Proteins
... A series of amino acids in a polypeptide chain Produced from the coding in the DNA of the nucleus Makes up 50% of the dry mass of cells Each cell may contain thousands of different proteins Each protein has a different task determined by shape They have the widest variety of structure and functions ...
... A series of amino acids in a polypeptide chain Produced from the coding in the DNA of the nucleus Makes up 50% of the dry mass of cells Each cell may contain thousands of different proteins Each protein has a different task determined by shape They have the widest variety of structure and functions ...
Biochemistry Ch 37 696-706 [4-20
... intracellular proteins for degradation by covalently binding to E-amino group of lysine residues accomplished by a 3 enzyme system -target is often polyubiquitinylated, forming long ubiquitin tails -a proteasome complex then degrades the targeted protein and releasing intact ubiquitin that can mark ...
... intracellular proteins for degradation by covalently binding to E-amino group of lysine residues accomplished by a 3 enzyme system -target is often polyubiquitinylated, forming long ubiquitin tails -a proteasome complex then degrades the targeted protein and releasing intact ubiquitin that can mark ...
File
... Similar in composition to lipids, but structurally composed of interconnected carbon rings Most common steroid is cholesterol Used to create sex hormones, hormones from the adrenal cortex, and vitamin D Found in large amounts in nerve tissue Component of gallstones ...
... Similar in composition to lipids, but structurally composed of interconnected carbon rings Most common steroid is cholesterol Used to create sex hormones, hormones from the adrenal cortex, and vitamin D Found in large amounts in nerve tissue Component of gallstones ...
Chapter 17 (part 2) - University of Nevada, Reno
... • Amino acid can be catabolized in muscle tissue where carbon skeletons are oxidized for energy. • Must remove toxic ammonia and transport to liver where it can be converted to urea. • Amino group from Glu is transferred to pyruvate to form alanine. • Alanine is exported to the liver via the blood s ...
... • Amino acid can be catabolized in muscle tissue where carbon skeletons are oxidized for energy. • Must remove toxic ammonia and transport to liver where it can be converted to urea. • Amino group from Glu is transferred to pyruvate to form alanine. • Alanine is exported to the liver via the blood s ...
PowerPoint
... formation of chlorophyll • Cell membrane destruction Many common herbicides have this mode of action!! • Ultra Blazer, Cobra, Goal, Reflex, Ronstar, Resource, Aim, Valor, Storm, Spartan, ET ...
... formation of chlorophyll • Cell membrane destruction Many common herbicides have this mode of action!! • Ultra Blazer, Cobra, Goal, Reflex, Ronstar, Resource, Aim, Valor, Storm, Spartan, ET ...
Biomolecules
... result of functional groups • Functional groups maintain chemical properties no matter where they occur • Polar molecules are hydrophilic • Nonpolar molecules are hydrophobic • The degree to which organic molecules interact with water affects their function • Hydroxyl group (-OH) is one of the most ...
... result of functional groups • Functional groups maintain chemical properties no matter where they occur • Polar molecules are hydrophilic • Nonpolar molecules are hydrophobic • The degree to which organic molecules interact with water affects their function • Hydroxyl group (-OH) is one of the most ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 3. Write the components that are involved in the synthesis of acetyl coenzyme A. 4. What would be the decarboxylated product of pyruvate in glycolysis? Mention the structure. 5. Define glycosuria. 6. What are ketone bodies? When and how are they formed in the body? 7. Calculate the energitics for pa ...
... 3. Write the components that are involved in the synthesis of acetyl coenzyme A. 4. What would be the decarboxylated product of pyruvate in glycolysis? Mention the structure. 5. Define glycosuria. 6. What are ketone bodies? When and how are they formed in the body? 7. Calculate the energitics for pa ...
Proteins - chem.uwec.edu
... At lower pH values the carbolylate group becomes protonated and the amino acid has a net charge of +1. b. At higher pH values the amino group becomes unprotonated and the amino acid has a net charge of -1. ...
... At lower pH values the carbolylate group becomes protonated and the amino acid has a net charge of +1. b. At higher pH values the amino group becomes unprotonated and the amino acid has a net charge of -1. ...
Course Name:
... The Faculty of Pharmacy offers two biochemistry courses to satisfy the needs of the Pharmacy students in this area. The first course covers the area of metabolism and biosynthesis of the biological molecules. The two courses have common aims and objectives. ...
... The Faculty of Pharmacy offers two biochemistry courses to satisfy the needs of the Pharmacy students in this area. The first course covers the area of metabolism and biosynthesis of the biological molecules. The two courses have common aims and objectives. ...
Exam1_actual
... 1. (4 points) The artificial sweetener NutraSweet®, also called aspartame, is a simple dipeptide, aspartylphenylalanine methyl ester, on which the free carboxyl of the dipeptide is esterified to methyl alcohol. Draw the structure of aspartame, showing the ionizable groups in the form they have at pH ...
... 1. (4 points) The artificial sweetener NutraSweet®, also called aspartame, is a simple dipeptide, aspartylphenylalanine methyl ester, on which the free carboxyl of the dipeptide is esterified to methyl alcohol. Draw the structure of aspartame, showing the ionizable groups in the form they have at pH ...
Handout (Original Version).
... Biochemical characteristics, like similarities in nuclear DNA, mitochondrial DNA, or protein structure, can be used to produce cladograms also. If there is strong agreement between the patterns produced using anatomical similarities and those produced by using biochemical structures, it provides wha ...
... Biochemical characteristics, like similarities in nuclear DNA, mitochondrial DNA, or protein structure, can be used to produce cladograms also. If there is strong agreement between the patterns produced using anatomical similarities and those produced by using biochemical structures, it provides wha ...
What is a Protein?
... Proteins are a vital part of both the structure and function of your body. The sequence of amino acids in a protein as well as the specific folding of each determines the final function of the protein. Proteins break down or are used up continuously in living organisms. Therefore new proteins have t ...
... Proteins are a vital part of both the structure and function of your body. The sequence of amino acids in a protein as well as the specific folding of each determines the final function of the protein. Proteins break down or are used up continuously in living organisms. Therefore new proteins have t ...
Figure 18.19 Regulation of a metabolic pathway
... The control of gene expression enable individual bacteria to adjust their metabolism to environmental change ...
... The control of gene expression enable individual bacteria to adjust their metabolism to environmental change ...
document
... Phenylalanine, valine, trptophan, threonine, isoleucine, methionine, histidine, arginine (neonate-child), leucine, lysine ...
... Phenylalanine, valine, trptophan, threonine, isoleucine, methionine, histidine, arginine (neonate-child), leucine, lysine ...
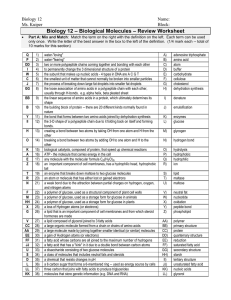
Biology 12 - Biologically Important Molecules – Review Worksheet
... the linear sequence of amino acids in a protein, which ultimately determines its shape the building block of protein -- there are 20 different kinds normally found in nature the bond that forms between two amino acids joined by dehydration synthesis the 3-D shape of a polypeptide chain due to it fol ...
... the linear sequence of amino acids in a protein, which ultimately determines its shape the building block of protein -- there are 20 different kinds normally found in nature the bond that forms between two amino acids joined by dehydration synthesis the 3-D shape of a polypeptide chain due to it fol ...
MolBioIntro
... proteins – tRNA acts in translation of biological macromolecules from the language of nucleic acids to amino acids ...
... proteins – tRNA acts in translation of biological macromolecules from the language of nucleic acids to amino acids ...
Chemistry in Biology - Welcome to teachers.olatheschools.com!
... 12---DESCRIBE the role of carbon in living organisms ...
... 12---DESCRIBE the role of carbon in living organisms ...
CHEM 121 Winter 2017
... Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: [email protected] ...
... Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: [email protected] ...