Protein Synthesis and Function: Chapter 3
... Isoleucine, Ile, I Leucine, Leu, L Methionine, Met, M Phenylalanine, Phe, F Tryptophan,Trp, W Valine, Val, V ...
... Isoleucine, Ile, I Leucine, Leu, L Methionine, Met, M Phenylalanine, Phe, F Tryptophan,Trp, W Valine, Val, V ...
Regulation of enzyme activity. Enzymodiagnostic. Enzymopathy
... Regulation of enzyme activity. Enzymodiagnostic. Enzymopathy. Enzymotherapy. ...
... Regulation of enzyme activity. Enzymodiagnostic. Enzymopathy. Enzymotherapy. ...
Biomolecule/Chemistry Flashcards- KEY - mvhs
... structure that is used as a storage form for carbohydrates in plants. Cellulose- A polysaccharide with a linear chain structure that is used for structural support in plants. Glycogen- A polysaccharide with a branched structure that is used as a storage form of carbohydrates in animals. ...
... structure that is used as a storage form for carbohydrates in plants. Cellulose- A polysaccharide with a linear chain structure that is used for structural support in plants. Glycogen- A polysaccharide with a branched structure that is used as a storage form of carbohydrates in animals. ...
Molecules of Life MBBS Prof. Fridoon
... The interactions of the hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic heads of phospholipids generate a phospholipid bilayer that is two molecules thick. The head groups are directed outward, where they interact with the surrounding water. The tails are packed together in the interior of the bilayer. ...
... The interactions of the hydrophobic tails and hydrophilic heads of phospholipids generate a phospholipid bilayer that is two molecules thick. The head groups are directed outward, where they interact with the surrounding water. The tails are packed together in the interior of the bilayer. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - No Slide Title
... tRNA is a partially double stranded RNA polymer. It folds into a threedimensional shape with the anticodon at one end and the amino acid attachment site at the other end. ...
... tRNA is a partially double stranded RNA polymer. It folds into a threedimensional shape with the anticodon at one end and the amino acid attachment site at the other end. ...
Gene expression PPT
... – tRNA molecule with complimentary anticodon binds to exposed codon on mRNA. The tRNA has many more nucleotides, but the three on the anticodon is what match up to the codon. – The codon determines which amino acid the tRNA carries as tRNA with a specific anticodon always carry the same amino acid. ...
... – tRNA molecule with complimentary anticodon binds to exposed codon on mRNA. The tRNA has many more nucleotides, but the three on the anticodon is what match up to the codon. – The codon determines which amino acid the tRNA carries as tRNA with a specific anticodon always carry the same amino acid. ...
Bio Honors Review Packet
... 10) Which pH has an equal concentration of H+ and OH- ions? a) 3 b) 5 c) 7 d) 9 e) 11 11) All of the following are true concerning lipids except a) their monomers consist of a glycerol and 3 fatty acids b) they are used for protection of vital organs c) plants may contain fats in their seeds d) satu ...
... 10) Which pH has an equal concentration of H+ and OH- ions? a) 3 b) 5 c) 7 d) 9 e) 11 11) All of the following are true concerning lipids except a) their monomers consist of a glycerol and 3 fatty acids b) they are used for protection of vital organs c) plants may contain fats in their seeds d) satu ...
Slide 1
... • Macromolecules - larger molecules made from smaller ones. • 4 major classes of macromolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. • 3 of these are polymers because they are made from individual building blocks called monomers. ...
... • Macromolecules - larger molecules made from smaller ones. • 4 major classes of macromolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. • 3 of these are polymers because they are made from individual building blocks called monomers. ...
Proteins - RHS AP Biology
... mRNA (codon = three base sequence). Amino acids are bonded together as the mRNA moves through the ribosome. Amino acids joined together make a protein. ...
... mRNA (codon = three base sequence). Amino acids are bonded together as the mRNA moves through the ribosome. Amino acids joined together make a protein. ...
Carbohydrates
... B. Polypeptides: very long chains of amino acids. The amino acids in the chains interact with each other, forming different types of structures: ...
... B. Polypeptides: very long chains of amino acids. The amino acids in the chains interact with each other, forming different types of structures: ...
Chapter 29 Biosynthetic Pathways 308 29.1 Your text states in
... carbons 9-10, 12-13, and 15-16). Those fatty acids are essential in the diet. 29.26 The building blocks to synthesize the phospholipid are: glycerol 3-phosphate (made from the reduction of dihydroxyacetone phosphate), the CoA esters of palmitate and laurate, and the amino acid serine in an activated ...
... carbons 9-10, 12-13, and 15-16). Those fatty acids are essential in the diet. 29.26 The building blocks to synthesize the phospholipid are: glycerol 3-phosphate (made from the reduction of dihydroxyacetone phosphate), the CoA esters of palmitate and laurate, and the amino acid serine in an activated ...
CH395 G Exam 3 Fall 2004 - Multiple Choice 1. Which of the
... 13. Dinitrophenol is an inhibitor that decreases the production of ATP by a. binding a proton on the acidic side of the membrane, diffusing through the membrane, and releasing the proton on the alkaline side of the membrane. b. incorporating into the inner mitochondrial membrane thereby making the m ...
... 13. Dinitrophenol is an inhibitor that decreases the production of ATP by a. binding a proton on the acidic side of the membrane, diffusing through the membrane, and releasing the proton on the alkaline side of the membrane. b. incorporating into the inner mitochondrial membrane thereby making the m ...
1D17 – BMI201 Page 1 of 3 Code Questions Answers 1 Discuss the
... enzymes in biological system might be due to this specific nature of enzymes. There are three types of enzyme specificity and they are as follows: 1. Stereospecificity: also called optical specificity. Stereo isomer are the substances which have same molecular formula but differ in their structural ...
... enzymes in biological system might be due to this specific nature of enzymes. There are three types of enzyme specificity and they are as follows: 1. Stereospecificity: also called optical specificity. Stereo isomer are the substances which have same molecular formula but differ in their structural ...
Biochemistry - Circle of Docs
... Malate a. ATP b. GTP and FADH2 c. ATP and NADH d. FADH2 and NADH 25. The most common way to enter the Krebs cycle for amino acids, fatty acids, and glucose is a. Citrate b. Acetyl-CoA c. Oxaloacetate d. Pyruvate 26. The rate limiting step of cholesterol synthesis is a. HMG CoA Mevalonate 27. Glucose ...
... Malate a. ATP b. GTP and FADH2 c. ATP and NADH d. FADH2 and NADH 25. The most common way to enter the Krebs cycle for amino acids, fatty acids, and glucose is a. Citrate b. Acetyl-CoA c. Oxaloacetate d. Pyruvate 26. The rate limiting step of cholesterol synthesis is a. HMG CoA Mevalonate 27. Glucose ...
Chapter Two Crossword Puzzle 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
... and are an important component of all cells. 8. _________ is a storage polysaccharide composed of glucose, which is hydrolyzed by animals when glucose is needed 9. Fats are often called ________ because of their structure. 10. ________ is a polymer of glucose that forms plant cell walls. ...
... and are an important component of all cells. 8. _________ is a storage polysaccharide composed of glucose, which is hydrolyzed by animals when glucose is needed 9. Fats are often called ________ because of their structure. 10. ________ is a polymer of glucose that forms plant cell walls. ...
Special aspects of renal metabolism
... The extracellular concentration of free amino is significantly lower than inside the cells The concentration gradient is maintained through active transport (requires ATP) that moves amino acids into cells Seven different transport systems are known that have overlapping specificities for diff ...
... The extracellular concentration of free amino is significantly lower than inside the cells The concentration gradient is maintained through active transport (requires ATP) that moves amino acids into cells Seven different transport systems are known that have overlapping specificities for diff ...
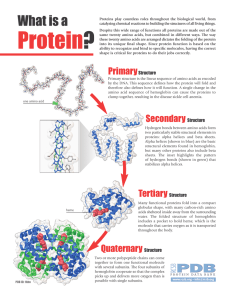
Protein?
... Proteins play countless roles throughout the biological world, from catalyzing chemical reactions to building the structures of all living things. Despite this wide range of functions all proteins are made out of the same twenty amino acids, but combined in different ways. The way these twenty amino ...
... Proteins play countless roles throughout the biological world, from catalyzing chemical reactions to building the structures of all living things. Despite this wide range of functions all proteins are made out of the same twenty amino acids, but combined in different ways. The way these twenty amino ...
... Chair of Texas Tech’s Meat Science and Muscle Biology Program, is currently working on researching the effects of adding amino acids to the diet of feedlot cattle supplemented with beta agonists. Amino acids are the building blocks for protein synthesis, allowing for the production of muscle fibers. ...
Biosynthesis of Macromolecules
... - use energy (ATP) from catabolism - use carbon from sugars, lipids, proteins, or any other carbon source (xenobiotics) to build cellular components ...
... - use energy (ATP) from catabolism - use carbon from sugars, lipids, proteins, or any other carbon source (xenobiotics) to build cellular components ...
Biochemistry
... Nitrogen Removal from Amino Acids • Liver is primary site of amino acid degradation – Muscle is secondary site of amino acid degradation for branched chain amino acids (e.g. L,I,V) ...
... Nitrogen Removal from Amino Acids • Liver is primary site of amino acid degradation – Muscle is secondary site of amino acid degradation for branched chain amino acids (e.g. L,I,V) ...