Fatty Acid oxidation
... * (which is also a precursor for fatty acid synthesis) inhibits Carnitine Palmitoyl Transferase I and thus, inhibits β-oxidation * Malonyl-CoA is produced from acetyl-CoA by the enzyme Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase ...
... * (which is also a precursor for fatty acid synthesis) inhibits Carnitine Palmitoyl Transferase I and thus, inhibits β-oxidation * Malonyl-CoA is produced from acetyl-CoA by the enzyme Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase ...
Document
... (A) The brain prefers glucose as an energy source, but can use ketone bodies. (B) Muscle cannot use fatty acids as an energy source. (C) In a well-fed human, about equal amounts of energy are stored as glycogen and as triacylglycerol. (D) Fatty acids cannot be used as an energy source in humans beca ...
... (A) The brain prefers glucose as an energy source, but can use ketone bodies. (B) Muscle cannot use fatty acids as an energy source. (C) In a well-fed human, about equal amounts of energy are stored as glycogen and as triacylglycerol. (D) Fatty acids cannot be used as an energy source in humans beca ...
Organic Compounds Overview - Kenwood Academy High School
... – Chitin (compound in exoskeletons) ...
... – Chitin (compound in exoskeletons) ...
Lipids WORD 1000 KB - Science Learning Hub
... ratio of omega 3:omega 6 in unsaturated fats to less than 1:10 is also recommended. Trans fatty acids The food industry uses fats and oils in the production of margarines, baked goods, sauces and chocolates. In addition to using naturally occurring lipids, fats and oils that have been altered in a p ...
... ratio of omega 3:omega 6 in unsaturated fats to less than 1:10 is also recommended. Trans fatty acids The food industry uses fats and oils in the production of margarines, baked goods, sauces and chocolates. In addition to using naturally occurring lipids, fats and oils that have been altered in a p ...
QUIZ #4 LIPID STRUCTURES AND METABOLISM
... Which of the following is FALSE concerning the insertion of double bonds in a fatty acid by a desaturase enzyme? a. Will not desaturate "deeper" than C9 from the COOH end b. Can form either cis or trans double bonds c. Second double bond cannot form distal to (from the delta end) to an existing doub ...
... Which of the following is FALSE concerning the insertion of double bonds in a fatty acid by a desaturase enzyme? a. Will not desaturate "deeper" than C9 from the COOH end b. Can form either cis or trans double bonds c. Second double bond cannot form distal to (from the delta end) to an existing doub ...
Metabolism II
... Fatty acid synthesis • Fat is an efficient way to store energy • It is usually surplus of carbohydrates that are converted to fat • The reactions are in principle a reversed -oxidation Synthesis of fatty acid starts with the carboxylation of acetylCoA to malonyl-CoA. This is the committed step, ma ...
... Fatty acid synthesis • Fat is an efficient way to store energy • It is usually surplus of carbohydrates that are converted to fat • The reactions are in principle a reversed -oxidation Synthesis of fatty acid starts with the carboxylation of acetylCoA to malonyl-CoA. This is the committed step, ma ...
NSC 602 - Department of Nutritional Sciences
... from Acetyl-CoA. Detail the steps of eta-oxidation of fatty acids and calculate the total number of ATP molecules that can be obtained from complete oxidation, this means all the way down to the Krebs cycle and respiratory chain. Be aware of differences in the oxidation of saturated and unsaturated ...
... from Acetyl-CoA. Detail the steps of eta-oxidation of fatty acids and calculate the total number of ATP molecules that can be obtained from complete oxidation, this means all the way down to the Krebs cycle and respiratory chain. Be aware of differences in the oxidation of saturated and unsaturated ...
palm butter - In
... 45/50% of oil and has consistency like soft butter at room temperature. Palm Butter may be used in the lipidic phase of an emulsion or of a lipogel acting both as a vegetal triglycerids and as consistency factor (it can substitute the whole oil phase of an emulsion), moreover it makes the skin soft ...
... 45/50% of oil and has consistency like soft butter at room temperature. Palm Butter may be used in the lipidic phase of an emulsion or of a lipogel acting both as a vegetal triglycerids and as consistency factor (it can substitute the whole oil phase of an emulsion), moreover it makes the skin soft ...
Chapter 6, Section 3
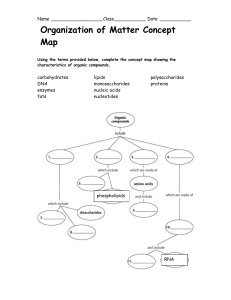
... Organic: contains carbon ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
... Organic: contains carbon ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
Polymers vs. monomers wkst. and concept map
... ________________________________________ 20. Your best friend tells you that they are deathly allergic to certain amino acids in food. Your mom has prepared dinner already, so you need to tell her not to serve what macromolecule to them? ...
... ________________________________________ 20. Your best friend tells you that they are deathly allergic to certain amino acids in food. Your mom has prepared dinner already, so you need to tell her not to serve what macromolecule to them? ...
biochem study guide
... 3. Describe the structure of a typical monosaccharide such as glucose. Write out a condensation reaction between two glucose molecules, and explain hydrolysis. 4. Explain the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated fatty acid. Explain how three fatty acids can react with glycerol to make a ...
... 3. Describe the structure of a typical monosaccharide such as glucose. Write out a condensation reaction between two glucose molecules, and explain hydrolysis. 4. Explain the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated fatty acid. Explain how three fatty acids can react with glycerol to make a ...
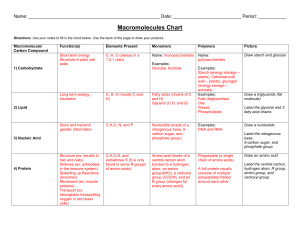
Enzymes/Macromolecules/Bonding
... ring form Starch macromolecule is a polysaccharide composed of 1000s of glucose units ...
... ring form Starch macromolecule is a polysaccharide composed of 1000s of glucose units ...
Name - MsOttoliniBiology
... Structure (ex: keratin in hair and nails) Defense (ex: antibodies in the immune system) Speeding up Reactions (enzymes) Movement (ex: muscle proteins) Transport (ex: hemoglobin transporting oxygen in red blood cells) ...
... Structure (ex: keratin in hair and nails) Defense (ex: antibodies in the immune system) Speeding up Reactions (enzymes) Movement (ex: muscle proteins) Transport (ex: hemoglobin transporting oxygen in red blood cells) ...
Midterm Review Project Ch 5
... primary structure: amino acid sequence; secondary structure: coils and folds as a result of hydrogen bonds, alpha- helix, beta-pleated sheet; tertiary structure: overall shape of polypeptide created by hydrophobic interaction ( hydrophobic side chains end up at core of protein) and disulfide bridges ...
... primary structure: amino acid sequence; secondary structure: coils and folds as a result of hydrogen bonds, alpha- helix, beta-pleated sheet; tertiary structure: overall shape of polypeptide created by hydrophobic interaction ( hydrophobic side chains end up at core of protein) and disulfide bridges ...
LIPIDS
... •Most lipids are insoluble in water but dissolve in other lipids and alcohol, acetone (NONPOLAR) ...
... •Most lipids are insoluble in water but dissolve in other lipids and alcohol, acetone (NONPOLAR) ...
Organic Molecules - Mr. Swords` Classes
... Speeds up reaction, can be used over and over again. The reaction does not change it (like a key!) ...
... Speeds up reaction, can be used over and over again. The reaction does not change it (like a key!) ...
g. ¶I - wwphs
... d. lack diversity of structure and function The information built into a protein’s amino acid sequence plus a coiled pattern of that chain and the addition of more folding yields the level of protein structure. [p.43] a. fourth b. primary c. second d. third ...
... d. lack diversity of structure and function The information built into a protein’s amino acid sequence plus a coiled pattern of that chain and the addition of more folding yields the level of protein structure. [p.43] a. fourth b. primary c. second d. third ...
Chapter 3 Review Questions
... 1. DNA and RNA are examples of ___nucleic acids______________. 2. Carbohydrates and lipids both contain the elements ____carbon__________, __hydrogen__________, and ________oxygen_________. 3. Proteins are made of ___amino acids________________ 4. __polynucleotides or nucleic acids____________ are m ...
... 1. DNA and RNA are examples of ___nucleic acids______________. 2. Carbohydrates and lipids both contain the elements ____carbon__________, __hydrogen__________, and ________oxygen_________. 3. Proteins are made of ___amino acids________________ 4. __polynucleotides or nucleic acids____________ are m ...
BIOMEDICAL IMPORTANCE Fatty acids are synthesized by an
... with increased concentrations of plasma free fatty acids, and an inverse relationship has been demonstrated between hepatic lipogenesis and the concentration of serum-free fatty acids. Lipogenesis is increased when such crose is fed instead of glucose because fructose bypasses the phosphofructokinas ...
... with increased concentrations of plasma free fatty acids, and an inverse relationship has been demonstrated between hepatic lipogenesis and the concentration of serum-free fatty acids. Lipogenesis is increased when such crose is fed instead of glucose because fructose bypasses the phosphofructokinas ...
lecture4
... Most lipids are ingested in the form of triacylglycerols but must be degraded to fatty acids for absorption across the intestinal epithelium. Recall that lipids are not easily solubilized, yet they must be in order to be degraded. Triacylglycerols in the intestinal lumen are incorporated into micell ...
... Most lipids are ingested in the form of triacylglycerols but must be degraded to fatty acids for absorption across the intestinal epithelium. Recall that lipids are not easily solubilized, yet they must be in order to be degraded. Triacylglycerols in the intestinal lumen are incorporated into micell ...
Most membrane phospholipids contain glycerol
... • sphingomyelin *** Most membrane phospholipids contain glycerol (lecithin, phosphatidylcholine phosphatidylserine and cardiolipin). Sphingomyelin contains a sphingosine backbone instead of glycerol. Phospholipids are lipids. Each molecule is made up of one glycerol molecule attached to two fatty ac ...
... • sphingomyelin *** Most membrane phospholipids contain glycerol (lecithin, phosphatidylcholine phosphatidylserine and cardiolipin). Sphingomyelin contains a sphingosine backbone instead of glycerol. Phospholipids are lipids. Each molecule is made up of one glycerol molecule attached to two fatty ac ...
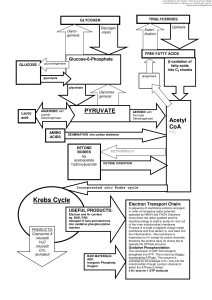
Chapter 19
... mitochondria of liver cells. Ketone bodies are used as energy source. • 3 Acetyl-CoA are condensed to β-hydroxyl-β-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA), and then break down to acetoacetate & acetyl-CoA by HMG-CoA lyase. 3. Fatty acid synthesis. • Occurs in cytoplasm in liver cells. • Fatty acyl is attached ...
... mitochondria of liver cells. Ketone bodies are used as energy source. • 3 Acetyl-CoA are condensed to β-hydroxyl-β-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA), and then break down to acetoacetate & acetyl-CoA by HMG-CoA lyase. 3. Fatty acid synthesis. • Occurs in cytoplasm in liver cells. • Fatty acyl is attached ...
Biochemistry II Test 2Q
... 51. To export ketone bodies to peripheral tissue ____ and ____ are required. 52. Ketone bodies may be metabolized by skeletal and cardiac muscle but requires ____ and ____. 53. The brain uses ketone bodies for ___% of its energy, but only during ___________. 54. When does glucagon activate lipolysis ...
... 51. To export ketone bodies to peripheral tissue ____ and ____ are required. 52. Ketone bodies may be metabolized by skeletal and cardiac muscle but requires ____ and ____. 53. The brain uses ketone bodies for ___% of its energy, but only during ___________. 54. When does glucagon activate lipolysis ...
Macromolecules in Organisms
... Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carbon and hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms. Fats are made of a glycerol (alcohol) and three fat ...
... Lipids are large, nonpolar (won't dissolve in water) molecules. Phospholipids make up cell membranes. Lipids also serve as waxy coverings on plants, pigments (chlorophyll), and steroids. Lipids have more carbon and hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms. Fats are made of a glycerol (alcohol) and three fat ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.