Control of intra-cellular (enzyme regulator)
... polysaccharides reside inside organelles called lysosomes. Fatty acid biosynthesis occurs in the cytosol, whereas fatty acid oxidation takes place within mitochondria Segregation of certain metabolic pathways within specialized cell types can provide further physical compartmentation. ...
... polysaccharides reside inside organelles called lysosomes. Fatty acid biosynthesis occurs in the cytosol, whereas fatty acid oxidation takes place within mitochondria Segregation of certain metabolic pathways within specialized cell types can provide further physical compartmentation. ...
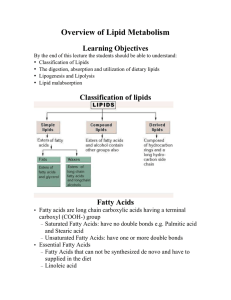
Overview of Lipid Metabolism
... Lipid transport from intestinal mucosa • Once inside the intestinal mucosal cells, the absorbed lipids are resynthesized into TG and CE ( cholesterol esters ) • Intestinal cells synthesize apolipoprotein B-48 and package TG and CE into Chylomicrons • Chylomicrons are secreted first into the lymphat ...
... Lipid transport from intestinal mucosa • Once inside the intestinal mucosal cells, the absorbed lipids are resynthesized into TG and CE ( cholesterol esters ) • Intestinal cells synthesize apolipoprotein B-48 and package TG and CE into Chylomicrons • Chylomicrons are secreted first into the lymphat ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5/e
... Plant peroxisome and glyoxysome use acetyl-CoA from boxation as a biosynthetic precursor 1. In plant, fatty acid oxidation does not occur primarily in mitochondria but in the peroxisomes of leaf tissue and in the glyoxysomes of ...
... Plant peroxisome and glyoxysome use acetyl-CoA from boxation as a biosynthetic precursor 1. In plant, fatty acid oxidation does not occur primarily in mitochondria but in the peroxisomes of leaf tissue and in the glyoxysomes of ...
Answer
... 47. Are lipids polar or nonpolar? What happens to lipids when they are placed in water? Non polar, they separate from water 48. Compared to carbohydrates, what is true about the ratio of carbon & hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms? If a compound has more bonds, what can it store more of in those bonds? ...
... 47. Are lipids polar or nonpolar? What happens to lipids when they are placed in water? Non polar, they separate from water 48. Compared to carbohydrates, what is true about the ratio of carbon & hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms? If a compound has more bonds, what can it store more of in those bonds? ...
Chapter 5 - glenbrook s hs
... Ester linkage: 3 fatty acids to 1 glycerol (dehydration formation) Triacyglycerol (triglyceride) Saturated vs. unsaturated fats; single vs. double bonds ...
... Ester linkage: 3 fatty acids to 1 glycerol (dehydration formation) Triacyglycerol (triglyceride) Saturated vs. unsaturated fats; single vs. double bonds ...
Correlation - EngineeringDuniya.com
... Glucose is phosphorylated to glucose-6-phosphate by enzyme glucokinase •In hepatocytes……it can undergo one of the following metabolic pathways depending upon current metabolic needs. •It is dephosphorylated to glucose by glucose-6-phosphatase to replenish blood sugar. ...
... Glucose is phosphorylated to glucose-6-phosphate by enzyme glucokinase •In hepatocytes……it can undergo one of the following metabolic pathways depending upon current metabolic needs. •It is dephosphorylated to glucose by glucose-6-phosphatase to replenish blood sugar. ...
Fatty Acid Catabolism - LSU School of Medicine
... rescue! – produces a trans- Δ3 enoyl product. This enoyl product can be converted by an enoylCoA isomerase to the trans- Δ2 enoyl CoA, which then proceeds normally through the beta-oxidation pathway. ...
... rescue! – produces a trans- Δ3 enoyl product. This enoyl product can be converted by an enoylCoA isomerase to the trans- Δ2 enoyl CoA, which then proceeds normally through the beta-oxidation pathway. ...
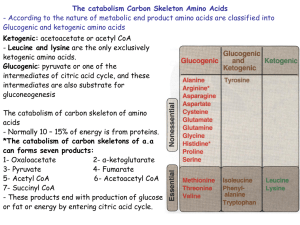
The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
... The catabolism Carbon Skeleton Amino Acids - According to the nature of metabolic end product amino acids are classified into Glucogenic and ketogenic amino acids Ketogenic: acetoacetate or acetyl CoA - Leucine and lysine are the only exclusively ketogenic amino acids. Glucogenic: pyruvate or one of ...
Hein and Arena - University of Wisconsin–Eau Claire
... • Vegetable oils, on the other hand, are liquids at room temperature because they contain a high percentage of unsaturated fatty acid residues and have melting points below room temperature. ...
... • Vegetable oils, on the other hand, are liquids at room temperature because they contain a high percentage of unsaturated fatty acid residues and have melting points below room temperature. ...
File
... • The unifying feature of lipids is having little or no affinity for water • Lipids are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons, which form nonpolar covalent bonds • The most biologically important lipids are fats, phospholipids, and steroids © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • The unifying feature of lipids is having little or no affinity for water • Lipids are hydrophobic because they consist mostly of hydrocarbons, which form nonpolar covalent bonds • The most biologically important lipids are fats, phospholipids, and steroids © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Human Physiology
... sides of the double bond, that is, one “up” and one “down” across from each other. • Naturally-occurring unsaturated vegetable oils have almost all cis bonds, but using oil for frying causes some of the cis bonds to convert to trans bonds ...
... sides of the double bond, that is, one “up” and one “down” across from each other. • Naturally-occurring unsaturated vegetable oils have almost all cis bonds, but using oil for frying causes some of the cis bonds to convert to trans bonds ...
Chapter 5: Microbial Metabolism
... a. Oxidation-reduction: A coupled reaction in which one substance is oxidized and one is reduced. b. The final electron acceptor in aerobic respiration is molecular oxygen; in anaerobic respiration, it is another inorganic molecule. c. In cyclic photophosphorylation, electrons are returned to chloro ...
... a. Oxidation-reduction: A coupled reaction in which one substance is oxidized and one is reduced. b. The final electron acceptor in aerobic respiration is molecular oxygen; in anaerobic respiration, it is another inorganic molecule. c. In cyclic photophosphorylation, electrons are returned to chloro ...
Chapter 29 Biosynthetic Pathways 308 29.1 Your text states in
... a nitrogen base, uracil; a sugar, ribose; and three phosphates. 29.14 The carbon atoms used in fatty acid synthesis have their origin in acetyl CoA. 29.15 (a) The biosynthesis of fatty acids occurs primarily in the cell cytoplasm. Here acetyl CoA is used to make palmitoyl CoA. Extension of the carbo ...
... a nitrogen base, uracil; a sugar, ribose; and three phosphates. 29.14 The carbon atoms used in fatty acid synthesis have their origin in acetyl CoA. 29.15 (a) The biosynthesis of fatty acids occurs primarily in the cell cytoplasm. Here acetyl CoA is used to make palmitoyl CoA. Extension of the carbo ...
lipids
... • Simple triacylglycerols are composed of three identical fatty acid side chains • mixed triacylglycerols have two or three different fatty acids. What are the characteristics of these fatty acids? • All fatty acid chains are unbranched, but they may be saturated or unsaturated. • Naturally occur ...
... • Simple triacylglycerols are composed of three identical fatty acid side chains • mixed triacylglycerols have two or three different fatty acids. What are the characteristics of these fatty acids? • All fatty acid chains are unbranched, but they may be saturated or unsaturated. • Naturally occur ...
Quantitative Analysis of Stearic Acid in Vulcanized Styrene
... acid content. There exists a need for a quantitative analytical method for the determination of stearic acid in rubber. This report illustrates two methods which can be used for the measurement of stearic acid in styrene butadiene rubber (SBR): thermal desorption (TD)-GC/MS and reactive thermal deso ...
... acid content. There exists a need for a quantitative analytical method for the determination of stearic acid in rubber. This report illustrates two methods which can be used for the measurement of stearic acid in styrene butadiene rubber (SBR): thermal desorption (TD)-GC/MS and reactive thermal deso ...
Slide 1 - Denton ISD
... Nitrogenous bases of DNA are Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine and Thymine. In RNA Uracil replaces Thymine. structurally similar to fats but a phosphate group replaces one of the fatty acid chains, thus giving this molecule a POLAR and NONPOLAR region. Structurally form two layers to create the plasma memb ...
... Nitrogenous bases of DNA are Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine and Thymine. In RNA Uracil replaces Thymine. structurally similar to fats but a phosphate group replaces one of the fatty acid chains, thus giving this molecule a POLAR and NONPOLAR region. Structurally form two layers to create the plasma memb ...
Biochemistry - Circle of Docs
... a. ATP b. GTP and FADH2 c. ATP and NADH d. FADH2 and NADH 25. The most common way to enter the Krebs cycle for amino acids, fatty acids, and glucose is a. Citrate b. Acetyl-CoA c. Oxaloacetate d. Pyruvate 26. The rate limiting step of cholesterol synthesis is a. HMG CoA Mevalonate 27. Glucose 6 phos ...
... a. ATP b. GTP and FADH2 c. ATP and NADH d. FADH2 and NADH 25. The most common way to enter the Krebs cycle for amino acids, fatty acids, and glucose is a. Citrate b. Acetyl-CoA c. Oxaloacetate d. Pyruvate 26. The rate limiting step of cholesterol synthesis is a. HMG CoA Mevalonate 27. Glucose 6 phos ...
Ch7METABOLISM
... Most of the energy is stored in the fatty acids (glycerol can be converted to glucose or pyruvate) Fatty acids cannot be converted to glucose Fatty acids usually produce substantially more energy than glucose ...
... Most of the energy is stored in the fatty acids (glycerol can be converted to glucose or pyruvate) Fatty acids cannot be converted to glucose Fatty acids usually produce substantially more energy than glucose ...
Fatty Acid Biosynthesis
... R-CH2CH2CH2CCH2C~SCoA O O 1 NADPH Elongation systems are NADH found in smooth ER and 2 - H2O ...
... R-CH2CH2CH2CCH2C~SCoA O O 1 NADPH Elongation systems are NADH found in smooth ER and 2 - H2O ...
NATURE`S BIOLOGICAL BUILDING BLOCKS
... Includes fatty, greasy and waxy compounds relatively insoluble in water, but soluble in organic solvents such as ether and benzene. Neutral Fats - high energy molecules consisting of glycerol and fatty acids. Phospholipids - neutral fat with one fatty acid molecule replaced by phosphate, choline, or ...
... Includes fatty, greasy and waxy compounds relatively insoluble in water, but soluble in organic solvents such as ether and benzene. Neutral Fats - high energy molecules consisting of glycerol and fatty acids. Phospholipids - neutral fat with one fatty acid molecule replaced by phosphate, choline, or ...
LB Fat metabolism A
... Thus, unlike carbohydrates and protein, most lipids do not use the enterohepatic circulatory system. This allows lipids to be cleared by the whole body and avoids overwhelming the liver with lipid. ...
... Thus, unlike carbohydrates and protein, most lipids do not use the enterohepatic circulatory system. This allows lipids to be cleared by the whole body and avoids overwhelming the liver with lipid. ...
Practice Exam II
... FSHN 167 Practice Exam II 1. Which of the following describes a fatty acid that has one double bond? a. Saturated b. Hydrogenated c. Monounsaturated d. Polyunsaturated 2. During the first few days of a fast, what energy source provides about 90% of the glucose needed to fuel the body? a. Protein b. ...
... FSHN 167 Practice Exam II 1. Which of the following describes a fatty acid that has one double bond? a. Saturated b. Hydrogenated c. Monounsaturated d. Polyunsaturated 2. During the first few days of a fast, what energy source provides about 90% of the glucose needed to fuel the body? a. Protein b. ...
Biological Molecules wHelp Sheet
... 2. Which type of molecule includes an example with a long-chain carbon backbone? 3. In the molecule referred to in the previous question, what is the dominant element attached to the carbon backbone? 4. The fatty acid chain of the lipids is often referred to as a hydrocarbon chain. Discuss with your ...
... 2. Which type of molecule includes an example with a long-chain carbon backbone? 3. In the molecule referred to in the previous question, what is the dominant element attached to the carbon backbone? 4. The fatty acid chain of the lipids is often referred to as a hydrocarbon chain. Discuss with your ...
Fatty acid synthesis

Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors through action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. It is an important part of the lipogenesis process, which – together with glycolysis – functions to create fats from blood sugar in living organisms.