2-A Chemical Compounds of Life Organic Compounds
... polymer + H2O 2.Hydrolysis: when large molecules are broken down, water must be ...
... polymer + H2O 2.Hydrolysis: when large molecules are broken down, water must be ...
Structural Genomics - University of Houston
... a positive and a negative charge Because of their ionic nature they have extremely high melting temperatures ...
... a positive and a negative charge Because of their ionic nature they have extremely high melting temperatures ...
Ch. 3 Review Guide
... Explain the processes of dehydration synthesis and the process of hydrolysis ...
... Explain the processes of dehydration synthesis and the process of hydrolysis ...
Complementation with wild type MamL-EGFP rescued 62
... S1 Text. Amino acid substitutions within MamL MamL contains nine basic and potentially positively charged (including histidine) amino acid residues close to or at its very C-terminus. The C-terminal accumulation of basic residues is a conserved feature in MamL and MamL-like homologs from other MTB ( ...
... S1 Text. Amino acid substitutions within MamL MamL contains nine basic and potentially positively charged (including histidine) amino acid residues close to or at its very C-terminus. The C-terminal accumulation of basic residues is a conserved feature in MamL and MamL-like homologs from other MTB ( ...
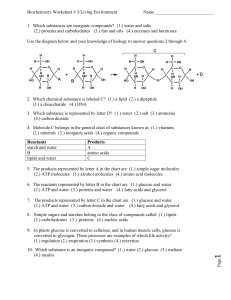
1. Which substances are inorganic compounds?
... (3.) flufferfication (4.) aerobic respiration 13. The reverse reaction indicated by arrow E illustrates (1.) chemical digestion (2.) synthesis (3.) flufferfication (4.) aerobic respiration ...
... (3.) flufferfication (4.) aerobic respiration 13. The reverse reaction indicated by arrow E illustrates (1.) chemical digestion (2.) synthesis (3.) flufferfication (4.) aerobic respiration ...
Modern Biology: Chapter 3
... – (CH2O)n general formula n = 3–8 monosaccharides – Hundreds of glucose monomers make glycogen (animals) or starch & cellulose (plants) ...
... – (CH2O)n general formula n = 3–8 monosaccharides – Hundreds of glucose monomers make glycogen (animals) or starch & cellulose (plants) ...
Amino acid catabolism I
... 2. deamination of other compounds N-containing side chains of nucleotides neurotransmitters 3. ammonia production in the large intestine by bacteria portal vein, direct transport of ammonia. Urea cycle Function: 1. prevents ammonia levels from rising too high when large amounts of amino acids are ca ...
... 2. deamination of other compounds N-containing side chains of nucleotides neurotransmitters 3. ammonia production in the large intestine by bacteria portal vein, direct transport of ammonia. Urea cycle Function: 1. prevents ammonia levels from rising too high when large amounts of amino acids are ca ...
Translation
... must then be translated into _____________. The processes of transcription and translation together are called _________________________. The process of transcription occurs in the ____________ of a cell. Translation occurs at the ______________, which can be found free in the cytoplasm or attached ...
... must then be translated into _____________. The processes of transcription and translation together are called _________________________. The process of transcription occurs in the ____________ of a cell. Translation occurs at the ______________, which can be found free in the cytoplasm or attached ...
Chapter 3 An Introduction to Organic Compounds - Linn
... Sometimes denaturation is reversible (sometimes not) ...
... Sometimes denaturation is reversible (sometimes not) ...
Analytical Questions
... deleted, the mutation will affect, not only that particular codon, but all subsequent codons since these will now have lost their original triplet groupings. This is called a frameshift mutation and following the frameshift different amino acids will be specified. This could by chance lead to the pr ...
... deleted, the mutation will affect, not only that particular codon, but all subsequent codons since these will now have lost their original triplet groupings. This is called a frameshift mutation and following the frameshift different amino acids will be specified. This could by chance lead to the pr ...
Amino Acid and Nucleobase Synthesis in Meteoritic Parent Bodies
... provides natural frequency of amino acids for first code. 2. Earliest code used smaller repertoire of amino acids – each with larger no. of codons – stripped down version of ours. - Lowest cost amino acids (eg. G) found in most highly ...
... provides natural frequency of amino acids for first code. 2. Earliest code used smaller repertoire of amino acids – each with larger no. of codons – stripped down version of ours. - Lowest cost amino acids (eg. G) found in most highly ...
Chapter 14 Proteins
... Isoelectric point, pI: The pH at which the majority of molecules of a compound in solution have no net charge. ...
... Isoelectric point, pI: The pH at which the majority of molecules of a compound in solution have no net charge. ...
Chapter 3 Protein Synthesis Life Science RNA – Ribonucleic Acid
... How to determine which codon codes for which one of the 20 different amino acids: 1. Find the 1st base on the left side of the table. 2. The middle base is then located on the top of the table. Where they intersect determines the 4 possible outcomes. 3. Find the 3rd base on the right side of the tab ...
... How to determine which codon codes for which one of the 20 different amino acids: 1. Find the 1st base on the left side of the table. 2. The middle base is then located on the top of the table. Where they intersect determines the 4 possible outcomes. 3. Find the 3rd base on the right side of the tab ...
CHE 4310 Fall 2011
... their breath had an uncharacteristic sweet smell, what disease might the patient have? ...
... their breath had an uncharacteristic sweet smell, what disease might the patient have? ...
CHE 4310 Fall 2011
... their breath had an uncharacteristic sweet smell, what disease might the patient have? ...
... their breath had an uncharacteristic sweet smell, what disease might the patient have? ...
Lecture Notes
... 2) Pyrimidines - smaller, single-ring molecules, and include cytosine (C) in DNA and RNA, thymine (T) in DNA, and uracil (U) in RNA. Nucleic acid polymers are formed when the phosphate group of one nucleotide binds to the hydroxyl group of another, releasing water and forming a phosphodiester bond. ...
... 2) Pyrimidines - smaller, single-ring molecules, and include cytosine (C) in DNA and RNA, thymine (T) in DNA, and uracil (U) in RNA. Nucleic acid polymers are formed when the phosphate group of one nucleotide binds to the hydroxyl group of another, releasing water and forming a phosphodiester bond. ...
Complete Protein - Kelloggs Nutrition
... Proteins, along with carbohydrates and fats, make up the bulk of our diet. We tend to think of proteins as body builders, and they are;; they form the structure of things like muscle, hair and connective tissue. They also make up hormones that regulate our system, enzymes that trigger chemical react ...
... Proteins, along with carbohydrates and fats, make up the bulk of our diet. We tend to think of proteins as body builders, and they are;; they form the structure of things like muscle, hair and connective tissue. They also make up hormones that regulate our system, enzymes that trigger chemical react ...
protein - 4J Blog Server
... at any level can affect the activity of the protein. • How proteins reach their final shape (conformation), the denaturing impact that heat and pH can have on protein structure, and how these may affect the organism. • The directionality of proteins (the amino and carboxyl ends). ...
... at any level can affect the activity of the protein. • How proteins reach their final shape (conformation), the denaturing impact that heat and pH can have on protein structure, and how these may affect the organism. • The directionality of proteins (the amino and carboxyl ends). ...
Ch.2-3 & 3 Notes - Green Local Schools
... • Organic cmpds: contain C atoms bonded to other elements such as H, O, & N • Functional groups: influence properties of a molecule – Ex: -NH2 for amino acids ...
... • Organic cmpds: contain C atoms bonded to other elements such as H, O, & N • Functional groups: influence properties of a molecule – Ex: -NH2 for amino acids ...
Biology Unit 2 Organic Notes The Chemistry of Carbon Organic
... Lipids can be used to store energy. Some lipids are important parts of biological membranes and waterproof coverings. ...
... Lipids can be used to store energy. Some lipids are important parts of biological membranes and waterproof coverings. ...