biologically important molecules
... into GLYCOGEN for storage. GLUCAGON hormone causes GLYCOGEN to be hydrolyzed back into individual glucose monomers and released into the bloodstream where it is transported to cells and used for energy. ...
... into GLYCOGEN for storage. GLUCAGON hormone causes GLYCOGEN to be hydrolyzed back into individual glucose monomers and released into the bloodstream where it is transported to cells and used for energy. ...
REVIEW Protein Synthesis with Analogies
... chance by using e-mail or fax to send his plans to the factory. They might be stolen by industrial spies! Donald knows his loyal brother would do anything for him, so he asks him to be a messenger and carry the plans to the factory. At the factory, the assembly line is set up and factory workers bri ...
... chance by using e-mail or fax to send his plans to the factory. They might be stolen by industrial spies! Donald knows his loyal brother would do anything for him, so he asks him to be a messenger and carry the plans to the factory. At the factory, the assembly line is set up and factory workers bri ...
Modern Biology: Chapter 3
... – Has 4 valence electrons – Can form single, double, or triple covalent bonds – Can form straight or branched chains of itself – Can form rings of itself ...
... – Has 4 valence electrons – Can form single, double, or triple covalent bonds – Can form straight or branched chains of itself – Can form rings of itself ...
Carbon Isomers
... – Functional units within a larger structure – Most proteins made of multiple domains that perform different parts of the protein’s function ...
... – Functional units within a larger structure – Most proteins made of multiple domains that perform different parts of the protein’s function ...
Name 1 Bio 451 12th November, 1999 EXAM III This
... glutaminase, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of glutamine to ammonia and glutamate, is high. Explain the metabolic significance of these tissue-specific differences in enzyme levels. ...
... glutaminase, which catalyzes the hydrolysis of glutamine to ammonia and glutamate, is high. Explain the metabolic significance of these tissue-specific differences in enzyme levels. ...
Model Description Sheet
... MppP is a PLP-Dependent L-Arginine α-deaminase, γ-Hydroxylase in the Enduracididine Biosynthetic Pathway. Biochemistry 54(47): 7029-7040. Format: Alpha carbon backbone RP: Zcorp with plaster Description: Antibiotic-resistant bacteria are common and hard to treat. There is potential to create synthet ...
... MppP is a PLP-Dependent L-Arginine α-deaminase, γ-Hydroxylase in the Enduracididine Biosynthetic Pathway. Biochemistry 54(47): 7029-7040. Format: Alpha carbon backbone RP: Zcorp with plaster Description: Antibiotic-resistant bacteria are common and hard to treat. There is potential to create synthet ...
AP Biology
... 1. What is a polymer and what are the building blocks of polymers called? Give an example of each? 2. Explain the process of dehydration synthesis. Why is hydrolysis the opposite of dehydration synthesis? 3. There is a tremendous variety of macromolecules found in living organisms. What is the basis ...
... 1. What is a polymer and what are the building blocks of polymers called? Give an example of each? 2. Explain the process of dehydration synthesis. Why is hydrolysis the opposite of dehydration synthesis? 3. There is a tremendous variety of macromolecules found in living organisms. What is the basis ...
lecture notes-molecular biology-cell regulation
... maximum transcription if a carbon-energy source (e.g. glucose) preferred to lactose is present. • Only when glucose is depleted, the cell will expend energy to create a pathway to utilize the less favorable carbon-energy source lactose. ...
... maximum transcription if a carbon-energy source (e.g. glucose) preferred to lactose is present. • Only when glucose is depleted, the cell will expend energy to create a pathway to utilize the less favorable carbon-energy source lactose. ...
Name Due date ______ Strive for a 5 – AP Biology Review Unit 1
... 20. A student added a strong acid to a beaker containing a solution with a functional protein. After adding the acid, the protein no longer functioned. Explain how adding the acid altered the protein’s structure and function. Be sure to include the following terms in your answer: protons, 3D structu ...
... 20. A student added a strong acid to a beaker containing a solution with a functional protein. After adding the acid, the protein no longer functioned. Explain how adding the acid altered the protein’s structure and function. Be sure to include the following terms in your answer: protons, 3D structu ...
河北交通职业技术学院教案 Lesion 5 Alcoholic Beverages (1) 课题引
... 二、例文中第二段的翻译学习(时间:15 分钟) Molasses or starch hydrolysates are generally used for commercial production of 糖蜜或者淀粉水解物通常被用来进行谷氨酸棒状杆菌和相关菌系的谷氨酸商品生产 ...
... 二、例文中第二段的翻译学习(时间:15 分钟) Molasses or starch hydrolysates are generally used for commercial production of 糖蜜或者淀粉水解物通常被用来进行谷氨酸棒状杆菌和相关菌系的谷氨酸商品生产 ...
Organic vs. Inorganic
... enzyme that can break down a long protein into smaller chains called peptides • Amylases - breaks down starch chains into ...
... enzyme that can break down a long protein into smaller chains called peptides • Amylases - breaks down starch chains into ...
1 - Chiropractic National Board Review Questions
... 23. Ketones results from? A. Glycolysis of glucose B. Gluconeogenesis of amino acids C. Beta oxidation D. Incomplete oxidation of fats 24. Which are pyrimidines? A. Uracil, cytosine B. Thiamine, adnine C. Adnine, guanine D. Guanine, cytosine 25. What type of bond holds DNA strands together A. H B. E ...
... 23. Ketones results from? A. Glycolysis of glucose B. Gluconeogenesis of amino acids C. Beta oxidation D. Incomplete oxidation of fats 24. Which are pyrimidines? A. Uracil, cytosine B. Thiamine, adnine C. Adnine, guanine D. Guanine, cytosine 25. What type of bond holds DNA strands together A. H B. E ...
BHS 150.1 – Biochemistry II Date: 2/8/2013, 2sndhalf Notetaker: Kim
... 12. Ascorbate in the aqueous is needed by the cornea for which two of the following functions: antioxidant properties collagen synthesis 13. A missense mutation occurs when the: amino acid sequence changes 14. During fasting, what are some possible sources of carbons for gluconeogenesis: amino acids ...
... 12. Ascorbate in the aqueous is needed by the cornea for which two of the following functions: antioxidant properties collagen synthesis 13. A missense mutation occurs when the: amino acid sequence changes 14. During fasting, what are some possible sources of carbons for gluconeogenesis: amino acids ...
Describe in simple terms the chemical nature of sugars, proteins
... When the pH level varies from the normal range, the carbonic acid-bicarbonate system allows the body to automatically balance out the pH level. It converts the strong acids and bases to weak acids and bases. ...
... When the pH level varies from the normal range, the carbonic acid-bicarbonate system allows the body to automatically balance out the pH level. It converts the strong acids and bases to weak acids and bases. ...
Getting the inside running on enzymes
... or understanding the way in which we can turn molecules or biochemical pathways on and off. These findings may also inform the design of new antibiotic therapies.” chemical reactions and the rate at which the chemical reaction takes place needs to be regulated and controlled. “You don’t want an enzy ...
... or understanding the way in which we can turn molecules or biochemical pathways on and off. These findings may also inform the design of new antibiotic therapies.” chemical reactions and the rate at which the chemical reaction takes place needs to be regulated and controlled. “You don’t want an enzy ...
Download PDF
... capture, proton and ion gradients, and conversion to mechanical energy. In addition, we will explore the thermodynamics of electron transport, proton pumping, and ATP biosynthesis. 3. Molecular biosynthesis. Most organisms can biosynthesize amino acids, lipids, nucleotides, vitamins, and cofactors u ...
... capture, proton and ion gradients, and conversion to mechanical energy. In addition, we will explore the thermodynamics of electron transport, proton pumping, and ATP biosynthesis. 3. Molecular biosynthesis. Most organisms can biosynthesize amino acids, lipids, nucleotides, vitamins, and cofactors u ...
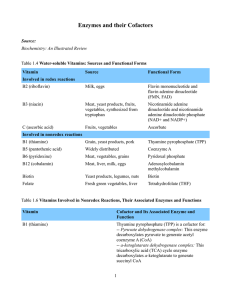
Enzymes and their Cofactors Source: Biochemistry: An Illustrated
... degrades odd-numbered fatty acids -- Methionine synthase/homocysteine methyltransferase: This enzyme transfers a methyl group from 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (N5-methylTHF) onto homocysteine to form methionine. Methionine reacts with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to generate S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) ...
... degrades odd-numbered fatty acids -- Methionine synthase/homocysteine methyltransferase: This enzyme transfers a methyl group from 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (N5-methylTHF) onto homocysteine to form methionine. Methionine reacts with adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to generate S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) ...