Slide 1
... sequential loss of acetyl groups from carbon chain of fatty acid) – Energy yield depends on length of carbon chain (ex. 16C palmitic acid results in 129 ATPs, ~3.5x more than glucose) – Ketoacidosis: results if oxaloacetate in short supply; acetyl-CoA converted into ketones, which are weak acids; ca ...
... sequential loss of acetyl groups from carbon chain of fatty acid) – Energy yield depends on length of carbon chain (ex. 16C palmitic acid results in 129 ATPs, ~3.5x more than glucose) – Ketoacidosis: results if oxaloacetate in short supply; acetyl-CoA converted into ketones, which are weak acids; ca ...
CHE 4310 Fall 2011
... the breakdown of fructose, lactose, or sucrose are defective. However, there are very few cases of people having a genetic disease in which one of the enzymes of glycolysis is severely affected. Why do you suppose such mutations are seen so rarely? ...
... the breakdown of fructose, lactose, or sucrose are defective. However, there are very few cases of people having a genetic disease in which one of the enzymes of glycolysis is severely affected. Why do you suppose such mutations are seen so rarely? ...
Reactions of the TCA Cycle
... Describe different steps of TCA cycle Discuss its biomedical importance Definition TCA cycle, Krebs cycle, citric acid cycle Cyclic process Sequence interMitochondrial matrix, aerobic ...
... Describe different steps of TCA cycle Discuss its biomedical importance Definition TCA cycle, Krebs cycle, citric acid cycle Cyclic process Sequence interMitochondrial matrix, aerobic ...
Metabolism08
... To begin breaking down fat, the body breaks triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids Most of the energy is stored in the fatty acids (glycerol can be converted to glucose or pyruvate) Fatty acids usually produce substantially more ATP than glucose (16 carbon fatty acid = 129 ATP) ...
... To begin breaking down fat, the body breaks triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids Most of the energy is stored in the fatty acids (glycerol can be converted to glucose or pyruvate) Fatty acids usually produce substantially more ATP than glucose (16 carbon fatty acid = 129 ATP) ...
1 - Wsfcs
... What type of molecule is this? __________________ This process is called a ___________________ ______________________. (on board) If you were to break this large molecule apart into the two original glucose molecules, the process would be ______________________ (on board). What would you have to add ...
... What type of molecule is this? __________________ This process is called a ___________________ ______________________. (on board) If you were to break this large molecule apart into the two original glucose molecules, the process would be ______________________ (on board). What would you have to add ...
Year 12 AS Biology Module 1: Biological Molecules Name: PAPER
... Calculate the Rf value of spot X. Show your working. ...
... Calculate the Rf value of spot X. Show your working. ...
File - Principles of Biology 103
... 11. The nonadjacent regions that form to create specific domains is termed: C. Tertiary structure 12. A nucleotide contains: A. A five carbon ring bonded to a nitrogen base and a phosphate group(s) 13. The breakdown of large molecules by the enzymatic addition of water is an example of what kind of ...
... 11. The nonadjacent regions that form to create specific domains is termed: C. Tertiary structure 12. A nucleotide contains: A. A five carbon ring bonded to a nitrogen base and a phosphate group(s) 13. The breakdown of large molecules by the enzymatic addition of water is an example of what kind of ...
Chapter 2
... -consists of glycerol joined to one, two, or three fatty acids -glycerol is a 3 carbon alcohol with 3 –OH groups -fatty acid is a straight chain of carbon atoms with carboxyl groups (-COOH) at one end. -glycerol and fatty acid(s) are joined by an ester bond between the –OH of glycerol and the –COOH ...
... -consists of glycerol joined to one, two, or three fatty acids -glycerol is a 3 carbon alcohol with 3 –OH groups -fatty acid is a straight chain of carbon atoms with carboxyl groups (-COOH) at one end. -glycerol and fatty acid(s) are joined by an ester bond between the –OH of glycerol and the –COOH ...
Practice Exam I
... store energy catalyze reactions contain hereditary information make up membranes ...
... store energy catalyze reactions contain hereditary information make up membranes ...
Metabolism of lipids
... Summary of the flow of electrons and protons through the four complexes of the respiratory chain. Electrons reach CoQ via Complexes I and II. CoQH2 serves as a mobile carrier of electrons and protons. It transfers electrons to Complex III, which transfers them to another mobile connecting link, cyto ...
... Summary of the flow of electrons and protons through the four complexes of the respiratory chain. Electrons reach CoQ via Complexes I and II. CoQH2 serves as a mobile carrier of electrons and protons. It transfers electrons to Complex III, which transfers them to another mobile connecting link, cyto ...
BiochemLectch10[1]
... Many lipids play a passive role for energy storage or as a barrier, some are active and play a role as messengers or signalling molecules such as hormones ...
... Many lipids play a passive role for energy storage or as a barrier, some are active and play a role as messengers or signalling molecules such as hormones ...
Food Chemistry for 1..
... apart if the temperature is higher • Peptide bonds can also be broken apart by acid ...
... apart if the temperature is higher • Peptide bonds can also be broken apart by acid ...
Lecture 1. Introduction to Biochemistry
... chains of phospholipids. The hydroxyl group of cholesterol forms hydrogen bonds with polar phospholipid head groups.However interaction with the relatively rigid cholesterol decreases the mobility of hydrocarbon tails of phospholipids. ...
... chains of phospholipids. The hydroxyl group of cholesterol forms hydrogen bonds with polar phospholipid head groups.However interaction with the relatively rigid cholesterol decreases the mobility of hydrocarbon tails of phospholipids. ...
lipid1
... chains of phospholipids. The hydroxyl group of cholesterol forms hydrogen bonds with polar phospholipid head groups.However interaction with the relatively rigid cholesterol decreases the mobility of hydrocarbon tails of phospholipids. ...
... chains of phospholipids. The hydroxyl group of cholesterol forms hydrogen bonds with polar phospholipid head groups.However interaction with the relatively rigid cholesterol decreases the mobility of hydrocarbon tails of phospholipids. ...
Organic Chem Biology
... storage, are composed of oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen, and are built from glycerol and three fatty acids. ...
... storage, are composed of oxygen, carbon, and hydrogen, and are built from glycerol and three fatty acids. ...
Microbial Metabolism Lipids and Proteins - ASAB-NUST
... • Some bacteria and fungi particularly pathogenic, food spoilage, and soil microorganisms can use proteins as their source of carbon and energy. • They secrete protease enzymes that hydrolyze proteins and polypeptides to amino acids, which are transported into the cell and catabolized ...
... • Some bacteria and fungi particularly pathogenic, food spoilage, and soil microorganisms can use proteins as their source of carbon and energy. • They secrete protease enzymes that hydrolyze proteins and polypeptides to amino acids, which are transported into the cell and catabolized ...
Macromolecules
... • 3 carbon backbone attached to three fatty acids – Saturated – all three fatty acids chains have maximum number of Hydrogen atoms • Butter – Unsaturated – contain less than the maximum number of hydrogen atoms in one or more of its fatty acid chains • fruits ...
... • 3 carbon backbone attached to three fatty acids – Saturated – all three fatty acids chains have maximum number of Hydrogen atoms • Butter – Unsaturated – contain less than the maximum number of hydrogen atoms in one or more of its fatty acid chains • fruits ...
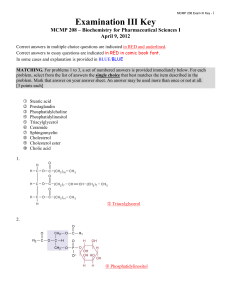
Examination III Key
... Protein prenylation (post-translational addition of an oligo-isoprene to proteins) 27. [6 points] Consider the enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of tyrosine as well as that catalyze the first step in the formation of catecholamines and the formation of serotonin. The substrates for each of these t ...
... Protein prenylation (post-translational addition of an oligo-isoprene to proteins) 27. [6 points] Consider the enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of tyrosine as well as that catalyze the first step in the formation of catecholamines and the formation of serotonin. The substrates for each of these t ...
Biochemistry PPT
... http://www.tv411.org/science/tv411whats-cooking/carbohydrates-sciencelesson/activity/1/1 ...
... http://www.tv411.org/science/tv411whats-cooking/carbohydrates-sciencelesson/activity/1/1 ...
Biochem 462 - public.asu.edu
... About how many protons are pumped into the intermembrane space of the mitochondrion for every oxygen molecule (O2) consumed during oxidation of NADH during oxidative phophorylation (notice this is a whole oxygen molecule we are ...
... About how many protons are pumped into the intermembrane space of the mitochondrion for every oxygen molecule (O2) consumed during oxidation of NADH during oxidative phophorylation (notice this is a whole oxygen molecule we are ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5/e
... Fatty acid synthesis takes place in the compartment in which NADPH is available for reductive synthesis (i.e., where the [NADPH]/[NADP+] ratio is high. The [NADH]/[NAD+] ratio is much smaller, so the NAD+-dependent oxidative catabolism of glucose take place in cytosol. In mitochondria, high [NADH]/[ ...
... Fatty acid synthesis takes place in the compartment in which NADPH is available for reductive synthesis (i.e., where the [NADPH]/[NADP+] ratio is high. The [NADH]/[NAD+] ratio is much smaller, so the NAD+-dependent oxidative catabolism of glucose take place in cytosol. In mitochondria, high [NADH]/[ ...
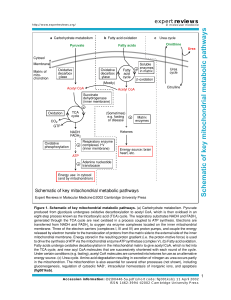
Schematic of key mitochondrial metabolic pathways
... Figure 1. Schematic of key mitochondrial metabolic pathways. (a) Carbohydrate metabolism. Pyruvate produced from glycolysis undergoes oxidative decarboxylation to acetyl CoA, which is then oxidised in an eight-step process known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. The respiratory substrates NADH ...
... Figure 1. Schematic of key mitochondrial metabolic pathways. (a) Carbohydrate metabolism. Pyruvate produced from glycolysis undergoes oxidative decarboxylation to acetyl CoA, which is then oxidised in an eight-step process known as the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. The respiratory substrates NADH ...
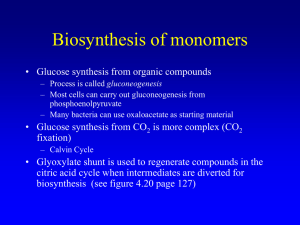
Biosynthesis of monomers
... Biosynthesis of monomers • Glucose synthesis from organic compounds – Process is called gluconeogenesis – Most cells can carry out gluconeogenesis from phosphoenolpyruvate – Many bacteria can use oxaloacetate as starting material ...
... Biosynthesis of monomers • Glucose synthesis from organic compounds – Process is called gluconeogenesis – Most cells can carry out gluconeogenesis from phosphoenolpyruvate – Many bacteria can use oxaloacetate as starting material ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.










![BiochemLectch10[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008282142_1-df4a08b94b9be33b5ca3e78e5274f1db-300x300.png)