* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Principle Cavities of the Body
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
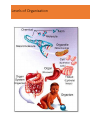
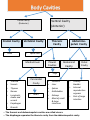
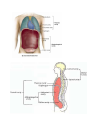
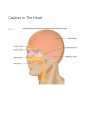
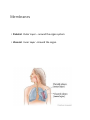
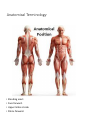
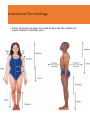
Anatomy and Physiology •Anatomy deals with the structure of the body and its parts •Physiology studies the functions of these parts Levels of Organization Level Explanation Example Atom Smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of the element. Oxygen, carbon , hydrogen Molecule a group atoms held together by a chemical bond. Water, glucose Macromolecule a group molecules held together by a chemical bond. Proteins, complex carbohydrates Organelle a structure in a cell that has a specialized function ribosome Cell Smallest unit of life skin cell, red blood cell Tissue Groups of cells with similar functions. Muscle, epithelial, connective Organ Two or more types of tissue working together to complete a specific task Heart, stomach Organ System A group of organs that carries out a more generalized set of functions Digestive, reproductive, Organism The Creator’s symphony of organ systems You functioning together. In one living unit. Characteristics of Life Metabolism is the sum total of all the chemical reactions in the body that break down and build up substances. o1. Movement o2. Responsiveness o3. Growth o4. Reproduction o5. Respiration o6. Digestion o7. Absorption o8. Circulation o9. Assimilation o10. Excretion Staying Alive Life depends on the availability of the following: oWater oFoods oOxygen oHeat oPressure Both the quality and quantity of these are important. Homeostasis Maintenance of a stable internal environment is called homeostasis. Receptors: provide info about stimuli/conditions in the internal environment. Set Point: tells what that that particular value should be. Effectors: responses that alter conditions in internal environment. Feedback Systems Negative Feedback Loop: Restores stable conditions. Most feedback mechanisms in the body are negative. Examples include temperature and blood pressure regulation. Positive Feedback Loop. Produces unstable conditions (so they are short lived). Examples are blood clotting and contractions during child birth. Video link: http://www.bozemanscience.com/positive-andnegative-feedback-loops Negative Feedback Loop Receptors: causes the response that alters the conditions in the internal environment to maintain homeostasis Effector: An organ that acts in response. Set Point: tells what that that particular value should be Stimulus: An action that evokes a response. Body Cavities Dorsal Cavity Ventral Cavity (Anterior) (Posterior) Cranial Cavity • brain • Spinal cord Mediastinum Pleural Cavities • • • • • • • • Trachea Vessels Thymus Nerves Lymphatic nodes and vessels Esophagus Bronchi Abdominopelvic Cavity Thoracic Cavity Vertebral Cavity Pericardial Cavity • heart • • • • • • Abdominal Cavity Pelvic Cavity lungs Stomach Liver Spleen Gallbladder Kidneys Most of small & large intestines • • • Urinary bladder Internal reproductive orgnans Part of large intestine o The thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities are called viscera. o The diaphragm separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity. Cavities In The Head Membranes • Parietal: Outer Layer – around the organ system • Visceral: Inner Layer - Around the organ. Body Systems Integumentary • Organs: skin, hair, nails, sweat glands, sebaceous glands •Functions: protect underlying tissue, help regulate body temperature, house a variety of sensory receptors, and synthesize certain products. Skeletal • Organs: bones, ligaments, cartilages. • Functions: provide framework and protective shields for softer tissues, are attachments for muscles, and act with muscles when body parts move. Muscular •Organs: muscles •Functions: move body parts, help maintain posture, and are the main source of body heat. Nervous • Organs: brain, spinal cord, nerves, and sense organs. • Functions: receive and interpret information outside the body, and respond to that information. Endocrine •Organs: glands that secrete hormones including the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal glands, pancreas, ovaries, testes, pineal gland, and thymus. •Functions: regulates hormones. Cardiovascular •Organs: heart, arteries, veins, capillaries, and blood •Functions: transports gases, nutrients, hormones, and wastes Lymphatic • Organs: lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, thymus, spleen, and “lymph” •Functions: transports some of the tissue fluid back to the bloodstream and carries certain fatty substances away from the digestive organs and into the bloodstream. They defend the body against infections by removing disease-causing microorganisms and viruses from tissue fluid. Digestive •Organs: mouth, tongue, teeth, salivary glands, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, small intestine, large intestine. •Functions: absorb nutrients and oxygen and excrete various wastes Respiratory • Organs: nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs • Functions: move air in and out and exchange gases between the blood and the air. Urinary •Organs: kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra • Functions: remove waste, store urine, maintain water and electrolyte concentrations and acidity. Reproductive •Organs: male: scrotum, testes, prostrate gland, penis, urethra, etc. • Female: ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, vagina, clitoris, vulva • Functions: produces whole new organisms Anatomical Terminology • Standing erect. • Face forward. • Upper limbs at side. • Palms forward. Anatomical Terminology • Terms of relative position are used to describe the location of a part relative to another part Superior: A body part is above another part. Inferior: Opposite of superior. A body part is below another part. Anterior: Means the same as ventral in humans. Towards the front. Posterior: Means the same as dorsal in humans. Towards the back. Medial: Towards the midline. Lateral: Towards the side (away from midline). Proximal: Is in reference to another part. It means closer to the point of origin. Distal: Is the opposite of proximal. It means farther from the point of origin. Superficial: Situated near to the surface. Deep: Situated far from the surface. Body Sections Sagittal: Divides the body into right and left portions. Mid sagittal: centrally divides body into equal left and right portions. Transverse (horizontal): Divides the body into superior and inferior portions. Frontal (coronal): A coronal section divides the body into anterior and posterior portions.