Chapter 3 Review Questions
... 10. _____Lipids___________ are a source of long-term stored energy. 11. Organic molecules that have the same chemical formula but different structural arrangements are called __isomers_________. 12. Carbohydrates are important because they __are the main source of energy for living things. 13. Meat, ...
... 10. _____Lipids___________ are a source of long-term stored energy. 11. Organic molecules that have the same chemical formula but different structural arrangements are called __isomers_________. 12. Carbohydrates are important because they __are the main source of energy for living things. 13. Meat, ...
Amino Acids 14.5 * 14.8
... Thyroxine differs from tyrosine. ‾ Has extra iodine-containing aromatic group on the side chain. ‾ Found only in the thyroid gland. ...
... Thyroxine differs from tyrosine. ‾ Has extra iodine-containing aromatic group on the side chain. ‾ Found only in the thyroid gland. ...
Regulation
... Assimilation of inorganic nitrogen: glutamic dehydrogenase vs. glutamine synthetase and glutamate synthetase. Glutamine synthetase (GS) composed of 12 identical subunits, each subunit has 8 distinct allosteric sites (96 potential allosteric sites). To have cumulative feedback inhibition GS must be c ...
... Assimilation of inorganic nitrogen: glutamic dehydrogenase vs. glutamine synthetase and glutamate synthetase. Glutamine synthetase (GS) composed of 12 identical subunits, each subunit has 8 distinct allosteric sites (96 potential allosteric sites). To have cumulative feedback inhibition GS must be c ...
List of protein families currently covered by SVMProt
... Appendix S2 Method for computing the feature vector of a protein sequence A protein sequence is represented by specific feature vector assembled from encoded representations of tabulated residue properties including amino acid composition, hydrophobicity, normalized Van der Waals volume, polarity, p ...
... Appendix S2 Method for computing the feature vector of a protein sequence A protein sequence is represented by specific feature vector assembled from encoded representations of tabulated residue properties including amino acid composition, hydrophobicity, normalized Van der Waals volume, polarity, p ...
Arginine is actively transported into Neurospow
... previously accumulated arginine occurs either in the Alanine ...
... previously accumulated arginine occurs either in the Alanine ...
AP Biology 042 – Biological Molecules Video
... monomers together in a certain sequence/order they have a. The process of “putting monomers together” is called b. What is lost during the process of #11? c. What kind of bond is formed generally? Specifically between amino acids of a protein? d. What must be added to break the bonds? e. What is the ...
... monomers together in a certain sequence/order they have a. The process of “putting monomers together” is called b. What is lost during the process of #11? c. What kind of bond is formed generally? Specifically between amino acids of a protein? d. What must be added to break the bonds? e. What is the ...
Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry 5/e
... The ammonia generated in this process is recycled and used in a variety of biosynthetic pathway The excess is either excreted directly or converted to urea or uric acid for excretion Excess ammonia generated in other tissues travels to the liver for conversion to the excretory form In cytosol of hep ...
... The ammonia generated in this process is recycled and used in a variety of biosynthetic pathway The excess is either excreted directly or converted to urea or uric acid for excretion Excess ammonia generated in other tissues travels to the liver for conversion to the excretory form In cytosol of hep ...
Unit Topic: Chemistry of Life
... 4. Draw how polymers break down to form monomers through hydrolysis reaction ...
... 4. Draw how polymers break down to form monomers through hydrolysis reaction ...
Exam1
... 4. In an aqueous solution, protein conformation is determined by two major factors. One is the formation of the maximum number of hydrogen bonds. The other is the: A) formation of the maximum number of hydrophilic interactions. B) maximization of ionic interactions. C) minimization of entropy by the ...
... 4. In an aqueous solution, protein conformation is determined by two major factors. One is the formation of the maximum number of hydrogen bonds. The other is the: A) formation of the maximum number of hydrophilic interactions. B) maximization of ionic interactions. C) minimization of entropy by the ...
Lecture 6 POWERPOINT here
... A complex pathway can further be regulated by a number of different feedback mechanisms - both up regulation and down regulation, feedback inhibition and feedback initiation, and other more complex interactions. ...
... A complex pathway can further be regulated by a number of different feedback mechanisms - both up regulation and down regulation, feedback inhibition and feedback initiation, and other more complex interactions. ...
carbon skeleton
... All organisms assimilate ammonia via two main reactions catalyed by glutamate dehydrogenase and glutamine synthetase giving rise to Glu and Gln, respectively. The amino nitrogen in Glu and Gln are then used in further biosynthetic reactions to give rise to other amino acids. ...
... All organisms assimilate ammonia via two main reactions catalyed by glutamate dehydrogenase and glutamine synthetase giving rise to Glu and Gln, respectively. The amino nitrogen in Glu and Gln are then used in further biosynthetic reactions to give rise to other amino acids. ...
Molecules of Life Review Topics
... functions: structure, transport, defense, movement, messengers, catalysts monomer – amino acid: carbon, amino, carboxyl, H and variable (R group) R group – how many – 20; important – cross links hold 3-D shape of protein Peptide bond- covalent, between amino acids Dipeptide, polypeptide – ...
... functions: structure, transport, defense, movement, messengers, catalysts monomer – amino acid: carbon, amino, carboxyl, H and variable (R group) R group – how many – 20; important – cross links hold 3-D shape of protein Peptide bond- covalent, between amino acids Dipeptide, polypeptide – ...
Chemistry/Biochemistry Review
... 23. Single units/building blocks of polymers 24. Type of lipid that is solid at room temperature 25. Supply main/primary source of energy for cells 26. The 4 macromolecules of life 27. Glucose, fructose and galactose are examples of 28. The process of forming large compounds by joining together smal ...
... 23. Single units/building blocks of polymers 24. Type of lipid that is solid at room temperature 25. Supply main/primary source of energy for cells 26. The 4 macromolecules of life 27. Glucose, fructose and galactose are examples of 28. The process of forming large compounds by joining together smal ...
Four Amino Acids Are Converted to Succinyl
... Homocysteine • Homocysteine has two fates. • If there is a deficiency of methionine, homocysteine may be remethylated to methionine. If methionine stores are adequate, homocysteine may enter the transsulfuration pathway, where it is converted to cysteine. • Homocysteine condenses with serine, formi ...
... Homocysteine • Homocysteine has two fates. • If there is a deficiency of methionine, homocysteine may be remethylated to methionine. If methionine stores are adequate, homocysteine may enter the transsulfuration pathway, where it is converted to cysteine. • Homocysteine condenses with serine, formi ...
02_-_translation___mutation_intro - Ms.Holli
... 4) Where does transcription take place in the cell? ...
... 4) Where does transcription take place in the cell? ...
Cut and Paste Macromolecule Instructions
... glucoses together by cutting off and -H- from one molecule and an -OH- from another and taping the 2 molecules together forming a glyosidic bond. Give your disaccharide a name, bearing in mind that sugar names end in “-ose” (glucose, fructose) and write that name on the bottom of the molecule. 3. Th ...
... glucoses together by cutting off and -H- from one molecule and an -OH- from another and taping the 2 molecules together forming a glyosidic bond. Give your disaccharide a name, bearing in mind that sugar names end in “-ose” (glucose, fructose) and write that name on the bottom of the molecule. 3. Th ...
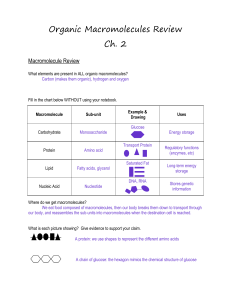
Organic Macromolecules Review Ch. 2
... The top picture shows a saturated fat: there are no double carbon bonds and it is a chain of C, H, and O. The picture on the right shows an amino acid. It also has a chain of C, H, and O, but it contains nitrogen so we know it has to be a protein. ...
... The top picture shows a saturated fat: there are no double carbon bonds and it is a chain of C, H, and O. The picture on the right shows an amino acid. It also has a chain of C, H, and O, but it contains nitrogen so we know it has to be a protein. ...
Proteins, Lipids, and Carbs!!!
... The protein has become renatured The protein has become denatured The protein has reached its highest level of organization A None of the above ...
... The protein has become renatured The protein has become denatured The protein has reached its highest level of organization A None of the above ...
Practice Exam II
... 17. What primary factor governs the quality of a food protein? a. Fat content b. Essential amino acid content c. Complex carbohydrate content d. Nonessential amino acid content 18. Which of the following structural features of fatty acids determines their susceptibility to spoilage by oxygen? a. Cha ...
... 17. What primary factor governs the quality of a food protein? a. Fat content b. Essential amino acid content c. Complex carbohydrate content d. Nonessential amino acid content 18. Which of the following structural features of fatty acids determines their susceptibility to spoilage by oxygen? a. Cha ...
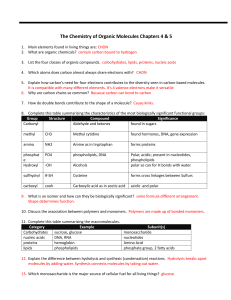
04-05 Biochem review sheet answers ws
... 4. Which atoms does carbon almost always share electrons with? CHON 5. Explain how carbon’s need for four electrons contributes to the diversity seen in carbon-based molecules. It is compatible with many different elements. It’s 4 valence electrons make it versatile 6. Why are carbon chains so commo ...
... 4. Which atoms does carbon almost always share electrons with? CHON 5. Explain how carbon’s need for four electrons contributes to the diversity seen in carbon-based molecules. It is compatible with many different elements. It’s 4 valence electrons make it versatile 6. Why are carbon chains so commo ...
Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins
... • Proteins are linear heteropolymers of -amino acids • Amino acids have properties that are well-suited to carry out a variety of biological functions ...
... • Proteins are linear heteropolymers of -amino acids • Amino acids have properties that are well-suited to carry out a variety of biological functions ...
2-BuildingBlocks
... molecules. These non-covalent bonds involve the AA side chains. Selecting from those listed in the box, which type(s) of amino acids would: A. form ionic bonds with negatively charged DNA. _________ B. form hydrogen bonds with water. __________ C. help hold together two water-soluble proteins.______ ...
... molecules. These non-covalent bonds involve the AA side chains. Selecting from those listed in the box, which type(s) of amino acids would: A. form ionic bonds with negatively charged DNA. _________ B. form hydrogen bonds with water. __________ C. help hold together two water-soluble proteins.______ ...