Biological Molecules
... Insoluble in water, though soluble in organic compounds such as ethanol. Saturated and unsaturated, refers to wether or not the maximum number of hydrogen bonds have been formed. Used as an excellent energy source (more calorific than carbs) and insulation, and bouyancy in marine life. ...
... Insoluble in water, though soluble in organic compounds such as ethanol. Saturated and unsaturated, refers to wether or not the maximum number of hydrogen bonds have been formed. Used as an excellent energy source (more calorific than carbs) and insulation, and bouyancy in marine life. ...
Transcription & Translation PowerPoint
... A certain gene codes for a polypeptide that is 120 amino acids long. Approximately how many nucleotides long is the mRNA that codes for this polypeptide likely to be? A. ...
... A certain gene codes for a polypeptide that is 120 amino acids long. Approximately how many nucleotides long is the mRNA that codes for this polypeptide likely to be? A. ...
How Does DNA Determine the Traits of a SNORK
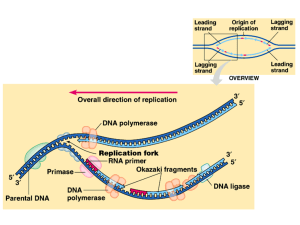
... 1) Where in the cell is the DNA located? _________________________ 2) Helicase does what to the DNA? ___________________________________ 3) Only one side of the DNA is copied. What is this side called? ____________________ 4) What is the side that is NOT copied called? ______________________________ ...
... 1) Where in the cell is the DNA located? _________________________ 2) Helicase does what to the DNA? ___________________________________ 3) Only one side of the DNA is copied. What is this side called? ____________________ 4) What is the side that is NOT copied called? ______________________________ ...
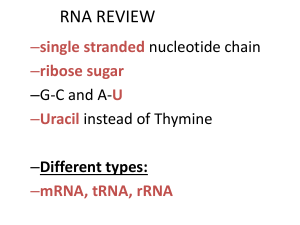
RNA and protein synthesis
... Protein synthesis occurs in two major parts transcription and translation. 1. Transcription: Process where DNA serves as a template to produce complementary mRNA 2. Translation: Process in which mRNA is used to link amino acids together to synthesize proteins. Involves tRNA and rRNA DNA ...
... Protein synthesis occurs in two major parts transcription and translation. 1. Transcription: Process where DNA serves as a template to produce complementary mRNA 2. Translation: Process in which mRNA is used to link amino acids together to synthesize proteins. Involves tRNA and rRNA DNA ...
Amino Acid Metabolism
... Metabolic Pool of Amino Acids • Metabolic pool AA has no storage form in mammals (as with other life forms) as free AA or as specialized storage form (such as glycogen for glucose, TG for FA) but a certain percentage of muscle & structural proteins are “expendable”. • AA are used for proteins, N co ...
... Metabolic Pool of Amino Acids • Metabolic pool AA has no storage form in mammals (as with other life forms) as free AA or as specialized storage form (such as glycogen for glucose, TG for FA) but a certain percentage of muscle & structural proteins are “expendable”. • AA are used for proteins, N co ...
1 Amino Acid Metabolism
... Metabolic Pool of Amino Acids • Metabolic pool AA has no storage form in mammals (as with other life forms) as free AA or as specialized storage form (such as glycogen for glucose, TG for FA) but a certain percentage of muscle & structural proteins are “expendable”. • AA are used for proteins, N co ...
... Metabolic Pool of Amino Acids • Metabolic pool AA has no storage form in mammals (as with other life forms) as free AA or as specialized storage form (such as glycogen for glucose, TG for FA) but a certain percentage of muscle & structural proteins are “expendable”. • AA are used for proteins, N co ...
AMINO ACIDS METABOLISM ** Dr. Mohammed Abdullateef **
... of free ammonia. This includes the reduction of protein in the diet, removal of excess ammonia, and replacement of intermediates missing from the urea ...
... of free ammonia. This includes the reduction of protein in the diet, removal of excess ammonia, and replacement of intermediates missing from the urea ...
III B.Sc. (CHEMISTRY) MODEL CURRICULUM FOR
... definition of isoelectric point. Chemical properties: General reactions due to amino and carboxyl groups – lactams from gamma and delta amino acids by heating peptide bond (amide linkage). Structure and nomenclature of peptides and proteins.(Elementary treatment only) Unit-III (physical chemistry- V ...
... definition of isoelectric point. Chemical properties: General reactions due to amino and carboxyl groups – lactams from gamma and delta amino acids by heating peptide bond (amide linkage). Structure and nomenclature of peptides and proteins.(Elementary treatment only) Unit-III (physical chemistry- V ...
Macromolecules Quiz
... Matching--Select the macromolecule that best matches the statement. Letters may be used once, more than once or not at all. a. Proteins b. Carbohydrates c. Lipids d. Nucleic Acids 1. These macromolecules possess large nonpolar regions making them insoluble in water. 2. This macromolecule is compose ...
... Matching--Select the macromolecule that best matches the statement. Letters may be used once, more than once or not at all. a. Proteins b. Carbohydrates c. Lipids d. Nucleic Acids 1. These macromolecules possess large nonpolar regions making them insoluble in water. 2. This macromolecule is compose ...
30_General pathways of amino acids transformation
... active dehydrogenase Present in both the cytosol and mitochondria of the liver ...
... active dehydrogenase Present in both the cytosol and mitochondria of the liver ...
called “organic molecules”
... (pH,temperature) can cause the protein to unravel.This is called “denaturation” ...
... (pH,temperature) can cause the protein to unravel.This is called “denaturation” ...
Protein Synthesis Continued
... Notice on the chart on p. 303 that several sequences code for “STOP” These are used to start or stop protein sythesis ...
... Notice on the chart on p. 303 that several sequences code for “STOP” These are used to start or stop protein sythesis ...
Macromolecules Notes File
... RNA carries the genetic code from the nucleus to the ribosomes where proteins are constructed ______________________________ (ATP) supplies energy to the cell. Other nucleotides and dinucleotides act as electron carriers and energy transfer molecules ...
... RNA carries the genetic code from the nucleus to the ribosomes where proteins are constructed ______________________________ (ATP) supplies energy to the cell. Other nucleotides and dinucleotides act as electron carriers and energy transfer molecules ...
C483 Final Exam Study Guide The final will be held in CH 001 at 8
... molecule that you store in your liver. Circle the pathways/cycles below that are part of this overall transformation. Cross out any that are not. Gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, glycogen synthesis, glycolysis, citric acid cycle B. Trace the metabolic path of this glutamate molecule throu ...
... molecule that you store in your liver. Circle the pathways/cycles below that are part of this overall transformation. Cross out any that are not. Gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, glycogen synthesis, glycolysis, citric acid cycle B. Trace the metabolic path of this glutamate molecule throu ...
prepex3
... Start your studies by knowing how amino acids are prepared for metabolism. Know what is meant by a 26S proteosome, the 20S proteosome, the N-rule, reactions involved in protein ubiquination. Know the mechanism of an aminotransferase, the role of glutamate/-Kg pair in the reaction, the different for ...
... Start your studies by knowing how amino acids are prepared for metabolism. Know what is meant by a 26S proteosome, the 20S proteosome, the N-rule, reactions involved in protein ubiquination. Know the mechanism of an aminotransferase, the role of glutamate/-Kg pair in the reaction, the different for ...
Protein Synthesis Translation
... Peptide bonds are formed between the amino acids creating a growing polypeptide Polypeptide = protein Protein molecule ...
... Peptide bonds are formed between the amino acids creating a growing polypeptide Polypeptide = protein Protein molecule ...
BCAA 4:1:1 - ProAction
... the processes of protein synthesis and degradation, we need to be aware that insulin, IGF-1 and GH influence these same processes too. The effect may be due to the vasodilation induced by the production of nitric oxide, stimulated by the guanylyl cyclase on the capillary endothelium - an important c ...
... the processes of protein synthesis and degradation, we need to be aware that insulin, IGF-1 and GH influence these same processes too. The effect may be due to the vasodilation induced by the production of nitric oxide, stimulated by the guanylyl cyclase on the capillary endothelium - an important c ...
Introduction to metabolism. Specific and general pathways of
... • Metabolite early in the pathway activates an enzyme further down the pathway ...
... • Metabolite early in the pathway activates an enzyme further down the pathway ...
Chapter 2-1 The Nature of Matter
... there is no oxidation so no speedy release of products. The inhibition is called competitive because if you increase the ratio of succinic to malonic acid in the mixture, you will gradually restore the rate of catalysis. At a 50:1 ratio, the two molecules compete on roughly equal terms for the bindi ...
... there is no oxidation so no speedy release of products. The inhibition is called competitive because if you increase the ratio of succinic to malonic acid in the mixture, you will gradually restore the rate of catalysis. At a 50:1 ratio, the two molecules compete on roughly equal terms for the bindi ...
Protein Metabolism
... (1) are synthesised in the body if an adequate amount is not present in the diet. (2) They are 11 amino acids, 10 of them can be produced from glucose, 11the one (tyrosine) is synthesised from essential amino acids (phenylalanine). Note:- one of 10 amino acids derived from glucose (cysteine) obtains ...
... (1) are synthesised in the body if an adequate amount is not present in the diet. (2) They are 11 amino acids, 10 of them can be produced from glucose, 11the one (tyrosine) is synthesised from essential amino acids (phenylalanine). Note:- one of 10 amino acids derived from glucose (cysteine) obtains ...