* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Anatomical Position NOTES
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
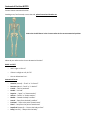
Anatomical Position NOTES Correct Human Anatomical Position Standing erect, face forward, arms at the side, palms forward and thumbs out. Notice the Parallel bones in the Forearm when in the correct anatomical position When do you reference the Correct Anatomical Position? RIGHT and LEFT • Who’s right or left is it? • If there is a Right or Left, PUT IT! • You can abbreviate R or L Anatomical Terms • • • • • • • • • • • • Anterior (ventral) – “front” or “in front of” Posterior (dorsal – “back” or “in back of” Cranial – “skull or head end” Caudal – “tail end” Superior – “upper” or “above another” Inferior – “below” or “below another” Medial – “toward the body’s midline” Lateral – “away from the body’s midline” Proximal – “close to the point of attachment” Distal – “away from the point of attachment” Superficial (external) – “close to the body surface” Deep (internal) – “deep within the body” Body Cavities • • Posterior (dorsal) cavity – Cranial cavity – Spinal cavity Anterior (ventral) cavity – Thoracic cavity • Pleural cavity – right and left lungs • Pericardial cavity - heart • Mediastinum – esophagus, trachea, thymus gland – Abdominopelvic cavity • Abdominal cavity – stomach, liver, gallbladder small and large intestine, pancreas, spleen, appendix • Pelvic cavity – urinary bladder, reproductive organs, rectum Body Planes • • • Sagittal plane – divides the body into right and left Frontal plane – divides the body into front and back Transverse plane – divides the body into top and bottom Hierarchy • • • • Cells Tissues – made up of a group of specialized cells Organs – made up of a group of specialized tissues Organ systems – group of organs used together to carry out specialized functions. – example: Digestive system – made up of teeth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestine Metabolism • • Anabolism – the building up of complex materials from simpler ones… such as proteins from components of cells. Catabolism – the breaking down and changing of complex substances into simpler ones… such as in the formation of energy Homeostasis • • The body’s ability to maintain itself in a steady state. This occurs through POSITIVE and NEGATIVE feedback mechanisms. Serous Membranes • Parietal – lines the cavity wall • Visceral – lines the organ • Pericardium - heart • Pleura – R & L Lungs • Peritoneum – Abdominal Cavity Retroperitoneal – behind the peritoneum Organs • • • • • • • • • • • • • Heart Lungs Diaphragm Stomach Liver Gallbladder Duodenum Small Intestine (duodenum, jejunum, ileum) Large Intestine (ascending, transverse, descending, sigmoid colon) Spleen Pancreas Urinary Bladder R & L Kidney