Microalgae as source of polyunsaturated fatty acids
... microalgae may have superior lipid stability compared to traditional PUFA because they are naturally rich in antioxidant carotenoids and vitamins and because lipids are microencapsulated by the algae cell wall. ...
... microalgae may have superior lipid stability compared to traditional PUFA because they are naturally rich in antioxidant carotenoids and vitamins and because lipids are microencapsulated by the algae cell wall. ...
Bio102 Problems
... 6. If the environmental temperature increases, it can kill a bacterial cell (which is prokaryotic). Increased temperature can cause many problems for cells, including problems with the cell membrane. A) What problem would increased temperature cause for a membrane? The membrane becomes too permeable ...
... 6. If the environmental temperature increases, it can kill a bacterial cell (which is prokaryotic). Increased temperature can cause many problems for cells, including problems with the cell membrane. A) What problem would increased temperature cause for a membrane? The membrane becomes too permeable ...
File
... There are 20 amino acids that are known to be used to create proteins Humans can only make 10 of those The other 10 must be taken in through diet essential ...
... There are 20 amino acids that are known to be used to create proteins Humans can only make 10 of those The other 10 must be taken in through diet essential ...
Chapter 21 Lipid Biosynthesis
... derivative. Fatty acid breakdown (1) employs NAD+ as electron acceptor; (2) involves acyl groups bound to coenzyme A; (3) occurs in the mitochondrial matrix; (4) does not involve malonylderivatives; (5) involves the L-stereoisomer of the -hydroxyacyl derivative. 14. Biosynthesis of fatty acids and ...
... derivative. Fatty acid breakdown (1) employs NAD+ as electron acceptor; (2) involves acyl groups bound to coenzyme A; (3) occurs in the mitochondrial matrix; (4) does not involve malonylderivatives; (5) involves the L-stereoisomer of the -hydroxyacyl derivative. 14. Biosynthesis of fatty acids and ...
Unit 3: Chemistry of Life
... • Lactose (Glucose + Galactose) • Sucrose (Fructose + Glucose) • Maltose (Glucose + Glucose) ...
... • Lactose (Glucose + Galactose) • Sucrose (Fructose + Glucose) • Maltose (Glucose + Glucose) ...
CP Biology
... FOOD LABELS REVIEW (Use the Food Label Analysis worksheet) 31. What ingredients would tell you carbohydrates are in the food? Simple- sugar, honey, corn syrup, fruit juice, words ending in “ose” ...
... FOOD LABELS REVIEW (Use the Food Label Analysis worksheet) 31. What ingredients would tell you carbohydrates are in the food? Simple- sugar, honey, corn syrup, fruit juice, words ending in “ose” ...
Lipid Metabolism
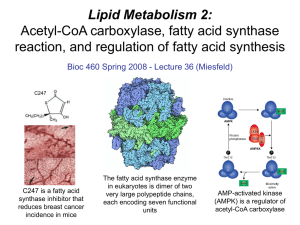
... • Acetyl-CoA carboxylase catalyses carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA via 2-steps reaction. • The enzyme is biotin bound. In mammals acetyl-CoA carboxylase is a large enzyme controlled by conversion inactive ══> active (inactive: protomers (4 subunits; one biotin); active: 1 unit) conversion ...
... • Acetyl-CoA carboxylase catalyses carboxylation of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA via 2-steps reaction. • The enzyme is biotin bound. In mammals acetyl-CoA carboxylase is a large enzyme controlled by conversion inactive ══> active (inactive: protomers (4 subunits; one biotin); active: 1 unit) conversion ...
File
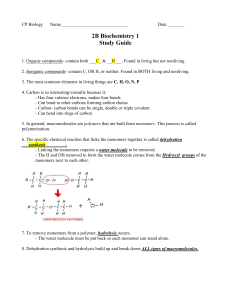
... Macromolecules Structure and Function Test (50 pts) (1 pt each) __ 1. Hydrolysis could be correctly described as the a) heating of a compound to drive off its excess water and concentrate its volume b) breaking of a long-chain compound into its subunits by adding water molecules to its structure bet ...
... Macromolecules Structure and Function Test (50 pts) (1 pt each) __ 1. Hydrolysis could be correctly described as the a) heating of a compound to drive off its excess water and concentrate its volume b) breaking of a long-chain compound into its subunits by adding water molecules to its structure bet ...
Lecture 36 - Lipid Metabolism 2
... • Fatty acid synthesis takes place in the cytosol, uses NADPH as coenzyme in redox reactions, and the building block is malonyl-CoA. • Acetyl-CoA carboxylase is the key regulated enzyme in fatty acid synthesis and is responsible for generating malonyl-CoA in a carboxylation reaction using acetyl-CoA ...
... • Fatty acid synthesis takes place in the cytosol, uses NADPH as coenzyme in redox reactions, and the building block is malonyl-CoA. • Acetyl-CoA carboxylase is the key regulated enzyme in fatty acid synthesis and is responsible for generating malonyl-CoA in a carboxylation reaction using acetyl-CoA ...
AS and A2 Biology resource
... Comparative Anatomy of the Gastro-Intestinal Tract Purpose A resource for A-level Biology students studying the digestive system. It could be used as an extension or homework task. Learning Objectives 1. Compare and discuss the anatomical differences of the digestive tract from different domestic sp ...
... Comparative Anatomy of the Gastro-Intestinal Tract Purpose A resource for A-level Biology students studying the digestive system. It could be used as an extension or homework task. Learning Objectives 1. Compare and discuss the anatomical differences of the digestive tract from different domestic sp ...
2.1 Molecules and metabolism
... • Application: Urea as an example of a compound that is produced by living organisms but can also be artificially synthesized. • Skill: Drawing molecular diagrams of glucose, ribose, a saturated fatty acid and a generalized amino acid. • Skill: Identification of biochemicals such as sugars, lipids o ...
... • Application: Urea as an example of a compound that is produced by living organisms but can also be artificially synthesized. • Skill: Drawing molecular diagrams of glucose, ribose, a saturated fatty acid and a generalized amino acid. • Skill: Identification of biochemicals such as sugars, lipids o ...
Chapter 4: The Chemical Basis of Life
... The four groups of organic compounds found in living things are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids Carbohydrates ________________________________ are the molecules that we often call sugars and starches o Made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms o Sugars are important becaus ...
... The four groups of organic compounds found in living things are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids Carbohydrates ________________________________ are the molecules that we often call sugars and starches o Made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms o Sugars are important becaus ...
Macromolecules Review ws Name the 6 main elements that make
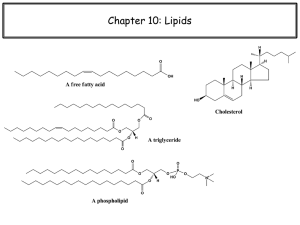
... and three fatty acids chains. This is known as a triglyceride 19. If there are all SINGLE bonds between carbons in the fatty acid chain, then it is said to be saturated ...
... and three fatty acids chains. This is known as a triglyceride 19. If there are all SINGLE bonds between carbons in the fatty acid chain, then it is said to be saturated ...
OILS
... • are the building blocks of many lipids. • are long chain carboxylic acids. • have long nonpolar tails responsible for fatty/oily characteristics. • The carboxyl group is very hydrophilic under conditions of physiological pH (exists as –COO-). ...
... • are the building blocks of many lipids. • are long chain carboxylic acids. • have long nonpolar tails responsible for fatty/oily characteristics. • The carboxyl group is very hydrophilic under conditions of physiological pH (exists as –COO-). ...
5.6. membrane lipids
... • They can be branched and saturated, unsaturated or polyunsaturated (contain ...
... • They can be branched and saturated, unsaturated or polyunsaturated (contain ...
Slides
... • Although humans and other mammals use various biosynthetic pathways to both break down and synthesize lipids, some essential lipids cannot be made this way and must be obtained from the diet. ...
... • Although humans and other mammals use various biosynthetic pathways to both break down and synthesize lipids, some essential lipids cannot be made this way and must be obtained from the diet. ...
Macromolecule Expert Sheets
... 8. How are “hydrogenated oils” changed chemically? (Not in the book! We will discuss this in class.) They have had hydrogen atoms atoms force on to make them more solid (breaking some of the double bonds between carbons), ...
... 8. How are “hydrogenated oils” changed chemically? (Not in the book! We will discuss this in class.) They have had hydrogen atoms atoms force on to make them more solid (breaking some of the double bonds between carbons), ...
Chapter 19 Lipid Metabolism
... Can synthesize fatty acids from sugars, some amino acids, and other fatty acids. →Fatty acids are synthesized from acetyl-CoA in the cytosol. The body synthesizes palmitic acid (16:0), and then modifies it to form other fatty acids. Synthesis of Palmitic Acid 8 acetyl-CoA + 7 ATP +14NADPH +14H+ → pa ...
... Can synthesize fatty acids from sugars, some amino acids, and other fatty acids. →Fatty acids are synthesized from acetyl-CoA in the cytosol. The body synthesizes palmitic acid (16:0), and then modifies it to form other fatty acids. Synthesis of Palmitic Acid 8 acetyl-CoA + 7 ATP +14NADPH +14H+ → pa ...
INTRODUCTORY BIOCHEMISTRY BI 28 Second Midterm
... showed that the production of CO2 by the extract increased when succinate was added. In fact, for every mole of succinate added, many extra moles of CO2 were produced. Explain this effect in terms of the known catabolic pathways. Ans: Succinate is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle that is not ...
... showed that the production of CO2 by the extract increased when succinate was added. In fact, for every mole of succinate added, many extra moles of CO2 were produced. Explain this effect in terms of the known catabolic pathways. Ans: Succinate is an intermediate in the citric acid cycle that is not ...
Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... -starch = glucose polymer in plants used for energy storage ( ...
... -starch = glucose polymer in plants used for energy storage ( ...
Slide 1
... maintenance of life. In metabolism some substances are broken down to yield energy for vital processes while other substances, necessary for life, are synthesized. B. Polymers – a large molecule that is made up of many small molecules linked (covalent bonds) together. 1. Dehydration synthesis – when ...
... maintenance of life. In metabolism some substances are broken down to yield energy for vital processes while other substances, necessary for life, are synthesized. B. Polymers – a large molecule that is made up of many small molecules linked (covalent bonds) together. 1. Dehydration synthesis – when ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.