nervous system worksheet
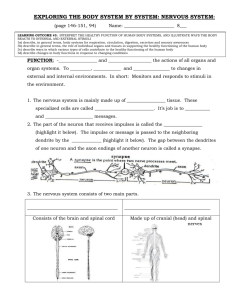
... specialized cells are called __________________________. It’s job is to ___________ and _____________________ messages. 2. The part of the neuron that receives impulses is called the _________________ (highlight it below). The impulse or message is passed to the neighboring dendrite by the _________ ...
... specialized cells are called __________________________. It’s job is to ___________ and _____________________ messages. 2. The part of the neuron that receives impulses is called the _________________ (highlight it below). The impulse or message is passed to the neighboring dendrite by the _________ ...
Physiology is the study of function of the body.
... It includes Gross anatomy (seen with naked eye) and Microscopic anatomy (seen with microscope). Physiology is the study of function of the body. Cellular physiology deals with cells & their function. Anatomy & Physiology are inter-related: function depends on the structure & vice versa LEVELS OF ORG ...
... It includes Gross anatomy (seen with naked eye) and Microscopic anatomy (seen with microscope). Physiology is the study of function of the body. Cellular physiology deals with cells & their function. Anatomy & Physiology are inter-related: function depends on the structure & vice versa LEVELS OF ORG ...
Pre-Lecture sheet Ear
... 3. The ______________________________ or the auditory canal is about _______________ long and extends to the ______________. 4. What are the function(s) of the ceruminous glands? __________________________________________________________________ 5. The tympanic membrane is the boundary between the _ ...
... 3. The ______________________________ or the auditory canal is about _______________ long and extends to the ______________. 4. What are the function(s) of the ceruminous glands? __________________________________________________________________ 5. The tympanic membrane is the boundary between the _ ...
divides the body or an organ into left and right sides
... • Frontal or coronal plane – divides the body or an organ into front (anterior) and back (posterior) portions ...
... • Frontal or coronal plane – divides the body or an organ into front (anterior) and back (posterior) portions ...
Body Cavities The internal body is divided into a number of spaces
... The organs of the body lie mostly within two major cavities: the Ventral cavity and Dorsal cavity. The Dorsal cavity lies within the skull and vertebral column and has two subdivisions: the Cranial cavity and the Spinal cavity. As the names suggest, the cranial cavity hosts the brain and the spinal ...
... The organs of the body lie mostly within two major cavities: the Ventral cavity and Dorsal cavity. The Dorsal cavity lies within the skull and vertebral column and has two subdivisions: the Cranial cavity and the Spinal cavity. As the names suggest, the cranial cavity hosts the brain and the spinal ...
Anatomy Joke - Mr. Bell`s Anatomy and Physiology
... – Support – framework and connection point for muscles; reason we have the shape we do – Movement – muscles attach to different parts of the skeleton to create movement upon muscle contraction – Protection – protecting covering around the heart/lungs and skull – Hematopoiesis – production of blood c ...
... – Support – framework and connection point for muscles; reason we have the shape we do – Movement – muscles attach to different parts of the skeleton to create movement upon muscle contraction – Protection – protecting covering around the heart/lungs and skull – Hematopoiesis – production of blood c ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Name Hour 1
... 8. Development is a process that begins with fertilization and ends with A. B. C. D. E. ...
... 8. Development is a process that begins with fertilization and ends with A. B. C. D. E. ...
Chapter 1 (Intro) ppt
... part relative to another part. Terms include: superior (closer to the head), inferior anterior (towards the front), posterior medial (closer to midline), lateral proximal (closer to trunk), distal superficial (towards the surface), deep ipsilateral (on same side), contralateral ...
... part relative to another part. Terms include: superior (closer to the head), inferior anterior (towards the front), posterior medial (closer to midline), lateral proximal (closer to trunk), distal superficial (towards the surface), deep ipsilateral (on same side), contralateral ...
unit 1 human body orientation ppt teacher
... **All systems work together to maintain the homeostasis of the body.** ...
... **All systems work together to maintain the homeostasis of the body.** ...
Anatomy and Physiology 2 nd Q study Guide for
... Which of the following substances is a compound? a. Mg c. H2 b. Fe d. salt One layer of the skin tends to thin with age. Which layer is it and what is the effect? a. The hypodermis thickens, causing an c. the dermis thins and the skin wrinkles intolerance of heat. b. The subcutaneous (hypodermis) th ...
... Which of the following substances is a compound? a. Mg c. H2 b. Fe d. salt One layer of the skin tends to thin with age. Which layer is it and what is the effect? a. The hypodermis thickens, causing an c. the dermis thins and the skin wrinkles intolerance of heat. b. The subcutaneous (hypodermis) th ...
Anatomy and Physiology (Marieb 2002)
... H. Growth – fetal, infant, child, and adolescent development Human Survival Needs A. Nutrients 1. Energy 2. Cell building B. Oxygen (REDOX REACTION WITH FOOD FOR ENERGY) C. Water – provides medium for chemical interactions as well as transport of molecules in the body D. Temperature E. Atmospheric p ...
... H. Growth – fetal, infant, child, and adolescent development Human Survival Needs A. Nutrients 1. Energy 2. Cell building B. Oxygen (REDOX REACTION WITH FOOD FOR ENERGY) C. Water – provides medium for chemical interactions as well as transport of molecules in the body D. Temperature E. Atmospheric p ...
Basic anatomy
... Direction is used, when the body is in the anatomical position to explain the location of a structure relative to the structures surrounding it. Anterior (or ventral): Towards the front of the body (in front of) e.g. The sternum lies anterior to the heart. Posterior (or dorsal): Towards the back ...
... Direction is used, when the body is in the anatomical position to explain the location of a structure relative to the structures surrounding it. Anterior (or ventral): Towards the front of the body (in front of) e.g. The sternum lies anterior to the heart. Posterior (or dorsal): Towards the back ...
The Nervous System
... The nervous system and the endocrine system regulate and control the activities of the other body systems The nervous system may be divided into two parts: ◦ central nervous system (CNS): made up of the brain and spinal cord ◦ peripheral nervous system (PNS): made up of cranial and spinal nerves ...
... The nervous system and the endocrine system regulate and control the activities of the other body systems The nervous system may be divided into two parts: ◦ central nervous system (CNS): made up of the brain and spinal cord ◦ peripheral nervous system (PNS): made up of cranial and spinal nerves ...
Small Cavities of the Head
... a. Parietal pericardium: lines heart cavity b. Visceral pericardium: lines surface of heart ...
... a. Parietal pericardium: lines heart cavity b. Visceral pericardium: lines surface of heart ...
Chapter 1 Lecture: The Human Body – An Orientation
... and surrounds the brain and the spinal cord. Crucial to protect and encased in bone. a. Cranial Cavity - The bones of the skull protect the brain. b. Spinal (Vertebral) Cavity - formed by the vertebrae of the spine and surrounds the spinal cord. 2. Ventral Cavity - located on the anterior/ventral su ...
... and surrounds the brain and the spinal cord. Crucial to protect and encased in bone. a. Cranial Cavity - The bones of the skull protect the brain. b. Spinal (Vertebral) Cavity - formed by the vertebrae of the spine and surrounds the spinal cord. 2. Ventral Cavity - located on the anterior/ventral su ...
TAKE HOME EXAM IV
... 3. Arteries function by carrying ________________________ blood away from the heart. 4. The foramen ovale is most closely associated with the ____________________ circulation pattern. 5. The term ____________________ refers to a contraction phase in the heart. 6. Pulmonary veins carry ______________ ...
... 3. Arteries function by carrying ________________________ blood away from the heart. 4. The foramen ovale is most closely associated with the ____________________ circulation pattern. 5. The term ____________________ refers to a contraction phase in the heart. 6. Pulmonary veins carry ______________ ...
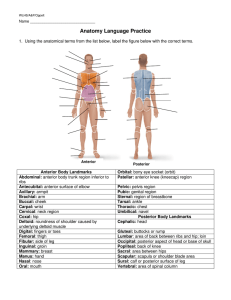
HANDOUT - Anatomy Language Practice
... In the anatomical position, the face and palms are on the (1) body surface, the buttocks and shoulder blades are on the (2) body surface, and the top of the head is the most (3) part of the body. The ears are (4) and the shoulders are (5) to the nose. The heart (6) is to the spine and (7) to the lun ...
... In the anatomical position, the face and palms are on the (1) body surface, the buttocks and shoulder blades are on the (2) body surface, and the top of the head is the most (3) part of the body. The ears are (4) and the shoulders are (5) to the nose. The heart (6) is to the spine and (7) to the lun ...
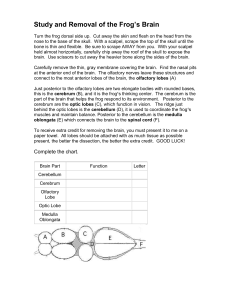
Study and Removal of the Frog`s Brain
... bone is thin and flexible. Be sure to scrape AWAY from you. With your scalpel held almost horizontally, carefully chip away the roof of the skull to expose the brain. Use scissors to cut away the heavier bone along the sides of the brain. Carefully remove the thin, gray membrane covering the brain. ...
... bone is thin and flexible. Be sure to scrape AWAY from you. With your scalpel held almost horizontally, carefully chip away the roof of the skull to expose the brain. Use scissors to cut away the heavier bone along the sides of the brain. Carefully remove the thin, gray membrane covering the brain. ...
Body Systems
... Adipose Tissue: type of connective tissue that stores fat cells Ligaments: strong, flexible bands of connective tissue that hold bones firmly together at the joints Tendons: white bands of connective tissue attaching skeletal muscle to bone Cartilage: firm, flexible support of the embryonic ...
... Adipose Tissue: type of connective tissue that stores fat cells Ligaments: strong, flexible bands of connective tissue that hold bones firmly together at the joints Tendons: white bands of connective tissue attaching skeletal muscle to bone Cartilage: firm, flexible support of the embryonic ...
• Anatomy = structure • Physiology = function • structure aids function
... unit of life group of similar cells different tissues ...
... unit of life group of similar cells different tissues ...
body organization and homeostasis
... Group of similar cells that perform the same function Four types: Muscle – can contract or shorten, make body move Nervous – carry electrical signals between brain and other body parts Connective – provides support for body and connects all parts Epithelial – covers surfaces of body both ins ...
... Group of similar cells that perform the same function Four types: Muscle – can contract or shorten, make body move Nervous – carry electrical signals between brain and other body parts Connective – provides support for body and connects all parts Epithelial – covers surfaces of body both ins ...
BODY ORGANIZATION AND HOMEOSTASIS
... Group of similar cells that perform the same function Four types: Muscle – can contract or shorten, make body move Nervous – carry electrical signals between brain and other body parts Connective – provides support for body and connects all parts Epithelial – covers surfaces of body both ins ...
... Group of similar cells that perform the same function Four types: Muscle – can contract or shorten, make body move Nervous – carry electrical signals between brain and other body parts Connective – provides support for body and connects all parts Epithelial – covers surfaces of body both ins ...
Unit 10 The Human Body - Jamestown Public Schools
... protects internal organs, provides for movement, stores mineral reserves, & provides a site for blood cell formation Bones provide a system of levers on which muscles act to produce movement ...
... protects internal organs, provides for movement, stores mineral reserves, & provides a site for blood cell formation Bones provide a system of levers on which muscles act to produce movement ...
Head and neck anatomy

This article describes the anatomy of the head and neck of the human body, including the brain, bones, muscles, blood vessels, nerves, glands, nose, mouth, teeth, tongue, and throat.