2.3 Outline
... • _________________________ such as starch are chains of three or more monosaccharides. 2. Lipids: • _________________________ are nonpolar molecules that are not soluble in water. They include fats, phospholipids, steroids, and waxes. • Fats are lipids that store energy. • A typical fat contains th ...
... • _________________________ such as starch are chains of three or more monosaccharides. 2. Lipids: • _________________________ are nonpolar molecules that are not soluble in water. They include fats, phospholipids, steroids, and waxes. • Fats are lipids that store energy. • A typical fat contains th ...
Classes of Biomolecules Lipids Biological Functions of Lipids
... constructing the honeycomb, • any of numerous substances of plant or animal origin that differ from fats in being less greasy, harder, and more brittle and in containing principally compounds of high molecular weight (as fatty acids, alcohols, and saturated hydrocarbons) • Long chain fatty acid wi ...
... constructing the honeycomb, • any of numerous substances of plant or animal origin that differ from fats in being less greasy, harder, and more brittle and in containing principally compounds of high molecular weight (as fatty acids, alcohols, and saturated hydrocarbons) • Long chain fatty acid wi ...
WEB
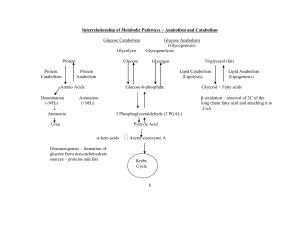
... Production of ketone bodies Starvation Glycogen = 1 day Amino acids Glc. BUT… Muscles can use fatty acids ( need for Glc) Gluconeogenesis ...
... Production of ketone bodies Starvation Glycogen = 1 day Amino acids Glc. BUT… Muscles can use fatty acids ( need for Glc) Gluconeogenesis ...
Chapter 21
... Glucose is converted to other hexoses and to di-, oligo-, and polysaccharides. • The common step in all of these syntheses is activation of glucose by uridine triphosphate (UTP) to form uridine diphosphate glucose (UDP-glucose) + Pi . ...
... Glucose is converted to other hexoses and to di-, oligo-, and polysaccharides. • The common step in all of these syntheses is activation of glucose by uridine triphosphate (UTP) to form uridine diphosphate glucose (UDP-glucose) + Pi . ...
Exam Name___________________________________
... 1) Why are triacylglycerols able to provide more energy than carbohydrates (gram for gram)? A) The triacylglycerols are less soluble in water than the carbohydrates. B) The carbohydrates contain fewer carbon-carbon bonds. C) The carbohydrates are already in a more oxidized state than the triacylglyc ...
... 1) Why are triacylglycerols able to provide more energy than carbohydrates (gram for gram)? A) The triacylglycerols are less soluble in water than the carbohydrates. B) The carbohydrates contain fewer carbon-carbon bonds. C) The carbohydrates are already in a more oxidized state than the triacylglyc ...
Fatty Acid Synthesis
... alcohol, her triglycerides dropped to 2 mM and her cholesterol to 193 mg/dL. Three years later, she is your patient, presenting with an enlarged liver and high blood lipid levels. Liver biopsy indicated infiltration of the liver cells ...
... alcohol, her triglycerides dropped to 2 mM and her cholesterol to 193 mg/dL. Three years later, she is your patient, presenting with an enlarged liver and high blood lipid levels. Liver biopsy indicated infiltration of the liver cells ...
Triacylglycerol Metabolism Gone Bad: A major cause of disease
... • Apolipoprotein B-100 synthesis is required for the transport of lipid out of the liver – If protein synthesis is reduced (e.g. by malnutrition) fat droplets accumulate in the liver. – If the rate of lipid synthesis is greatly elevated with respect to protein synthesis (e.g. in type I diabetes or ...
... • Apolipoprotein B-100 synthesis is required for the transport of lipid out of the liver – If protein synthesis is reduced (e.g. by malnutrition) fat droplets accumulate in the liver. – If the rate of lipid synthesis is greatly elevated with respect to protein synthesis (e.g. in type I diabetes or ...
Abstract of the project nr. 16
... fish fillet is so prone to the oxidation during the storage period. Therefore frozen stoarge of fish fillet subsequently can cause off flavour and make rancid taste and form some unfavourable substances and nutritional losses (for instance decrease in the n-3 fatty acids which have beneficial health ...
... fish fillet is so prone to the oxidation during the storage period. Therefore frozen stoarge of fish fillet subsequently can cause off flavour and make rancid taste and form some unfavourable substances and nutritional losses (for instance decrease in the n-3 fatty acids which have beneficial health ...
Biology 12 - Biologically Important Molecules – Review Worksheet
... a polymer of glucose, used as a storage form for glucose in animals a polymer of glucose, used as a storage form for glucose in plants a loss of Hydrogen atoms (or electrons) a lipid that is an important component of cell membranes and from which steroid hormones are made a lipid composed of glycero ...
... a polymer of glucose, used as a storage form for glucose in animals a polymer of glucose, used as a storage form for glucose in plants a loss of Hydrogen atoms (or electrons) a lipid that is an important component of cell membranes and from which steroid hormones are made a lipid composed of glycero ...
Slide 1
... 4 carbon rings, no fatty acid tails Cholesterol, testosterone, estrogen, other hormones Some regulate vitamin D function Regulate cell membrane fluidity ...
... 4 carbon rings, no fatty acid tails Cholesterol, testosterone, estrogen, other hormones Some regulate vitamin D function Regulate cell membrane fluidity ...
Exam II answer key
... converted into something that can enter a primary metabolic pathway. Draw the mechanism of this/these steps. Propionyl CoA biotin dependent carboxylation to methyl malonyl CoA, B-12 dependent rearrangement to succinyl CoA. See mechanisms on web site and book. 10. (10 pts) Describe the structure of g ...
... converted into something that can enter a primary metabolic pathway. Draw the mechanism of this/these steps. Propionyl CoA biotin dependent carboxylation to methyl malonyl CoA, B-12 dependent rearrangement to succinyl CoA. See mechanisms on web site and book. 10. (10 pts) Describe the structure of g ...
Exam II
... converted into something that can enter a primary metabolic pathway. Draw the mechanism of this/these steps. Propionyl CoA biotin dependent carboxylation to methyl malonyl CoA, B-12 dependent rearrangement to succinyl CoA. See mechanisms on web site and book. 10. (10 pts) Describe the structure of g ...
... converted into something that can enter a primary metabolic pathway. Draw the mechanism of this/these steps. Propionyl CoA biotin dependent carboxylation to methyl malonyl CoA, B-12 dependent rearrangement to succinyl CoA. See mechanisms on web site and book. 10. (10 pts) Describe the structure of g ...
FALSE degradation also needs to be considered. A change in
... a. Why would gluconeogenesis from alanine require increased transport of malate across the mitochondrial membrane, whereas gluconeogenesis from lactate would not. The conversion of lactate to pyruvate in the cytosol generates an NADH molecule from NAD.. If alanine is transaminated in the mitochondri ...
... a. Why would gluconeogenesis from alanine require increased transport of malate across the mitochondrial membrane, whereas gluconeogenesis from lactate would not. The conversion of lactate to pyruvate in the cytosol generates an NADH molecule from NAD.. If alanine is transaminated in the mitochondri ...
Qualitative tests of lipids 2
... Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds ,side chian are a)Short chain From 4 to 10 Carbon atoms ,and present as liquid in room Temp. e.g acetic acid and butyric acid a)Long chain: More than 10 Carbone atoms, present in solid at room Temp. e.g. Palmatic (16) acid and Stearic(18) acid ...
... Saturated fatty acids have no double bonds ,side chian are a)Short chain From 4 to 10 Carbon atoms ,and present as liquid in room Temp. e.g acetic acid and butyric acid a)Long chain: More than 10 Carbone atoms, present in solid at room Temp. e.g. Palmatic (16) acid and Stearic(18) acid ...
Lipids - An-Najah National University
... • These three-dimensional molecular projections show the Cis and Trans configurational isomers of 9-octadecenoic acid with the hydrogen atoms shown in blue. The Latin prefixes Cis and Trans describe the orientation of the hydrogen atoms with respect to the double bond. Cis means "on the same side" ...
... • These three-dimensional molecular projections show the Cis and Trans configurational isomers of 9-octadecenoic acid with the hydrogen atoms shown in blue. The Latin prefixes Cis and Trans describe the orientation of the hydrogen atoms with respect to the double bond. Cis means "on the same side" ...
Chem*3560 Lecture 22: Fatty acid desaturation Relationship of
... elongation is carried out by the fatty acid elongase system. Elongase is a set of four more loosely associated enzymes on the endoplasmic reticulum membrane that act on acyl-CoA derivatives rather than acyl-ACP (Lehninger p.781). The individual enzymes make the elongation process less efficient than ...
... elongation is carried out by the fatty acid elongase system. Elongase is a set of four more loosely associated enzymes on the endoplasmic reticulum membrane that act on acyl-CoA derivatives rather than acyl-ACP (Lehninger p.781). The individual enzymes make the elongation process less efficient than ...
Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Two
... from the intestine to all body tissues via the bloodstream. complex lipid (17.5) a lipid that is bonded to other types of molecules. diglyceride (17.3) the product of the esterification of glycerol with fatty acids at two positions. eicosanoid (17.2) any of the derivatives of 20-carbon fatty acids, ...
... from the intestine to all body tissues via the bloodstream. complex lipid (17.5) a lipid that is bonded to other types of molecules. diglyceride (17.3) the product of the esterification of glycerol with fatty acids at two positions. eicosanoid (17.2) any of the derivatives of 20-carbon fatty acids, ...
lecture_22 - WordPress.com
... Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase: an enzyme similar to succinate dehydrogenase ...
... Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase: an enzyme similar to succinate dehydrogenase ...
Begin by going to the address below
... 18. What three types of side groups do all amino acids have? ...
... 18. What three types of side groups do all amino acids have? ...
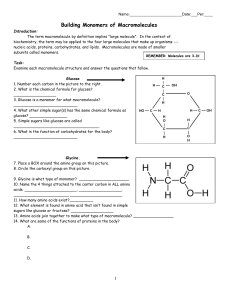
Building Monomers of Macromolecules
... Building Monomers of Macromolecules Introduction: The term macromolecule by definition implies "large molecule". In the context of biochemistry, the term may be applied to the four large molecules that make up organisms --nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Macromolecules are made of ...
... Building Monomers of Macromolecules Introduction: The term macromolecule by definition implies "large molecule". In the context of biochemistry, the term may be applied to the four large molecules that make up organisms --nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. Macromolecules are made of ...
Trans Fatty Acids
... acids? • Hydrogenation- a process to transform saturated fatty acids in the form of oils to a more viscous unsaturated form. (eg. Vegetable oil margarine). • This process results in a combination of cis and trans unsaturated fatty acids. ...
... acids? • Hydrogenation- a process to transform saturated fatty acids in the form of oils to a more viscous unsaturated form. (eg. Vegetable oil margarine). • This process results in a combination of cis and trans unsaturated fatty acids. ...
Cell structure and Bioenergetics
... - diffuse freely without carnitine esterification into the mitochondria Long chain ( > 14 carbons) - found in triglycerol (fat) and structural lipids - require the carnitine shuttle to move form cytosol into the mitochondria ...
... - diffuse freely without carnitine esterification into the mitochondria Long chain ( > 14 carbons) - found in triglycerol (fat) and structural lipids - require the carnitine shuttle to move form cytosol into the mitochondria ...
Covalent Reactions Atoms SHARE electrons
... between carbon atoms (saturated) – Unsaturated Fatty Acid= has double bonds between carbon atoms ...
... between carbon atoms (saturated) – Unsaturated Fatty Acid= has double bonds between carbon atoms ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.