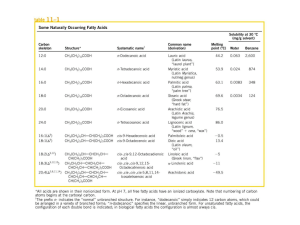
Sample exam 1
... Sample mid-quarter exam 1 (Lipids, amino acid metabolism, membrane transport) 1. The enzyme that acts on ketone bodies to convert them into a form that can be broken down into acetyl CoA is present in brain, but not in liver. What type of reaction is catalyzed by this enzyme? a. Oxidation. b. Dehydr ...
... Sample mid-quarter exam 1 (Lipids, amino acid metabolism, membrane transport) 1. The enzyme that acts on ketone bodies to convert them into a form that can be broken down into acetyl CoA is present in brain, but not in liver. What type of reaction is catalyzed by this enzyme? a. Oxidation. b. Dehydr ...
Modern Biology: Chapter 3
... Carbon Compounds • Organic compounds – primarily Carbon atoms – Large, complex molecules essential for life – Contributes to diversity of life ...
... Carbon Compounds • Organic compounds – primarily Carbon atoms – Large, complex molecules essential for life – Contributes to diversity of life ...
Macromolecules Test Review Test Date: 1. What does the term
... 11. What does it mean for a molecule to be “organic”? 12. How many amino acids exist? 13. Give two examples of a monosaccharide. 14. What is the formula for fructose? 15. Why are unsaturated fatty acids better for your health? 16. What type of fatty acid has no double bond? 17. What is a monomer? 18 ...
... 11. What does it mean for a molecule to be “organic”? 12. How many amino acids exist? 13. Give two examples of a monosaccharide. 14. What is the formula for fructose? 15. Why are unsaturated fatty acids better for your health? 16. What type of fatty acid has no double bond? 17. What is a monomer? 18 ...
3rd Fall - rci.rutgers.edu
... B) A thioester derivative of D-β-hydroxybutyrate is an intermediate in the synthetic path, but not in the degradative path; C) Fatty acid biosynthesis uses NADPH exclusively, whereas β oxidation uses NAD+ exclusively; D) Fatty acid degradation is catalyzed by enzymes of the mitochondrial matrix; fat ...
... B) A thioester derivative of D-β-hydroxybutyrate is an intermediate in the synthetic path, but not in the degradative path; C) Fatty acid biosynthesis uses NADPH exclusively, whereas β oxidation uses NAD+ exclusively; D) Fatty acid degradation is catalyzed by enzymes of the mitochondrial matrix; fat ...
biomolecule notes
... f. Examples: Triglycerides = butter, waxes = waterproof coatings, steroids = testosterone & cholesterol ...
... f. Examples: Triglycerides = butter, waxes = waterproof coatings, steroids = testosterone & cholesterol ...
chapter 5 large biological molecules
... o Starch – storage form for plants made entirely of glucose monomers, ex. amylose. Angles make them helical. o Glycogen – storage form for animals, more branched. Humans and other vertebrates store glycogen in liver and muscle cells. In humans glycogen bank can be depleted within one day. o Cellulos ...
... o Starch – storage form for plants made entirely of glucose monomers, ex. amylose. Angles make them helical. o Glycogen – storage form for animals, more branched. Humans and other vertebrates store glycogen in liver and muscle cells. In humans glycogen bank can be depleted within one day. o Cellulos ...
Chapter 5 – Quiz #2-A Take Home Quiz
... 9. Which of the following is/are a precursor of bile, vitamin D, and some sex hormones? a. phospholipids b. triglycerides c. cholesterol d. alpha-linolenic acid True or False: Place a T or an F to the left of the number of the question. 10. LDL is a type of lipoprotein that carries digested fat from ...
... 9. Which of the following is/are a precursor of bile, vitamin D, and some sex hormones? a. phospholipids b. triglycerides c. cholesterol d. alpha-linolenic acid True or False: Place a T or an F to the left of the number of the question. 10. LDL is a type of lipoprotein that carries digested fat from ...
Biological Molecules - Princeton High School
... Each Enzyme bonds with a specific Substrate for form the Active Site ...
... Each Enzyme bonds with a specific Substrate for form the Active Site ...
Lipid Biosynthesis
... – When fuel is high, acetyl CoA is plentiful, and malonyl CoA is produced – Malonyl CoA may decrease appetite – Malonyl CoA inhibits acylcarnitine transferase • No Fatty acids can get into mitochondria for oxidation ...
... – When fuel is high, acetyl CoA is plentiful, and malonyl CoA is produced – Malonyl CoA may decrease appetite – Malonyl CoA inhibits acylcarnitine transferase • No Fatty acids can get into mitochondria for oxidation ...
Various University Examination Questions on Fatty acid
... 14. Explain the biochemical basis: Neurological symptoms in Refsum’s disease. ...
... 14. Explain the biochemical basis: Neurological symptoms in Refsum’s disease. ...
ETC Details
... • Broken into amino acids, then converted into either pyruvic acid, acetyl CoA, or 1 of the molecules used in Krebs • Where it enters, depends on what’s made ...
... • Broken into amino acids, then converted into either pyruvic acid, acetyl CoA, or 1 of the molecules used in Krebs • Where it enters, depends on what’s made ...
Macromolecule WebQuest
... answer the questions below as they will help you understand the different structures and functions of biological molecules. Follow the link ...
... answer the questions below as they will help you understand the different structures and functions of biological molecules. Follow the link ...
PPT
... Energy-rich compounds with low densities Storage form of energy for plants and animals Structural components, especially in cellular membrane formation ...
... Energy-rich compounds with low densities Storage form of energy for plants and animals Structural components, especially in cellular membrane formation ...
Document
... 24.3: Fatty Acid Biosynthesis. Fatty acid biosynthesis is performed by a cluster of discrete enzymes in bacteria, and a very large multi-protein assembly in animals (fatty acid synthase, FAS). The fatty acid is attached to an acyl carrier protein (ACP), while other proteins perform an iterative two ...
... 24.3: Fatty Acid Biosynthesis. Fatty acid biosynthesis is performed by a cluster of discrete enzymes in bacteria, and a very large multi-protein assembly in animals (fatty acid synthase, FAS). The fatty acid is attached to an acyl carrier protein (ACP), while other proteins perform an iterative two ...
The process of beta oxidation is named after the carbon atom in the
... acid cycle which yields an additional 96 mols of ATP for all 8 acetyl-CoA units oxidized in the process. The total energy yield of palmitic acid oxidation results in some 130 mols of ATP, 34 units from the beta-oxidation cycle and 96 form the citric acid cycle. Beta oxidation of odd numbered fatty a ...
... acid cycle which yields an additional 96 mols of ATP for all 8 acetyl-CoA units oxidized in the process. The total energy yield of palmitic acid oxidation results in some 130 mols of ATP, 34 units from the beta-oxidation cycle and 96 form the citric acid cycle. Beta oxidation of odd numbered fatty a ...
Bio II HName list2
... Chapter 3- Biological Molecules Organic compounds Hydrocarbons Functional groups Monomers Polymers Alcohols Enzymes Condensation reaction Hydrolysis Carbohydrate Sugar Monosaccharides Ribose Deoxyribose Glucose Oligosaccharide Sucrose Lactose Polysaccharide Cellulose Starch Glycogen Chitin Lipids Fa ...
... Chapter 3- Biological Molecules Organic compounds Hydrocarbons Functional groups Monomers Polymers Alcohols Enzymes Condensation reaction Hydrolysis Carbohydrate Sugar Monosaccharides Ribose Deoxyribose Glucose Oligosaccharide Sucrose Lactose Polysaccharide Cellulose Starch Glycogen Chitin Lipids Fa ...
Apoptosis
... Arachidonic acid is the precursor of eicosanoids, including the prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. ...
... Arachidonic acid is the precursor of eicosanoids, including the prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. ...
Fatty acid catabolism leture2-3
... This condition is called “acidosis” which can lead to com or death. High concentration of ketone bodies in blood and urine is referred as “ketosis”. Due to high concentration of acetoacetate, which is converted to acetone, the breath and urine of theuntreated diabetic ...
... This condition is called “acidosis” which can lead to com or death. High concentration of ketone bodies in blood and urine is referred as “ketosis”. Due to high concentration of acetoacetate, which is converted to acetone, the breath and urine of theuntreated diabetic ...
Biology Study Guide for Section (Macromolecules) Test
... Sugars- Similar to starch, cellulose is a complex carbohydrate. This compound makes up cellulose. Nitrogen- Carbohydrates contain all C,H,O but no nitrogen. Amino acids are the building blocks of protein. Glucose-is also called a monosaccharide. Starch- plants store energy in this form. Structural s ...
... Sugars- Similar to starch, cellulose is a complex carbohydrate. This compound makes up cellulose. Nitrogen- Carbohydrates contain all C,H,O but no nitrogen. Amino acids are the building blocks of protein. Glucose-is also called a monosaccharide. Starch- plants store energy in this form. Structural s ...
2-A Chemical Compounds of Life Organic Compounds
... reactants to form products C. Catalyst: a substance that lowers the activation energy needed to start a chemical reaction • Makes the reaction faster ...
... reactants to form products C. Catalyst: a substance that lowers the activation energy needed to start a chemical reaction • Makes the reaction faster ...
biological_molecules_facts
... All proteins contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. Some also contain sulphur. Amino acids are the monomers. The structural formula of an amino acid is: There are 20 amino acids, each with a different R group. Many amino acids are joined by condensation reactions to form polypeptides. The li ...
... All proteins contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. Some also contain sulphur. Amino acids are the monomers. The structural formula of an amino acid is: There are 20 amino acids, each with a different R group. Many amino acids are joined by condensation reactions to form polypeptides. The li ...
Answers - Shelton State
... 20. DNA is sometimes made from RNA by retro viruses. This process is called reverse transcription. 21. Nucleic acids are synthesized from their 5’ end to their 3’ end. 22. Define: antiparallel, termination code, enzyme, frame shift mutaion. See Your Notes or book. 23. Give two other names for the tr ...
... 20. DNA is sometimes made from RNA by retro viruses. This process is called reverse transcription. 21. Nucleic acids are synthesized from their 5’ end to their 3’ end. 22. Define: antiparallel, termination code, enzyme, frame shift mutaion. See Your Notes or book. 23. Give two other names for the tr ...
fatty acid oxid final
... Increase requirement Pregnancy, Infections, Burns, Trauma o Losses can also occur in hemodialysis • SYMPTOMS: Hypoglycemia during fast ...
... Increase requirement Pregnancy, Infections, Burns, Trauma o Losses can also occur in hemodialysis • SYMPTOMS: Hypoglycemia during fast ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.