chapter 5 the structure & function of macromolecules
... What is the male sex hormone? What is the female sex hormone? ...
... What is the male sex hormone? What is the female sex hormone? ...
Essential Fatty Acids (EFAs): Your Brain and Body
... Essential Fatty Acids (EFAs): Your Brain and Body Fatty acids are the basic building blocks of which fats and oils are composed. Contrary to popular myth, the body does need fat. It must be the right kind, however. The fatty acids that are necessary for health and that cannot be made by the body are ...
... Essential Fatty Acids (EFAs): Your Brain and Body Fatty acids are the basic building blocks of which fats and oils are composed. Contrary to popular myth, the body does need fat. It must be the right kind, however. The fatty acids that are necessary for health and that cannot be made by the body are ...
Lecture 37
... Aspirin and ibuprofen inhibit the production of PGH2 by irreversibly blocking the cycloxygenase activity of prostaglandin synthase. It turns out that aspirin and ibuprogen inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2, although ibuprofen is more potent than aspirin. The COX-2 isoform is considered the key proinflam ...
... Aspirin and ibuprofen inhibit the production of PGH2 by irreversibly blocking the cycloxygenase activity of prostaglandin synthase. It turns out that aspirin and ibuprogen inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2, although ibuprofen is more potent than aspirin. The COX-2 isoform is considered the key proinflam ...
Powerpoint Slides for Chapter Seven
... a living system Our emphasis will be on harvesting energy from nutrient molecules ...
... a living system Our emphasis will be on harvesting energy from nutrient molecules ...
Group A_lipid - UniMAP Portal
... carotenoids- which differ in structure and function are considered as lipids Lipids – Those substances from living organisms that dissolve in nonpolar solvents eg. Ether, chloroform, acetone but not in ...
... carotenoids- which differ in structure and function are considered as lipids Lipids – Those substances from living organisms that dissolve in nonpolar solvents eg. Ether, chloroform, acetone but not in ...
Classifying Organic Molecules Lab
... 11. How many amino acids do you have in your set? 12. Which of the CHNOPS elements are contained in ALL amino acids? Group 3: Sugars – building blocks of carbohydrates 13. Sugars are literally hydrates of carbon, having the general formula “Cn(H2O) n. Sugars are burned “oxidized” to release energy i ...
... 11. How many amino acids do you have in your set? 12. Which of the CHNOPS elements are contained in ALL amino acids? Group 3: Sugars – building blocks of carbohydrates 13. Sugars are literally hydrates of carbon, having the general formula “Cn(H2O) n. Sugars are burned “oxidized” to release energy i ...
Selected Solutions to End of Chapter 17 Problems
... cleaves fatty acids from triacylglycerol is 7X more active than Pheasant. This also goes for entry to CAC. Pheasant has faster rates for using glycogen and glycolysis. b. What would you predict the oxygen consumption rates for these two birds would be? Pigeon would us more oxygen, a full bore CAC! c ...
... cleaves fatty acids from triacylglycerol is 7X more active than Pheasant. This also goes for entry to CAC. Pheasant has faster rates for using glycogen and glycolysis. b. What would you predict the oxygen consumption rates for these two birds would be? Pigeon would us more oxygen, a full bore CAC! c ...
Slide 1
... In Animals In the presence of oxygen pyruvate is transported into the mitochondria where it enters the next major metabolic pathway for the production of ATP energy. The citric acid cycle. Aerobic. If there is no oxygen present then the pyruvate is converted to a substance called lactate. ...
... In Animals In the presence of oxygen pyruvate is transported into the mitochondria where it enters the next major metabolic pathway for the production of ATP energy. The citric acid cycle. Aerobic. If there is no oxygen present then the pyruvate is converted to a substance called lactate. ...
fatty acids synthesis
... 1. Transport of acetyl CoA into cytosol 2. Carboxylation of acetyl CoA 3. Assembly of fatty acid chain The reactions of fatty acid synthesis all take place in the cytosol, the starting material for synthesis of fatty acid is acetyl CoA which is made in the mitochondria and can't cross the inner memb ...
... 1. Transport of acetyl CoA into cytosol 2. Carboxylation of acetyl CoA 3. Assembly of fatty acid chain The reactions of fatty acid synthesis all take place in the cytosol, the starting material for synthesis of fatty acid is acetyl CoA which is made in the mitochondria and can't cross the inner memb ...
4 TYPES OF LIPIDS Triglycerides, Phospholipids, Waxes, Steroids
... Store energy effectively in C-H bonds ...
... Store energy effectively in C-H bonds ...
MAKEUP: Briefly discuss functions of the liver
... • Once maximal glycogen stores → glucose metabolised to pyruvate → AcetylCoA → fatty acid Cholesterol / phospholipid formation o Protein synthesis Lipoproteins - Catabolic Functions: o CHO: Glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis (via acetyl CoA formation from fatty acid breakdown) → maintain BSL o Fats ...
... • Once maximal glycogen stores → glucose metabolised to pyruvate → AcetylCoA → fatty acid Cholesterol / phospholipid formation o Protein synthesis Lipoproteins - Catabolic Functions: o CHO: Glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis (via acetyl CoA formation from fatty acid breakdown) → maintain BSL o Fats ...
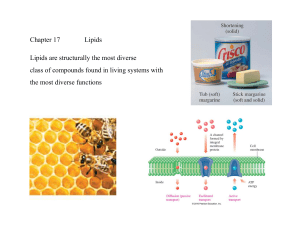
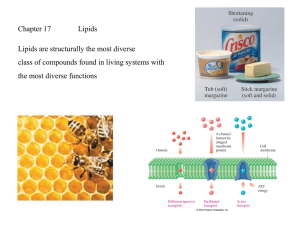
Chapter 17 Lipids Lipids are structurally the most diverse
... Remenber these acids are present as triglycerides in fish oil and other sources ...
... Remenber these acids are present as triglycerides in fish oil and other sources ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5/e
... produced by one round of the citric acid cycle? • CAC: 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, ...
... produced by one round of the citric acid cycle? • CAC: 3 NADH, 1 FADH2, ...
C483 Final Exam Study Guide The final will be held in CH 001 at 8
... 5. Given a name, draw chemical structures of: ATP, all amino acids, all glycolysis intermediates, acetyl CoA, all citric acid cycle intermediates 6. Explain the logic of these pathway regulations: A. Phosphofructokinase, not hexokinase, is the main regulation site of glycolysis. B. SuccinylCoA inhib ...
... 5. Given a name, draw chemical structures of: ATP, all amino acids, all glycolysis intermediates, acetyl CoA, all citric acid cycle intermediates 6. Explain the logic of these pathway regulations: A. Phosphofructokinase, not hexokinase, is the main regulation site of glycolysis. B. SuccinylCoA inhib ...
Grade 12 University Biology
... between the individual carbon atoms of the fatty acid chain. That is, the chain of carbon atoms is fully "saturated" with hydrogen atoms. ...
... between the individual carbon atoms of the fatty acid chain. That is, the chain of carbon atoms is fully "saturated" with hydrogen atoms. ...
2008b(12): Detail the protective and regulatory roles of the liver
... 2008b(12): Detail the protective and regulatory roles of the liver. General: the liver is the largest gland in the body and has multiple functions involved in many essential processes in the body. It is the interface between the gut and the body and therefore has a role in protection from organisms ...
... 2008b(12): Detail the protective and regulatory roles of the liver. General: the liver is the largest gland in the body and has multiple functions involved in many essential processes in the body. It is the interface between the gut and the body and therefore has a role in protection from organisms ...
1 - Chiropractic National Board Review Questions
... D. High-fat levels 18. Which of the following states produces the most fatty acids? A. Starvation B. High carbohydrate diet C. High fatty diet D. High protein diet 19. After Glycogen has been depleted from the body what is the source of carbon? A. Proteins B. Ketones C. Dietary fats D. Endogenous fa ...
... D. High-fat levels 18. Which of the following states produces the most fatty acids? A. Starvation B. High carbohydrate diet C. High fatty diet D. High protein diet 19. After Glycogen has been depleted from the body what is the source of carbon? A. Proteins B. Ketones C. Dietary fats D. Endogenous fa ...
Remediation/Corrections Packet
... 10. ______________ bonds form when water is removed to hold _________ acids together. 11. Describe the four levels of protein structure: a. Primary _________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ b. Seconda ...
... 10. ______________ bonds form when water is removed to hold _________ acids together. 11. Describe the four levels of protein structure: a. Primary _________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ b. Seconda ...
Differential effects of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on tendon
... metabolism by phosphorylating key enzymes including acetyl-CoA carboxylase, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA-reductase, lipase and sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase. We have shown the presence of AMPK at the apical membrane of airway epithelium and a human bronchial epithelial cell line (HBE). H ...
... metabolism by phosphorylating key enzymes including acetyl-CoA carboxylase, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA-reductase, lipase and sn-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase. We have shown the presence of AMPK at the apical membrane of airway epithelium and a human bronchial epithelial cell line (HBE). H ...
Fatty acids in food supplements: Can you assume what you
... In order to determine the distributions of individual fatty acids in your saponified extract, you will need to use a technique that combines a separation component with a detection method. From your Session 2 prelaboratory exercise, you should have found that two suitable methods for achieving this ...
... In order to determine the distributions of individual fatty acids in your saponified extract, you will need to use a technique that combines a separation component with a detection method. From your Session 2 prelaboratory exercise, you should have found that two suitable methods for achieving this ...
File
... 1. Carbonyl carbon of acetyl group to C2 of Malonyl-Acp, lose CO2 with malonyl carboxyl group 2. B-Ketone reduce using NADPH (from PPS) 3. Alchohol dehydrated double bond 4. Double bond reduced to butyryl-ACP from NADPH 5. Butyryl transferred to CE exposing ACP SH site to a 2 nd ...
... 1. Carbonyl carbon of acetyl group to C2 of Malonyl-Acp, lose CO2 with malonyl carboxyl group 2. B-Ketone reduce using NADPH (from PPS) 3. Alchohol dehydrated double bond 4. Double bond reduced to butyryl-ACP from NADPH 5. Butyryl transferred to CE exposing ACP SH site to a 2 nd ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.