* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Murder for body parts wikipedia , lookup
Body Worlds wikipedia , lookup
Body snatching wikipedia , lookup
History of anatomy wikipedia , lookup
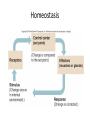
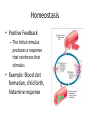
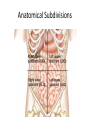
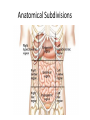
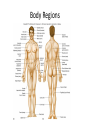
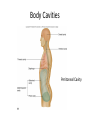
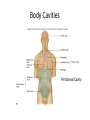
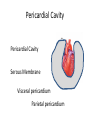
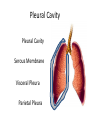
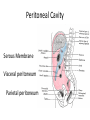
HAP Chapter 1 Anatomy and Physiology • Anatomy – study of structure (appearances, locations and relationships of body parts). (Greek – “a cutting up”) • Physiology – study of function (Greek – “relationship to nature”) Theme: Structure determines function Theme: Homeostasis • Body’s maintenance of a stable internal environment • Homeostatic Mechanisms – monitor aspects of the internal environment and correct any changes – Receptors - provide information about stimuli – Control center - tells what a particular value should be (includes a set point) – Effectors - elicit responses that change conditions in the internal environment Homeostasis Homeostasis • Negative Feedback – A Variation outside the normal limits triggers an automatic response that corrects the situation • Example: Temperature regulation Homeostasis • Positive Feedback – The initial stimulus produces a response that reinforces that stimulus • Example: Blood clot formation, child birth, histamine response Disease • When homeostatic regulation fails, organ systems begin to malfunction, and the individual experiences symptoms of illness. Anatomical Terminology • Anatomical Position – standing erect, facing forward, upper limbs at the sides, palms facing forward Terms of Relative Position – Superior versus Inferior – Anterior versus Posterior – Medial versus Lateral – Proximal versus Distal – Superficial versus Deep Body Sections Sections of Cylindrical Organs • Cross Section • Oblique Section • Longitudinal Section Anatomical Subdivisions Anatomical Subdivisions Body Regions Body Cavities Peritoneal Cavity Body Cavities Peritoneal Cavity 3 Serous membranes in the body cavities Pericardium Pleura Peritoneum Describe Location Two terms to describe positions of membranes Visceral (Surrounds the organ) Parietal (Lines the cavity) Pericardial Cavity Pericardial Cavity Serous Membrane Visceral pericardium Parietal pericardium Pleural Cavity Pleural Cavity Serous Membrane Visceral Pleura Parietal Pleura Peritoneal Cavity Serous Membrane Visceral peritoneum Parietal peritoneum