Sugar
... • A slight change in the primary structure of a protein affects its ability to function – The substitution of one amino acid for another in ...
... • A slight change in the primary structure of a protein affects its ability to function – The substitution of one amino acid for another in ...
Elements Found in Living Things
... pH from neutral, etc. change the shape of enzymes and their active sites so the enzyme is unable to work. Some enzymes have a second site where a coenzyme attaches to help make the substrate better fit the active site of the enzyme. Color the enzyme purple, the substrate yellow, and the coenzyme gre ...
... pH from neutral, etc. change the shape of enzymes and their active sites so the enzyme is unable to work. Some enzymes have a second site where a coenzyme attaches to help make the substrate better fit the active site of the enzyme. Color the enzyme purple, the substrate yellow, and the coenzyme gre ...
Lab #8
... the browning reaction faster than does D-fructose. Application of heat is generally required for nonenzymatic browning. While Maillard reactions are useful, they also have a negative side. Reaction of reducing sugars with amino acids destroys the amino acid. This is of particular importance with lys ...
... the browning reaction faster than does D-fructose. Application of heat is generally required for nonenzymatic browning. While Maillard reactions are useful, they also have a negative side. Reaction of reducing sugars with amino acids destroys the amino acid. This is of particular importance with lys ...
File
... that is also the start code. So every protein starts with methionine when it is translated » Now, the ribosome moves over one codon a new tRNA will attach to the A site. » Note that the first amino acid left the tRNA and attached to the next one ...
... that is also the start code. So every protein starts with methionine when it is translated » Now, the ribosome moves over one codon a new tRNA will attach to the A site. » Note that the first amino acid left the tRNA and attached to the next one ...
The Chemistry of Life
... or the accumulation of product Rate of reaction is the slope of the linear portion of the graph Reaction rate is affected by pH, substrate conc., enzyme conc., temperature, and ...
... or the accumulation of product Rate of reaction is the slope of the linear portion of the graph Reaction rate is affected by pH, substrate conc., enzyme conc., temperature, and ...
PRENTICE HALL- ONLINE ACTIVITY 14
... 5. How do scientists use homologous structure information? 6. Explain how these homologous structures suggest a common ancestor. 7. If the human, cat, whale, and bat did not have a common ancestor, how likely is it that these four species would possess the same basic forelimb bone structure? ...
... 5. How do scientists use homologous structure information? 6. Explain how these homologous structures suggest a common ancestor. 7. If the human, cat, whale, and bat did not have a common ancestor, how likely is it that these four species would possess the same basic forelimb bone structure? ...
Notes handout for Basic Biochemistry
... Proteins are polymers – ____________________________ – of amino acids held together by Peptide bonds with the amine end of one amino acid linked to the carboxyl end of the next. The order or _____________________________ of the amino acids determine the function of the protein ...
... Proteins are polymers – ____________________________ – of amino acids held together by Peptide bonds with the amine end of one amino acid linked to the carboxyl end of the next. The order or _____________________________ of the amino acids determine the function of the protein ...
CHM 112
... structure. The tertiary structure is maintained by disulfide bridges (between amino acids with thiol groups), hydrogen bonds (between polar groups), salt bridges (between amines and carboxylic acid groups), and hydrophobic or dispersion forces (between non-polar groups). ...
... structure. The tertiary structure is maintained by disulfide bridges (between amino acids with thiol groups), hydrogen bonds (between polar groups), salt bridges (between amines and carboxylic acid groups), and hydrophobic or dispersion forces (between non-polar groups). ...
Slide 1
... signal transduction pathways which ultimately result in the activation of the actual DNAbinding proteins. ...
... signal transduction pathways which ultimately result in the activation of the actual DNAbinding proteins. ...
Princeton H - SchoolNotes
... A. What is an enzyme? B. What are enzymes made of? C. What is a substrate? D. What is a co-enzyme? vitamin? E. What are the effects of heat on an enzyme? Be able to interpret graph. F. What are the effects of pH change on enzymes? Be able to Interpret graph. G. What are the effects of increasing sub ...
... A. What is an enzyme? B. What are enzymes made of? C. What is a substrate? D. What is a co-enzyme? vitamin? E. What are the effects of heat on an enzyme? Be able to interpret graph. F. What are the effects of pH change on enzymes? Be able to Interpret graph. G. What are the effects of increasing sub ...
Protein Synthesis
... • Ribosome moves along mRNA to the next codon, the anti-codon binds to the codon and the new amino acid attaches to the first amino acid forming a polypeptide chain until a stop codon occurs ...
... • Ribosome moves along mRNA to the next codon, the anti-codon binds to the codon and the new amino acid attaches to the first amino acid forming a polypeptide chain until a stop codon occurs ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 3. State the principle of VD Bergh reaction. 4. Which amino acid is considered as an effective physiological buffer? Why? 5. Define Bohr’s effect 6. How Sodium content is regulated when Aldosterone is high? 7. Explain the condition of hyperuricaemia:: 8. Give the significance of second messengers: 9 ...
... 3. State the principle of VD Bergh reaction. 4. Which amino acid is considered as an effective physiological buffer? Why? 5. Define Bohr’s effect 6. How Sodium content is regulated when Aldosterone is high? 7. Explain the condition of hyperuricaemia:: 8. Give the significance of second messengers: 9 ...
Solid Tumour Section t(2;2)(p23;q13) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... 1430 amino acids; 6867 N-term amino acid from RANBP2, fused to the 562 C-term amino acids from ALK (i.e. the leucine-rich domain, including the leucine zipper, of RANBP2 and the entire cytoplasmic portion of ALK with the tyrosine kinase domain). Oncogenesis The leucine zipper of RANBP2 could mediate ...
... 1430 amino acids; 6867 N-term amino acid from RANBP2, fused to the 562 C-term amino acids from ALK (i.e. the leucine-rich domain, including the leucine zipper, of RANBP2 and the entire cytoplasmic portion of ALK with the tyrosine kinase domain). Oncogenesis The leucine zipper of RANBP2 could mediate ...
Pipe-Cleaner Proteins
... 5. Suppose that there is an attraction between the blue and the orange amino acids. Also, suppose that a “disulfide bridge” (a covalent bond that forms between sulfur atoms in “R” groups) forms between the red and green amino acid. Let’s further suppose that there is repulsion between the purple an ...
... 5. Suppose that there is an attraction between the blue and the orange amino acids. Also, suppose that a “disulfide bridge” (a covalent bond that forms between sulfur atoms in “R” groups) forms between the red and green amino acid. Let’s further suppose that there is repulsion between the purple an ...
Molecules of Life – Part 2
... 1. These are formed from individual units called monomers (“Building Blocks”). 2. Monomers are linked together by covalent bonds. Organisms need these to stay intact so the strongest type of bond is used. 3. These are another example of the theme: Structure = Function. B. Macromolecules are formed b ...
... 1. These are formed from individual units called monomers (“Building Blocks”). 2. Monomers are linked together by covalent bonds. Organisms need these to stay intact so the strongest type of bond is used. 3. These are another example of the theme: Structure = Function. B. Macromolecules are formed b ...
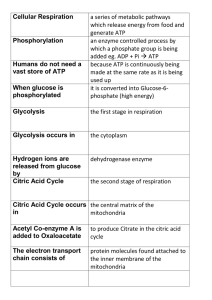
Carbohydrates
... Nucleic acids are composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorous. These elements are organized into small units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids There are two types of nucleic acids: DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid. It is found in the cell’s nucleus ...
... Nucleic acids are composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorous. These elements are organized into small units called nucleotides. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids There are two types of nucleic acids: DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid. It is found in the cell’s nucleus ...
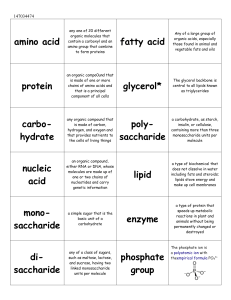
Amino Acids - Chavis Biology
... Amino acids are the basic units from which proteins are made. Plants can manufacture all of the amino acids they required from simpler molecules, but animals must obtain a number of ready-made amino acids (called essential amino acids) from their diet. All other amino acids can be constructed from t ...
... Amino acids are the basic units from which proteins are made. Plants can manufacture all of the amino acids they required from simpler molecules, but animals must obtain a number of ready-made amino acids (called essential amino acids) from their diet. All other amino acids can be constructed from t ...
Nitrogen Metabolism
... • Therefore, a supply of all 20 aa is necessary. • Higher plants are able to synthesize all 20 aas. • Many microorganisms and higher animals make fewer • Humans make 10 of the 20 aas (these are called nonessential amino acids. • The remainder must be supplied in the diet, usually in the form of plan ...
... • Therefore, a supply of all 20 aa is necessary. • Higher plants are able to synthesize all 20 aas. • Many microorganisms and higher animals make fewer • Humans make 10 of the 20 aas (these are called nonessential amino acids. • The remainder must be supplied in the diet, usually in the form of plan ...