Modern Biology: Chapter 3
... • Organic compounds – primarily Carbon atoms – Large, complex molecules essential for life – Contributes to diversity of life ...
... • Organic compounds – primarily Carbon atoms – Large, complex molecules essential for life – Contributes to diversity of life ...
File
... organic compounds • Anything made up of carbon is called ORGANIC • Carbon forms 4 covalent bonds (form different arrangements of atoms: straight, branched, rings) ...
... organic compounds • Anything made up of carbon is called ORGANIC • Carbon forms 4 covalent bonds (form different arrangements of atoms: straight, branched, rings) ...
amino acid - proffittscience
... The basic structure of the amino acids is common. There are 22 different protein-making amino acids, though only 20 are coded for in genetic code. Each has its own unique R-group. Some are polar, others non-polar and their different properties determine their interactions and the shape of the final ...
... The basic structure of the amino acids is common. There are 22 different protein-making amino acids, though only 20 are coded for in genetic code. Each has its own unique R-group. Some are polar, others non-polar and their different properties determine their interactions and the shape of the final ...
dopamineSummary
... Tyrosine (Tyr or Y) is a non-essential amino acid that can be synthesized in the human body from the amino acid phenylalanine. Tyrosine is composed of the standard amino acid backbone with an aromatic ring containing a hydroxyl (OH) group on the fourth carbon of the ring. Version 1.4 -11/2015 ...
... Tyrosine (Tyr or Y) is a non-essential amino acid that can be synthesized in the human body from the amino acid phenylalanine. Tyrosine is composed of the standard amino acid backbone with an aromatic ring containing a hydroxyl (OH) group on the fourth carbon of the ring. Version 1.4 -11/2015 ...
35 Amino acid breakdown Amino acids comprise one of the three
... The later steps vary depending on the structure of the amino acid. Isoleucine is metabolized by reactions identical to those in a b-oxidation spiral, yielding an acetyl-CoA and a propionyl-CoA. The metabolism of valine is slightly more complex, but the pathway also results in propionyl-CoA. Propion ...
... The later steps vary depending on the structure of the amino acid. Isoleucine is metabolized by reactions identical to those in a b-oxidation spiral, yielding an acetyl-CoA and a propionyl-CoA. The metabolism of valine is slightly more complex, but the pathway also results in propionyl-CoA. Propion ...
Transcription and Translation
... made at a *If the protein is going to be packaged for use outside the cell, it will be made on a ribosome attached to the ...
... made at a *If the protein is going to be packaged for use outside the cell, it will be made on a ribosome attached to the ...
molecular biology and phylogeny
... similarities in nuclear DNA, mitochondrial DNA, or protein structure, can be used to produce cladograms also. If there is strong agreement between the patterns produced using anatomical similarities and those produced by using biochemical structures, it provides what we call "independent confirmatio ...
... similarities in nuclear DNA, mitochondrial DNA, or protein structure, can be used to produce cladograms also. If there is strong agreement between the patterns produced using anatomical similarities and those produced by using biochemical structures, it provides what we call "independent confirmatio ...
Protein structure - Manning`s Science
... joins with the OH from the carboxyl group. This forms a water molecule. The Nitrogen atom them combines with the carbon atom forming a peptide bond. ...
... joins with the OH from the carboxyl group. This forms a water molecule. The Nitrogen atom them combines with the carbon atom forming a peptide bond. ...
WP2: Diets with varying amount and amino acid composition
... implications for the treatment of obesity and metabolic diseases [14]. Compared to white fat, BAT is more metabolically active and burns off energy to heat and it has been suggested that dietary increased brown fat metabolism may induce weight loss – where high leucine may be one dietary factor acti ...
... implications for the treatment of obesity and metabolic diseases [14]. Compared to white fat, BAT is more metabolically active and burns off energy to heat and it has been suggested that dietary increased brown fat metabolism may induce weight loss – where high leucine may be one dietary factor acti ...
Study Guide Test 3 * Organic Chemistry
... The characteristics of the side chain (polar or non-polar) will determine how they interact and cause the polypeptide to fold up into a complex structure (2nd, 3rd and 4th levels of structure). 8. What is meant by the phrase “a proteins’ function is determined by its shape” Without a specific shape, ...
... The characteristics of the side chain (polar or non-polar) will determine how they interact and cause the polypeptide to fold up into a complex structure (2nd, 3rd and 4th levels of structure). 8. What is meant by the phrase “a proteins’ function is determined by its shape” Without a specific shape, ...
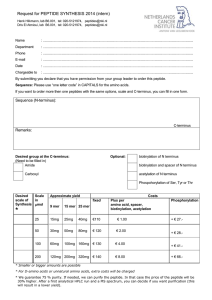
Scale - Netherlands Cancer Institute
... By submitting you declare that you have permission from your group leader to order this peptide. Sequence: Please use “one letter code” in CAPITALS for the amino acids. If you want to order more then one peptides with the same options, scale and C-terminus, you can fill in one form. ...
... By submitting you declare that you have permission from your group leader to order this peptide. Sequence: Please use “one letter code” in CAPITALS for the amino acids. If you want to order more then one peptides with the same options, scale and C-terminus, you can fill in one form. ...
Protein Synthesis Test Review
... Directions: Use your notes and examples to complete the review. Study until you are sure you’ll make an A, and then continue to study for another 20 minutes after that time (studying does NOT consist of staring at the review and/or putting your head down on the review….we have covered osmosis…it onl ...
... Directions: Use your notes and examples to complete the review. Study until you are sure you’ll make an A, and then continue to study for another 20 minutes after that time (studying does NOT consist of staring at the review and/or putting your head down on the review….we have covered osmosis…it onl ...
Enzymes
... proper membrane permeability and fluidity. In addition, cholesterol is an important component for the manufacture of bile acids, steroid hormones, and Vitamin D. ...
... proper membrane permeability and fluidity. In addition, cholesterol is an important component for the manufacture of bile acids, steroid hormones, and Vitamin D. ...
Fall `94
... (4) Once amine groups are removed, the carbon skeletons of amino acids can be catabolized much like carbohydrates. The most common amino acid is alanine; if it is transaminated, what product remains? __________________. How much energy, in integral ATP units, can be gained by oxidizing this product ...
... (4) Once amine groups are removed, the carbon skeletons of amino acids can be catabolized much like carbohydrates. The most common amino acid is alanine; if it is transaminated, what product remains? __________________. How much energy, in integral ATP units, can be gained by oxidizing this product ...
LAB-AIDS^ #505-12 Molecules ot Lite Kit Student
... enzymes or hormones. Proteins always contain nitrogen in addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Phosphorus and sulfur are also found in many proteins. The amino acid is the basic structural unit of all proteins. There are only about 20 different amino acids known to exist in proteins; all of them ...
... enzymes or hormones. Proteins always contain nitrogen in addition to carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Phosphorus and sulfur are also found in many proteins. The amino acid is the basic structural unit of all proteins. There are only about 20 different amino acids known to exist in proteins; all of them ...
macromolecule_sheets
... 2. How does the number of H atoms in a carbohydrate compare to the number of oxygen atoms? 3. What is the simplest type of carbohydrate? 4. What two functional groups are found in monosaccharides? 5. Name three common monosaccharides and give the molecular formula for each. 6. What suffix is commonl ...
... 2. How does the number of H atoms in a carbohydrate compare to the number of oxygen atoms? 3. What is the simplest type of carbohydrate? 4. What two functional groups are found in monosaccharides? 5. Name three common monosaccharides and give the molecular formula for each. 6. What suffix is commonl ...
Macromolecules Worksheet
... polypeptide or protein_ 8. What is a long chain of amino acids called? covalent_ 9. What type of bond involves the sharing of electrons? deoxyribose_ 10. What sugar does DNA contain? base or alkaline_ 11. When the pH is greater than 7, it is called this. ribose_ 12. What sugar does RNA contain? elec ...
... polypeptide or protein_ 8. What is a long chain of amino acids called? covalent_ 9. What type of bond involves the sharing of electrons? deoxyribose_ 10. What sugar does DNA contain? base or alkaline_ 11. When the pH is greater than 7, it is called this. ribose_ 12. What sugar does RNA contain? elec ...
A1 B1 C1 D1 A2 B2 C2 D2 A1 B1 C1 A2 B2 C2
... The model that results from this activity is very simplistic, but shows the three-dimensional structure of proteins. Depending on the level of the students, the exact chemical properties of the amino acids may be discussed (hydrophobic and hydrophilic, polar and nonpolar). Because amino acids are ri ...
... The model that results from this activity is very simplistic, but shows the three-dimensional structure of proteins. Depending on the level of the students, the exact chemical properties of the amino acids may be discussed (hydrophobic and hydrophilic, polar and nonpolar). Because amino acids are ri ...
View PDF - OMICS International
... Proteins are vital for health. They act like saviour of each cell by participating in all anabolic as well catabolic processes in the body. They are known to build the muscle mass and repair the damaged cells. However, the human body has limited capacity to store excess protein hence need regular su ...
... Proteins are vital for health. They act like saviour of each cell by participating in all anabolic as well catabolic processes in the body. They are known to build the muscle mass and repair the damaged cells. However, the human body has limited capacity to store excess protein hence need regular su ...