the human body, including the brain, bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, glands, nose, mouth, teeth, tongue, and throat.