Quizon ch5-6-7-8new.doc
... 1. Which of the following processes does a cell use to take up molecules against their concentration gradient? a. simple diffusion b. facilitated diffusion c. active transport d. endocytosis e. Both the c and d are correct. 2. Proteins which act as catalysts of chemical reactions [in cells] are call ...
... 1. Which of the following processes does a cell use to take up molecules against their concentration gradient? a. simple diffusion b. facilitated diffusion c. active transport d. endocytosis e. Both the c and d are correct. 2. Proteins which act as catalysts of chemical reactions [in cells] are call ...
Food Utilization
... • Ingested chemical used for growth, repair or maintenance • Macronutrients • Micronutrients • Recommended daily allowances (RDA) – safe estimate of daily intake for standard needs • Essential nutrients can not be synthesized – minerals, vitamins, 8 amino acids and 1-3 fatty acids ...
... • Ingested chemical used for growth, repair or maintenance • Macronutrients • Micronutrients • Recommended daily allowances (RDA) – safe estimate of daily intake for standard needs • Essential nutrients can not be synthesized – minerals, vitamins, 8 amino acids and 1-3 fatty acids ...
FRESHMEN
... Lead(II) chromate is used as a yellow pigment to designate traffic lanes, but has been banned from house paint because of the potential for lead poisoning. The compound from chromite (FeCr2O4), an ore of chromium: FeCr2O4 (s) + K2CO3 (aq) + O2 (g) Fe2O3 (s) + K2CrO4 (aq) + CO2 (g) Lead(II) ion the ...
... Lead(II) chromate is used as a yellow pigment to designate traffic lanes, but has been banned from house paint because of the potential for lead poisoning. The compound from chromite (FeCr2O4), an ore of chromium: FeCr2O4 (s) + K2CO3 (aq) + O2 (g) Fe2O3 (s) + K2CrO4 (aq) + CO2 (g) Lead(II) ion the ...
Inorganic Chemistry PP
... • The study of carbon compounds (C) atomic number = 6 mass number = 12 • There > 100 elements • Living organisms are composed of almost entirely six elements. P, C, H, O, N, S ...
... • The study of carbon compounds (C) atomic number = 6 mass number = 12 • There > 100 elements • Living organisms are composed of almost entirely six elements. P, C, H, O, N, S ...
RESEARCH NOTES
... Wild type Neuro~oro crow 74-OR23-1A (FGSC”987) was grown on Vogel’s medium N with 2% ogor ot 25’C for 5 days. The conidio were harvested o&T&red to remove myceliol frogments. An oliquot of the resulting suspension was dried ot 55’C and the volume of the suspension was adjusted to obtain a concentrat ...
... Wild type Neuro~oro crow 74-OR23-1A (FGSC”987) was grown on Vogel’s medium N with 2% ogor ot 25’C for 5 days. The conidio were harvested o&T&red to remove myceliol frogments. An oliquot of the resulting suspension was dried ot 55’C and the volume of the suspension was adjusted to obtain a concentrat ...
Carbohydrate PPT Notes
... – Bond to form larger sugars • Polymer: Polysaccharide – Complex sugars ...
... – Bond to form larger sugars • Polymer: Polysaccharide – Complex sugars ...
Slide 1
... •Bond between amino acids called peptide bond •After protein is formed it is shaped and folded in order to carry out a specific function ...
... •Bond between amino acids called peptide bond •After protein is formed it is shaped and folded in order to carry out a specific function ...
amino acids - 11 College Biology
... “KINKS” made in the fatty acid chains allow for space. Liquid at room temperature. Example: olive oil ...
... “KINKS” made in the fatty acid chains allow for space. Liquid at room temperature. Example: olive oil ...
Exam IV answers
... The uptake of dietary amino acids by enterocytes is coupled to potassium export by these cells. Sodium Non-essential amino acids are ones that in a healthy young adult are not needed for protein synthesis. Can be synthesized in sufficient amounts to maintain homeostasis The transamination of lysine ...
... The uptake of dietary amino acids by enterocytes is coupled to potassium export by these cells. Sodium Non-essential amino acids are ones that in a healthy young adult are not needed for protein synthesis. Can be synthesized in sufficient amounts to maintain homeostasis The transamination of lysine ...
Sample Free Response Biochem Answers
... a) Explain why the two different enzymes are needed for the synthesis of glycogen from glucose phosphate (2) There are two separate linkages in glycogen – the 14 linkage and the 16 linkages. Specificity in protein design requires two separate proteins – the active site is specifically tailored for ...
... a) Explain why the two different enzymes are needed for the synthesis of glycogen from glucose phosphate (2) There are two separate linkages in glycogen – the 14 linkage and the 16 linkages. Specificity in protein design requires two separate proteins – the active site is specifically tailored for ...
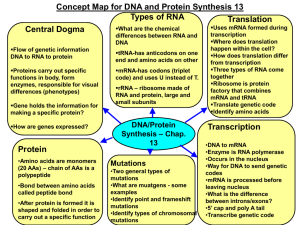
LEARNING GOALS - PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Main Idea
... LEARNING GOALS - PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Main Idea: 3.A.1: DNA, and in some cases RNA, is the primary source of heritable information. a. The sequence of RNA bases, together with the structure of the RNA ...
... LEARNING GOALS - PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Main Idea: 3.A.1: DNA, and in some cases RNA, is the primary source of heritable information. a. The sequence of RNA bases, together with the structure of the RNA ...
The Molecules of Life
... Misfolded proteins are associated with many diseases, including some severe nervous system disorders Some treatments can cause proteins to lose their 3-D shape The change can be reversible or irreversible ...
... Misfolded proteins are associated with many diseases, including some severe nervous system disorders Some treatments can cause proteins to lose their 3-D shape The change can be reversible or irreversible ...
Dan`s poster - The University of Sheffield
... Nitrogen, a key resource for plants, is required for the synthesis of proteins and many other important types of molecule. Amino acids are the major ‘nitrogen currency’ of plants, being translocated between different cells and to different organs in response to the needs of the plant. This places gr ...
... Nitrogen, a key resource for plants, is required for the synthesis of proteins and many other important types of molecule. Amino acids are the major ‘nitrogen currency’ of plants, being translocated between different cells and to different organs in response to the needs of the plant. This places gr ...
Representations of 3D Structures
... lengths/angles and standard information about atom-atom interactions such as minimum distance (i.e. Van der Waals radii) •With all this information you can generate a model of the structure. Important: NMR gives you a number of possible solutions (all almost identical, rmsd <1Å), This can range from ...
... lengths/angles and standard information about atom-atom interactions such as minimum distance (i.e. Van der Waals radii) •With all this information you can generate a model of the structure. Important: NMR gives you a number of possible solutions (all almost identical, rmsd <1Å), This can range from ...
The Molecules of Life
... Misfolded proteins are associated with many diseases, including some severe nervous system disorders Some treatments can cause proteins to lose their 3-D shape The change can be reversible or irreversible ...
... Misfolded proteins are associated with many diseases, including some severe nervous system disorders Some treatments can cause proteins to lose their 3-D shape The change can be reversible or irreversible ...
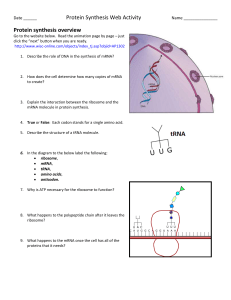
Crossword Puzzle: Protein Synthesis
... 3. Sequence of nucleotides on DNA to with RNA polymerase will attach to start transcription 4. mRNA copying DNA's nucleotide sequence 5. 3 nucleotides on tRNA that match to a specific codon on mRNA 6. Type of RNA that helps make up ribosomes 7. Instructions for making proteins in cells 14. The numbe ...
... 3. Sequence of nucleotides on DNA to with RNA polymerase will attach to start transcription 4. mRNA copying DNA's nucleotide sequence 5. 3 nucleotides on tRNA that match to a specific codon on mRNA 6. Type of RNA that helps make up ribosomes 7. Instructions for making proteins in cells 14. The numbe ...